In cell biology and molecular biology research, nuclear proteins are essential functional molecules that play critical roles in numerous physiological processes. They are extensively involved in gene expression regulation, transcription, translation, RNA splicing, and DNA repair. The functions of nuclear proteins are often closely associated with their specific localization within the nucleus and their interactions with other nuclear components. As such, nuclear proteins have become focal points in the investigation of cellular functions and disease mechanisms, especially in the fields of cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and genetic diseases. However, isolating nuclear proteins presents significant technical challenges due to their complex intracellular localization and tight association with other cellular components. Nuclear proteins often form complexes with DNA, RNA, and the nuclear matrix, making it technically demanding to efficiently and stably extract pure nuclear proteins from cells or tissues.
To address the need for high-purity and high-efficiency nuclear protein extraction in life science research, MtoZ Biolabs has developed the nuclear protein extraction kit enables rapid and efficient extraction of nuclear proteins from a wide range of cell and tissue samples. It overcomes the limitations of traditional methods (such as low yield and cumbersome procedures) greatly enhancing the reliability and reproducibility of nuclear protein isolation.
Product Overview
The nuclear protein extraction kit utilizes advanced separation technology and is specifically designed for the extraction and purification of nuclear proteins. It enables the efficient isolation of high-quality nuclear proteins from a wide variety of cell and tissue types. The unique formulation of the kit includes a series of optimized buffers and chemical reagents that effectively disrupt both the plasma and nuclear membranes while protecting the integrity of intranuclear proteins. In addition, the reagents help minimize nucleic acid contamination, ensuring high purity of the extracted proteins.
One of the core advantages of the nuclear protein extraction kit lies in its user-friendly and streamlined workflow. Researchers can easily complete cell lysis and nuclear protein separation simply by following the step-by-step reagent addition protocol, significantly reducing the technical complexity and time requirements of the process. The kit is compatible with a wide range of common cell types and is also highly effective for extracting nuclear proteins from various tissue samples. It is well suited for applications in proteomics, signal transduction studies, transcriptional regulation research, and other related fields.
Product Details
|
Product Details |
Size |
Storage Conditions |
|
Nuclear Protein Extraction Reagent A |
30 mL |
Store at -20°C, valid for one year. Can be stored at 4°C if used within one month. |
|
Nuclear Protein Extraction Reagent B |
5 mL |
|
|
Nuclear Protein Wash Buffer A |
30 mL |
|
|
Nuclear Protein Wash Buffer B |
30 mL |
|
|
Nuclear Protein Dilution Buffer |
30 mL |
|
|
Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (100×) |
1 mL |
Protocol
1. Reagent Preparation
Thaw all reagents from the nuclear protein extraction kit at room temperature and place them on ice after thawing. Pre-cool the centrifuge to 4°C in advance. Based on the sample amount, aliquot the appropriate volumes of Nuclear Protein Extraction Reagent A, Nuclear Protein Extraction Reagent B, Nuclear Protein Wash Buffer A, and Nuclear Protein Wash Buffer B. Before use, supplement each with 1% (v/v) of 100× protease inhibitor cocktail.
2. Sample Preprocessing
(1) For cells:
Harvest cells and centrifuge at 500 ×g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Wash the cell pellet twice with pre-chilled PBS and carefully aspirate any residual PBS. Place the sample on ice, and add 1 mL of pre-chilled nuclear protein extraction reagent A per 20-50 million cells.
(2) For tissues:
Take fresh animal tissue and rinse thoroughly with pre-chilled PBS to remove fat, blood, and other impurities. Blot dry with filter paper and weigh the tissue. Mince the tissue on ice, and add 1 mL of pre-chilled Nuclear Protein Extraction Reagent A per 100 mg of tissue.
3. Homogenization
(1) Transfer the sample into a pre-chilled glass homogenizer of appropriate size. Homogenize the sample on ice.
Note: The number of homogenization strokes required varies by sample type. For cultured cells, 1-2 strokes are recommended; for tissue samples, 5-10 strokes are suggested.
Assessment method: Take 20 µL of the homogenized sample and mix with an equal volume of 0.4% Trypan Blue solution. Examine under a microscope and calculate the percentage of Trypan Blue-positive (blue-stained) cells. Stop homogenization when approximately 50% of the cells appear positively stained (blue). Avoid over-homogenization. If the percentage is below 50%, perform 1-2 additional strokes and reassess using the same Trypan Blue staining method.
(2) For cultured cells, alternative lysis methods such as vortexing or freeze-thaw cycles may also be used:
a. Vortexing method: Vortex the sample (already mixed with nuclear protein extraction reagent A in Step 2) vigorously for 1 minute (10 seconds on, 10 seconds off). Place the sample on ice for 2 minutes. Repeat the vortexing and ice incubation three times. Then take a small aliquot for Trypan Blue staining to evaluate the degree of cell lysis.
b. Freeze-thaw method: Subject the sample (already mixed with Nuclear Protein Extraction Reagent A in Step 2) to 3-5 cycles of freezing in liquid nitrogen followed by thawing at room temperature. Then take a small aliquot and use Trypan Blue staining to determine the extent of cell disruption.
4. Nuclear Protein Separation
(1) Place the homogenized sample on ice for 10 minutes, gently inverting the tube every 2 minutes. Centrifuge at 6,500 ×g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Collect the supernatant as the cytoplasmic protein fraction.
Note: Do not disturb the pellet during supernatant collection. It is acceptable to leave a small volume of supernatant above the pellet.
(2) Resuspend the pellet in 1 mL of pre-chilled Nuclear Protein Wash Buffer A. Centrifuge at 6,500 ×g for 5 minutes at 4°C, and retain the pellet.
(3) Resuspend the pellet in 1 mL of Nuclear Protein Wash Buffer B. Vortex vigorously for 1 minute (10 seconds on, 10 seconds off). Centrifuge at 6,500 ×g for 5 minutes at 4°C, and retain the pellet.
5. Nuclear Protein Extraction
(1) Resuspend the pellet in 100 µL of Nuclear Protein Extraction Reagent B. Vortex vigorously for 2 minutes (10 seconds on, 10 seconds off), then place the tube on ice for 10 minutes. Repeat the vortexing and ice incubation steps three times.
(2) Centrifuge the mixture at 16,000 ×g for 10 minutes at 4°C. Collect the supernatant, which contains the extracted nuclear proteins.
(3) Add four volumes of Nuclear Protein Dilution Buffer to the collected nuclear protein extract. If the sample appears highly viscous, sonicate until the viscosity is reduced.
Note: If high viscosity prevents separation of pellet and supernatant after Step 5.(2), first add four volumes of dilution buffer, then sonicate the sample and repeat centrifugation at 16,000 ×g for 10 minutes at 4°C. Collect the resulting supernatant as the nuclear protein fraction.
6. Storage and Application
The extracted nuclear proteins can be aliquoted and stored at -80°C for long-term preservation or used immediately for downstream applications. Protein concentration should be determined using the BCA assay; the Bradford assay is not recommended for this purpose. The nuclear protein extract is directly compatible with Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, mass spectrometry analysis, and other experimental procedures.
Figures
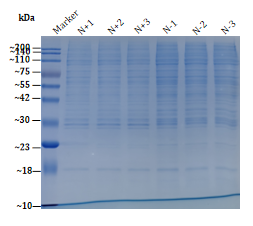
Figure 1. SDS-PAGE Gel Image of Nuclear Proteins Extracted Using the Kit.
Features and Benefits
1. High-Efficiency Extraction
The nuclear protein extraction kit is specifically formulated for nuclear protein isolation, with optimized lysis buffer and an efficient membrane disruption system, enabling rapid and effective extraction of nuclear proteins from cells or tissues. Whether extracting transcription factors, nuclear receptors, or DNA-binding proteins, high-yield recovery can be ensured.
2. High Purity
Effectively eliminates cytoplasmic contaminants and other impurities, yielding nuclear protein preparations with high purity. The extracts are suitable for a wide range of downstream applications such as Western blotting, co-immunoprecipitation, and mass spectrometry.
3. Simplified Workflow
Integrated and user-friendly protocol eliminates the need for complex procedures. Researchers can obtain high-quality nuclear proteins by following the provided instructions with minimal hands-on time.
4. Preservation of Native Protein Structure
Inclusion of protease inhibitors and mild detergents protects the native conformation and functionality of nuclear proteins during extraction, ensuring their integrity for functional and structural studies.
5. Broad Sample Compatibility
Compatible with a variety of sample types including animal cells, plant cells, and selected microbial cells. It performs efficiently on suspension or adherent cells as well as tough tissue samples, accommodating diverse experimental requirements.
6. Versatile Applications
The extracted nuclear proteins are suitable for proteomics, transcriptional regulation studies, DNA repair research, and signaling pathway analysis, supporting a wide range of life science investigations.
Applications
1. Proteomics Research
Following nuclear protein extraction, samples can be analyzed by mass spectrometry or Western blot to investigate the functional roles and molecular mechanisms of nuclear proteins.
2. Transcriptional Regulation Studies
As key regulators of gene expression, nuclear proteins, especially transcription factors, can be studied for their interactions with DNA to uncover gene regulatory mechanisms.
3. DNA Repair Mechanism Research
Many nuclear proteins are involved in DNA repair pathways. The extracted proteins using the nuclear protein extraction kit are suitable for downstream assays aimed at exploring DNA repair functions and regulatory networks.
4. Signaling Pathway Analysis
Nuclear proteins frequently participate in intracellular signaling. Investigating their interactions with other signaling molecules can offer insights into the molecular basis of various diseases.
5. Clinical Research Applications
Support the extraction of high-quality nuclear proteins from cells or tissues, facilitating research into transcriptional regulation and genetic alterations in cancer and other diseases, providing valuable tools for precision medicine.
FAQs
Q1: How Should the Extracted Nuclear Proteins Be Stored?
A1: The extracted nuclear proteins should be stored at -80°C. To maintain their activity and stability, repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided. It is recommended to determine the protein concentration before use and dilute the sample according to experimental requirements.
Q2: Can the Nuclear Protein Extraction Kit Extract High-Quality Nuclear Proteins for Mass Spectrometry Analysis?
A2: Yes. The nuclear proteins extracted using the kit are of high purity, making them well-suited for high-precision applications such as mass spectrometry and proteomics analysis.
Q3: How Can I Ensure the Quality and Purity of the Extracted Nuclear Proteins?
A3: The kit utilizes gentle lysis and detergent-based components to efficiently disrupt cell membranes and extract nuclear proteins while minimizing contamination from cytoplasmic or non-nuclear materials. Centrifugation-based separation ensures sample purity. Protein concentration can be assessed using the BCA assay to support reliable downstream applications.
Q4: Will the Extraction Process Compromise the Activity of Nuclear Proteins?
A4: No. The kit contains protease inhibitors to prevent protein degradation. Additionally, the entire extraction procedure is performed under low-temperature conditions to preserve the native structure and functional activity of nuclear proteins for subsequent analysis.










