Untargeted Lipidomics Analysis Service
Lipids are the main components of biological membranes. Lipids are not only the main form of energy storage in living cells but also serve as mediators of cell signaling. The lipidome consists of 8 major classes, over 80 main categories, 300 subclasses, and thousands of lipids at different concentrations. Lipidomics is the systematic study of all lipid molecules (> 30,000 species) within a biological system, tissue, body fluid, or cell. Comprehensive identification and precise quantification of lipids are crucial for understanding cellular physiology and pathophysiology in lipidomics research.
Untargeted lipidomics can analyze hundreds to thousands of different lipids simultaneously, which is valuable for assessing an individual's health condition. Lipidomic differences have been widely used in studies of cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, and cardiovascular diseases. These detailed lipid profiles can be used to evaluate medical risks, monitor, and optimize patient treatment, forming the basis of the concept of precision medicine. The applications of untargeted lipidomics include agricultural science, biomarkers, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, obesity research, clinical diagnostics, drug discovery, and systems biology.
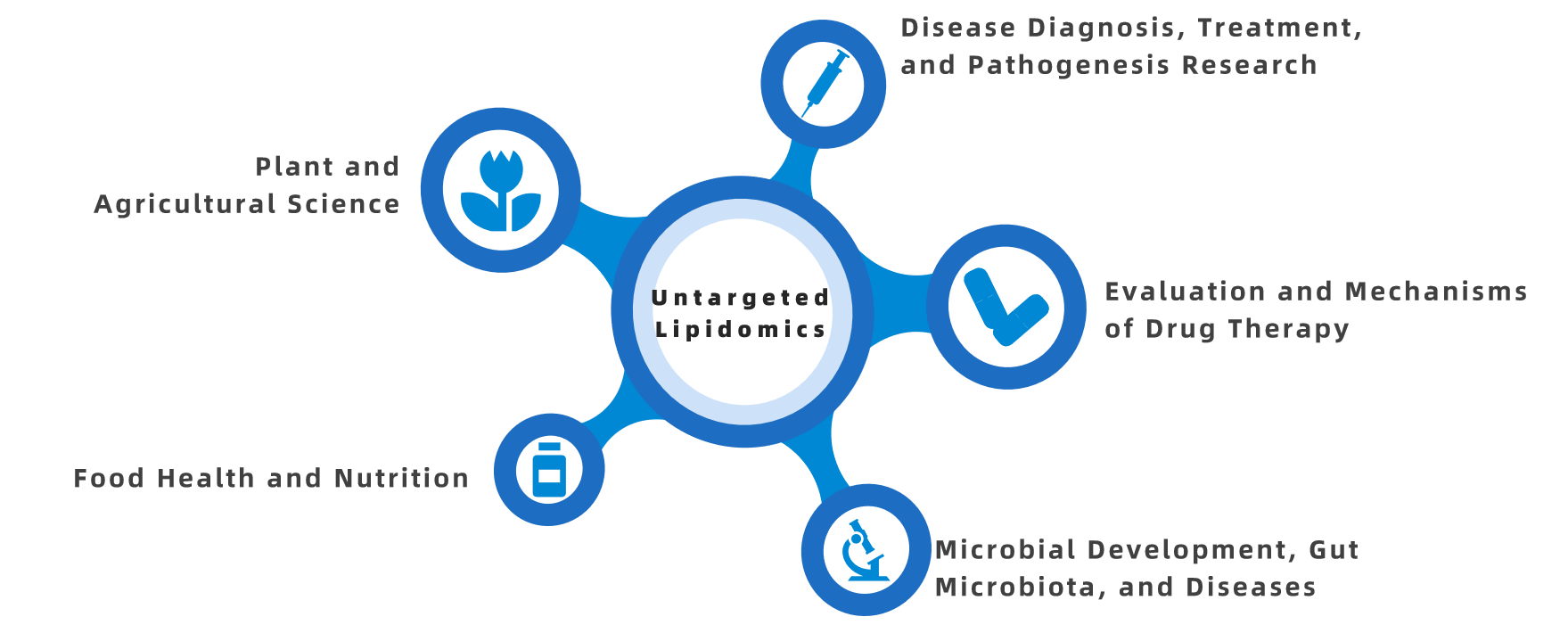
Figure 1. Applications of Untargeted Lipidomics
Although lipids are major components of the metabolome, the insolubility of many lipids in aqueous solutions necessitates different methods from those used for more water-soluble components in metabolomics. Mass spectrometry (MS) is the primary analytical platform for lipidomics, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is also widely used in metabolomics. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was the main tool for lipid analysis in the past, replaced by desorption ionization techniques connected to MS such as atmospheric pressure ionization (API) and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI). API is usually electrospray ionization (ESI), often coupled with a liquid chromatography (LC) system for sample separation before MS analysis. MALDI is mainly performed under vacuum, typically not connected with an LC separation system, but can be used in conjunction with thin-layer chromatography (TLC) plates. MALDI-MS imaging (MSI) is increasingly used in lipidomics analysis because it can provide spatial information of lipids within tissues. By measuring the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of ionized substances, MS can provide molecular weight information. Many modern mass spectrometers can achieve mass accuracy of 0.001-0.002 m/z, allowing lipid profiles to be matched in databases through m/z searches or identification of ionized molecules using various commercial or open-source software. Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) or multistage fragmentation (MSn) experiments can provide structural information.
MtoZ Biolabs offers reliable, rapid, and cost-effective UPLC-Q-TOF Untargeted Lipidomics Service based on high stability, repeatability, and sensitivity of the separation, characterization, identification, and quantification systems.
Service Advantages
1. State-of-the-Art Platform
Employs a high-resolution mass spectrometry platform (resolution >100,000) combined with optimized chromatographic methods.
2. Specialized Lipidomics Database - LipidSearch
Features a comprehensive database with 1.7 million lipid molecular spectra.
3. Superior Qualitative Performance
Capable of detecting over 2,000 lipid molecules from a single sample.
Sample Submission Requirements
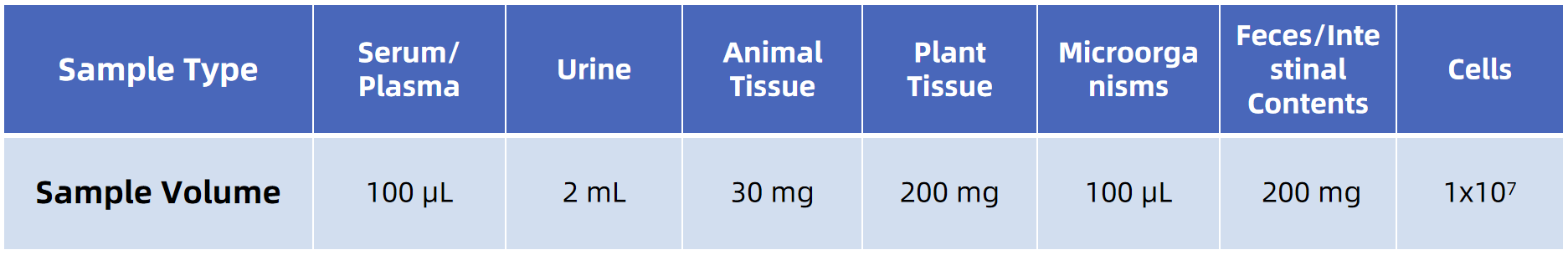
For more sample details, please consult our technical team.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







