Histones, as the core components of eukaryotic chromatin structure, not only serve as carriers of genetic information but also act as critical executors of epigenetic regulation. Their covalent modifications, such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination, are directly involved in regulating gene expression, DNA repair, and chromosomal remodeling. These processes are essential for understanding disease mechanisms, drug development, and fundamental biological research. However, the strong binding affinity between histones and DNA, the strict extraction conditions required to preserve modification stability, and the difficulty in removing transcription factor contaminants all pose significant challenges to efficient histone extraction.
To address these issues, MtoZ Biolabs has developed the histone extraction kit which employs a proprietary lysis buffer that specifically dissociates histone-DNA complexes. The kit features a unique workflow for removing small-molecule contaminants and enables the efficient extraction of high-purity histones from the nucleus. The optimized low-temperature protocol, combined with a broad-spectrum protease inhibitor cocktail, helps preserve post-translational modifications, ensuring the reliability and stability of downstream applications.
Product Overview
The histone extraction kit is specifically designed for the efficient extraction of histones from cells. Utilizing a unique lysis buffer formulation, it effectively disrupts both the plasma membrane and nuclear envelope to release histones into solution while minimizing contamination from other cellular components. Additionally, the kit preserves post-translational modifications of histones, ensuring accurate downstream analysis. The procedure is straightforward and does not require complex solvent handling.
It is suitable for various cell types, including mammalian cells, plant cells, and certain fungal cells. The exacted histones are compatible with downstream applications such as Western blotting, mass spectrometry, co-immunoprecipitation, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and are widely used in research areas including epigenetics, cell biology, and molecular biology.
Product Details
|
Product Details |
Size |
Storage Conditions |
|
Lysis Buffer A |
50 mL |
4℃ |
|
Lysis Buffer B |
20 mL |
4℃ |
|
Reagent A |
5 mL |
RT |
|
Reagent B |
20 mL |
4℃ |
Protocol
1. Cell Samples
(1) Collect no fewer than 1×10⁷ cells. Centrifuge at 1000 ×g for 5 minutes at 4°C, then wash the cells 2-3 times with pre-chilled PBS.
(2) Add Lysis Buffer A to the cell pellet to achieve a final concentration of 1×10⁷ cells/mL. Incubate on a rotator at 4°C for at least 30 minutes.
(3) After incubation, centrifuge at 10000 ×g for 10 minutes at 4°C. Discard the supernatant and retain the pellet.
2. Animal Tissue Samples
(1) Weigh the tissue and cut it into small pieces (1-2 mm³) using scissors or a scalpel. Wash the tissue 2-3 times with pre-chilled PBS.
(2) Add 1 mL of Lysis Buffer A for every 200 mg of tissue. Mix thoroughly. Homogenize the tissue using a tissue grinder.
(3) After homogenization, centrifuge at 10000 ×g for 10 minutes at 4°C. Discard the supernatant and retain the pellet.
Note: After the above steps, the supernatant will contain cytoplasmic components, while intact nuclei will remain in the pellet.
3. Add 400 μL of Lysis Buffer B to the pellet obtained in step 1 or 2 (per 1×10⁷ cells or 200 mg tissue). Incubate on a rotator at 4°C for at least 30 minutes.
4. After incubation, centrifuge at 12000 ×g for 10 minutes at 4°C. Transfer the supernatant to a new tube.
5. Add Reagent A at a volume of 1/10 of the amount of Lysis Buffer B used (e.g., if 400 μL of Lysis Buffer B was used in step 3, add 40 μL of Reagent A here). Incubate on a rotator at 4°C for 1.5 hours, then place on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge at 12000 ×g for 10 minutes at 4°C and discard the supernatant.
6. Add 100-200 μL of pre-chilled Reagent B to the pellet, pipette to mix thoroughly, and centrifuge again at 12000 ×g for 10 minutes at 4°C. Discard the supernatant and repeat the wash once.
7. Air-dry the pellet. Add 40 μL of ultrapure water to resuspend. Mix gently, aliquot, and store at -80°C.
This extraction method is simple and efficient and maximally preserves the native structure and post-translational modifications of histones, making it suitable for high-quality histone research.
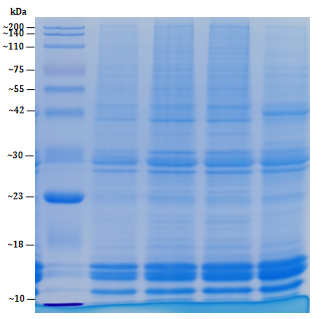
Features and Benefits
1. Efficient Histone Extraction
With an optimized lysis buffer formulation and dedicated extraction protocol, histone can be rapidly and effectively isolated from the cell nucleus while preserving their native conformation and post-translational modifications.
2. Reduced Risk of Degradation and Denaturation
The histone extraction kit contains protease inhibitors that effectively suppress intracellular protease activity, minimizing histone degradation during extraction and ensuring structural integrity.
3. Simple Operation
The extraction process does not require complex organic solvent handling. The simplified procedure saves considerable time and effort.
4. High-Purity Yield
It yields highly purified histones with minimal contamination from other cellular components or impurities, making it suitable for downstream applications such as Western blotting, mass spectrometry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP).
5. Broad Applicability
Compatible with various cell types including animal cells, plant cells, and certain fungal cells, the extracted histones are ideal for epigenetics and gene regulation studies across diverse research settings.
Applications
1. Epigenetics Research
Post-translational modifications of histones (e.g., acetylation, methylation) play key roles in gene expression regulation. By extracting histones, researchers can investigate their functions in chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation.
2. Cell and Molecular Biology Studies
Histones are central to biological processes such as cell division, DNA repair, and gene activation or silencing. Histone extraction kit enables the study of histone involvement in processes like the cell cycle and DNA damage repair.
3. Disease Mechanism Research
Abnormal histone modifications are closely linked to various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. By analyzing histone modifications, researchers can explore changes during disease progression and identify potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets.
4. Gene Expression and Transcriptional Regulation
Histone modifications directly influence transcriptional activity. Extracting and analyzing histones provides insight into molecular mechanisms of gene regulation, supporting research in transgenics, epigenetics, and beyond.
FAQs
Q1: Is Histone Extraction Suitable for All Cell Types?
A1: Yes, the histone extraction kit is compatible with a variety of cell types, including animal cells, plant cells, and some fungal cells. However, for certain specialized cell types, optimization of lysis conditions or incubation time may be required.
Q2: Are the Extracted Histones Suitable for Western Blot Analysis?
A2: Yes, the extracted histones are of high purity and fully compatible with downstream applications such as Western Blot. For optimal results, it is recommended to adjust the protein concentration as needed.
Q3: How Can the Purity of Histone Extraction Be Improved?
A3: If impurities are present during extraction, increasing the number of centrifugation steps or using dedicated filtration steps can help further purify the sample. Additionally, extending lysis time or adjusting buffer concentration may improve extraction efficiency.
Q4: What Should I Do If Protein Degradation Occurs after Extraction?
A4: Maintain low temperatures throughout the extraction process to minimize protease activity. Using sufficient protease inhibitors and reducing the lysis time can also help prevent degradation.










