Membrane proteins are key structural and functional molecules on cell membranes and various endomembrane systems (such as mitochondrial membranes, Golgi membranes, endoplasmic reticulum membranes, etc.). They play a key role in life processes such as signal transduction, substance transport, cell recognition, maintenance of transmembrane potential, cell adhesion and immune regulation. As important targets for drug action, about 60% of small molecule drugs and antibody drugs achieve therapeutic effects by regulating membrane proteins (such as ion channels, enzyme receptors, etc.). Therefore, studying the structure and function of membrane proteins is of great significance for revealing life processes, analyzing disease mechanisms and developing new targeted drugs.
Despite the vital role of membrane proteins in basic research and drug development, their extraction and purification processes have long faced challenges. First, membrane proteins are significantly hydrophobic and have low water solubility, and are very easy to aggregate or precipitate in aqueous solutions, which poses a threat to their stability in vitro. Secondly, membrane proteins form tight complexes with lipids and other membrane components and need to be dissociated with the help of detergents or organic reagents, but overly strong dissociation conditions may destroy their spatial conformation and functional domains. In addition, the content of membrane proteins is usually low and their distribution in cells is limited. Conventional lysis and extraction methods often make it difficult to achieve efficient enrichment. Especially in epigenetic studies that require maintaining the natural modification state of membrane proteins (such as glycosylation and phosphorylation), the mildness and specificity of the extraction environment are more critical.
Product Overview
The membrane protein extraction kit can effectively extract membrane proteins from cells or tissues in a short time and retain their natural structure and biological activity to the maximum extent through optimized lysis buffer and membrane protein extraction scheme. The lysis buffer in the kit contains specially designed detergent components that can selectively dissolve cell membranes and release membrane proteins. Through graded purification technology, membrane proteins can be simply and quickly separated from membrane lipids, non-membrane proteins and other components. The kit is suitable for membrane protein extraction from a variety of cells and tissues, including animals, plants and certain microorganisms, and has good compatibility. The extracted membrane proteins can be directly used in downstream experiments such as SDS-PAGE, Western Blot, enzyme activity assay, immunoprecipitation, mass spectrometry analysis (LC-MS/MS), etc.
Product Details
|
Product Details |
Size |
Storage Conditions |
|
Lysis Buffer A |
30 mL |
-20℃ |
|
Lysis Buffer B |
10 mL |
|
|
Protease Inhibitor (100×) |
0.5 mL |
Protocol
1. Steps for Extracting Membrane Proteins from Cell Samples
(1) Sample Preparation
Centrifuge at low speed (500-600 ×g, 5 minutes) to collect no less than 1×107 cells. Wash cells three times with pre-cooled pure water or PBS, 500-600 ×g for 5 minutes each time.
(2) Lysis Treatment
Add 1 mL of lysis buffer A to the above cell sample (before use, add 10μL of protease inhibitor per mL of lysis buffer A and pre-cool on ice). Place on ice for 10-15 minutes. Ultrasonicate the cells in an ice bath for 30 sec each time, 3 to 4 times, with 1 min interval between each time, and store on ice. After ultrasonic disruption of cells, microscopic examination should be performed, and the cell disruption rate should be no less than 90%.
(3) Low-Speed Centrifugation to Remove Cell Debris
Centrifuge at 4ºC, 700 ×g for 5 minutes (to precipitate intact cell nuclei and a very small number of intact cells that have not been broken), and carefully collect the supernatant into a new centrifuge tube. Do not touch the precipitate when aspirating the supernatant.
(4) Separation of Membrane Proteins by High-Speed Centrifugation
Centrifuge at 4°C, 16,000 ×g for 30 minutes (extending the centrifugation time can increase the yield), and discard the supernatant (the supernatant is the cytoplasmic component and can be stored if necessary). Add 200-300 μl of lysis buffer B to the precipitate, shake vigorously for 5 seconds to resuspend the precipitate, and place on ice for 5-10 minutes. Repeat the shaking-ice bath twice. Subsequently, centrifuge at 4°C, 16,000 ×g for 5 minutes, and collect the supernatant as the cell membrane protein solution.
(5) Protein Quantification and Downstream Experiments
The membrane protein concentration is determined using the BCA method. After adjusting the protein concentration, the devices can be frozen in a -80°C refrigerator or used for experiments such as Western Blot, enzyme activity detection, immunoprecipitation, and mass spectrometry analysis.
2. Tissue Sample Membrane Protein Extraction Operation Steps
(1) Sample Preparation
Take about 200 mg of tissue, try to remove non-target tissues such as adipose tissue and connective tissue, cut it into pieces on ice, wash it three times with pre-cooled pure water or PBS, and remove impurities such as blood.
(2) Tissue Grinding and Lysis
Freeze the small pieces of tissue in liquid nitrogen and grind them in liquid nitrogen using a mortar. Immediately add 1 mL of lysis buffer A (before use, add 10 μL of protease inhibitor per mL of lysis buffer A and pre-cool it on ice).
(3) Incubation and Lysis
Place in an ice bath for 10-15 minutes. Place the tissue in a pre-cooled glass homogenizer at 4°C and homogenize it manually for 30-50 times until there are no obvious small pieces of tissue.
(4) Low-Speed Centrifugation to Remove Tissue Residues
Centrifuge at 4°C, 700 ×g for 5 minutes (to precipitate tissue residues), carefully collect the supernatant into a new centrifuge tube, and do not touch the precipitate when aspirating the supernatant.
(5) Separation of Membrane Proteins by High-Speed Centrifugation
Centrifuge at 4°C, 16,000 ×g for 30 minutes (extending the centrifugation time can increase the yield), and discard the supernatant. Add 200-300 μl of lysis buffer B to the precipitate, shake vigorously for 5 seconds to resuspend the precipitate, and place on ice for 5-10 minutes. Repeat the shaking-ice bath twice. Then, centrifuge at 4°C, 16,000 ×g for 5 minutes, and collect the supernatant as the cell membrane protein solution.
(6) Protein Quantification and Downstream Experiments
The membrane protein concentration was determined using the BCA method. After adjusting the protein concentration, the samples can be stored in a -80°C refrigerator or used for Western Blot, enzyme activity detection, immunoprecipitation, mass spectrometry analysis and other experiments.
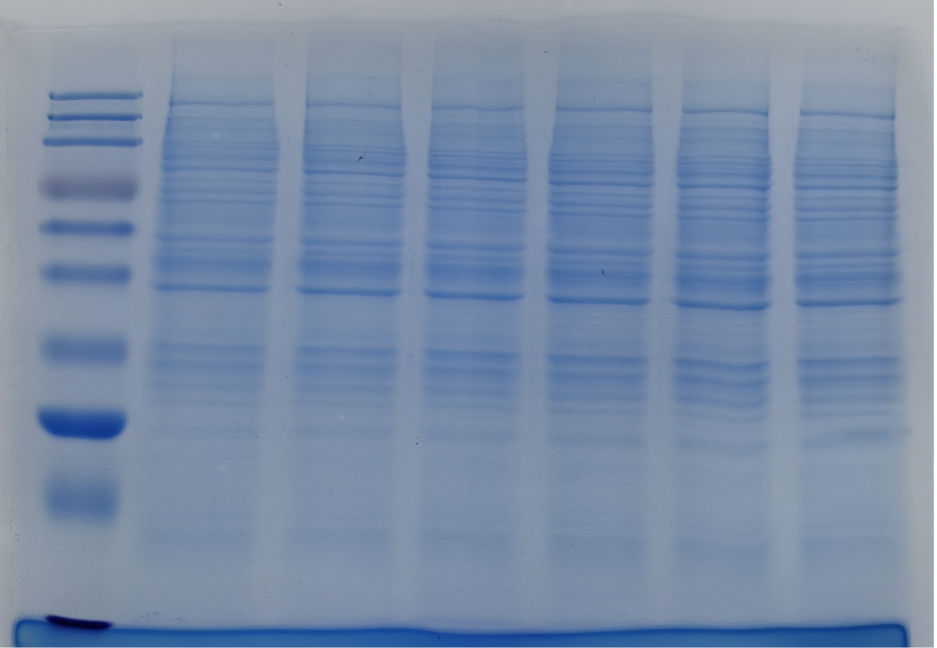
Figure 1. Extraction Effect Diagram of Membrane Protein Extraction Kit.
Features and Benefits
1. Efficient Extraction of Membrane Proteins
Through optimized lysis buffer and specially designed extraction process, membrane proteins can be efficiently extracted membrane proteins from cells or tissues and maintain their natural structure and function to the greatest extent.
2. Efficient Removal of Impurities
Through multiple centrifugation and purification steps, other components in the cell (such as non-membrane proteins, lipids, etc.) are effectively removed to ensure that the extracted membrane proteins are of high purity and suitable for sensitive downstream analysis.
3. Retain Protein Modification and Activity
The addition of protease inhibitors and other protective components during the extraction process can effectively retain the post-translational modification and activity of membrane proteins and ensure their accuracy in subsequent experiments.
4. Wide Applicability
The membrane protein extraction kit is suitable for a variety of cells and tissues, including animal cells, plant cells and microorganisms, and has good compatibility to meet different experimental needs.
5. Simplify Operation and Save Time
The ready-to-use formula that is easy to operate. Usually, the extraction and purification of membrane proteins can be completed in a short time, saving a lot of time and effort.
Applications
1. Membrane Protein Function Research
The extracted membrane proteins can be used for functional research, such as activity detection of ion channels, receptor proteins, transmembrane transport proteins, and their role in physiological processes.
2. Membrane Protein Transport and Signal Transduction Research
The membrane protein extraction kit can be used to study the role of membrane proteins in cell signal transduction, transmembrane transport, cell membrane remodeling, etc., and provide basic data for cell biology, pathology and immunology research.
3. Structural Research of Membrane Proteins
Study the structure and conformation of membrane proteins to provide samples for crystallographic analysis, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) research, electron microscopy analysis, etc. of membrane proteins.
4. Drug Screening and Design
The extracted membrane proteins can be used as targets for drug screening, especially in the discovery of new drugs or the development of treatments for membrane proteins, which has important application value.
5. Post-Translational Modification Research of Membrane Proteins
The membrane protein extraction kit can be used to study post-translational modifications of membrane proteins such as acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation, and understand the role of these modifications in protein function and cell regulation.
FAQs
Q1: Can Frozen Samples Be Used to Extract Membrane Proteins?
A1: Frozen samples can be used for tissue samples, but cell samples must be collected fresh. Frozen cells may damage the cell structure due to ice crystals, resulting in cross-contamination of components and reduced yield.
Q2: Can Membrane Proteins Be Used for Functional Experiments after Extraction?
A2: Yes. The membrane proteins extracted by the kit are effectively guaranteed in purity and stability, and are suitable for various functional experiments, such as enzyme activity assays, membrane protein binding experiments, etc.
Q3: How to Ensure the Activity of Membrane Proteins during the Extraction Process?
A3: The membrane protein extraction kit provided by MtoZ Biolabs contains protease inhibitors, which can effectively prevent protein degradation. At the same time, the extraction process is carried out under low temperature conditions to ensure the activity and natural conformation of the protein.
Q4: How to Store the Extracted Membrane Protein?
A4: The extracted membrane protein should be stored at -80℃ to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. If not used immediately, it is recommended to aliquot the protein to prevent degradation.










