Exosome-Mediated Protein Delivery Service
- Passive incubation for small or hydrophobic proteins
- Electroporation or sonication for large or charged proteins
- Transfection or expression system for endogenously packaged fusion proteins
- Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) for size and concentration
- Western blot or ELISA for exosome markers (CD63, CD81, TSG101)
- Protein quantification and structural integrity assessment
- Targeted Enzyme Replacement Therapy: Delivery of functional enzymes to replace defective or missing proteins in metabolic disorders.
- Intracellular Antibody Delivery: Intracellular delivery of therapeutic antibodies or nanobodies to inhibit specific signaling proteins in cancer or viral infections.
- Immune Modulation: Transport of cytokines or regulatory proteins to modulate immune cell responses in autoimmunity and transplantation.
- Gene Expression Control: Delivery of transcription factors or regulatory proteins to manipulate gene expression profiles in target tissues.
- Comprehensive experimental details (materials, instruments, and methods)
- Purified exosomes loaded with proteins
- Characterization report including size, concentration, and loading efficiency
- Bioactivity verification of delivered proteins
- Summary of surface modifications (if applicable)
- Quality control documentation
- Custom reports tailored to research needs and project goals
Protein-based therapeutics have emerged as a powerful strategy in treating various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and genetic conditions. However, the delivery of functional proteins into target cells remains a major challenge due to their large molecular weight, structural complexity, and vulnerability to degradation by proteases. Traditional delivery systems such as liposomes and viral vectors often encounter limitations, including low biocompatibility, immunogenicity, and inefficient intracellular trafficking.
Exosomes, a class of extracellular vesicles typically ranging from 30 to 150 nanometers in size, have gained considerable attention as natural nanocarriers for therapeutic delivery. Originating from endosomal pathways and secreted by nearly all cell types, exosomes possess inherent advantages such as biocompatibility, low immunogenicity, stability in circulation, and the unique ability to cross biological barriers, including the blood-brain barrier. These characteristics make exosomes an ideal vehicle for intracellular delivery of functional proteins. Exosome-mediated protein delivery involves loading therapeutic or functional proteins into exosomes and utilizing their natural cell-communication pathways to transport these biomolecules into recipient cells. This approach offers a non-toxic, targeted, and efficient platform to deliver proteins that modulate signaling pathways, replace defective enzymes, or serve as immune modulators.
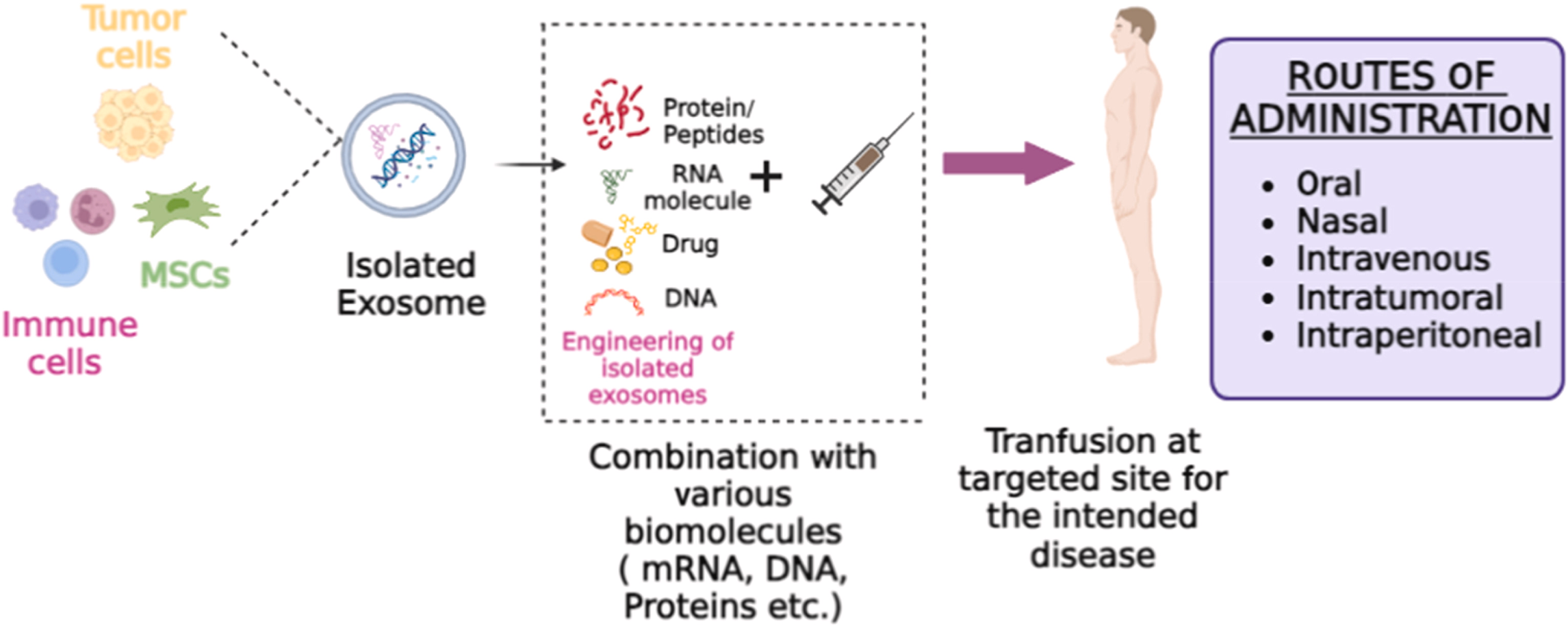
Figure 1. An Overview of Drug Delivery using Exosomes
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers an end-to-end Exosome-Mediated Protein Delivery Service that includes exosome isolation, protein cargo loading, surface modification, quality control, and bioactivity validation. Our service supports the efficient and reproducible development of exosome-based protein delivery systems tailored to specific research or therapeutic goals. We work with a variety of proteins including enzymes, transcription factors, antibodies, and cytokines. In addition to supporting exosome-mediated protein delivery, we also offer customized services for RNA and small molecule drug delivery. Our tailored solutions ensure that RNA-based therapies such as mRNA, siRNA, miRNA, and circRNA, as well as small molecule drugs, are efficiently delivered using exosomes, providing a versatile platform for a wide range of therapeutic applications.
Our service covers, but is not limited to, the following capabilities:
1. Exosome Source Selection
Selection of appropriate donor cell lines or tissue sources, including mesenchymal stem cells, HEK293 cells, or custom-engineered lines.
2. Exosome Isolation and Purification
Exosomes are isolated using ultracentrifugation, tangential flow filtration, or size exclusion chromatography, depending on the sample type and purity requirements.
3. Protein Loading
Proteins are loaded into exosomes using methods such as:
4. Exosome Characterization
5. Targeting and Labeling
Optional functionalization with targeting peptides, antibodies, or dyes for tracking and cell-specific delivery.
6. Validation and Reporting
Delivery efficiency and functional validation in cellular models; preparation of a comprehensive data report with recommendations.
Service Advantages
✔️End-to-End Customization
Provides fully integrated services from exosome isolation to in vitro functional validation, tailored to meet the specific needs of drug development and academic research.
✔️High Cargo Loading Efficiency
Utilizes advanced loading techniques such as electroporation, sonication, and transfection-based methods to ensure efficient and stable encapsulation of protein cargos.
✔️Preservation of Protein Bioactivity
Optimized protocols maintain the structural integrity and functional activity of proteins post-loading, ensuring effective delivery and biological relevance.
✔️Scalable and Reproducible Workflow
Ensures consistent quality and batch-to-batch reproducibility through standardized operating procedures and rigorous quality control.
Applications
The major applications of Exosome-mediated protein delivery service include:
Deliverables
Our Exosome-Mediated Protein Delivery Service is designed to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality. Free project evaluation, welcome to learn more details.
Related Services
|
Comprehensive Exosome Analysis Services by MtoZ Biolabs |
|||
|
Ultracentrifugation and Microfiltration based Exosome Purification |
Classical method for enriching exosomes from large-volume samples; suitable for preparative applications. |
||
|
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) based Exosome Purification |
Gentle, size-based separation preserving exosome integrity; ideal for downstream functional studies. |
||
|
High-purity isolation targeting specific exosome surface markers using antibody-conjugated platforms. |
|||
|
Physical Characterization |
Measures particle size distribution and concentration; widely used for routine exosome quality assessment. |
||
|
Provides direct visualization of exosome morphology; considered the gold standard for structural validation. |
|||
|
Enables single-particle analysis of size, concentration, and zeta potential with high precision. |
|||
|
Confirms exosome identity and purity by detecting classical (e.g., CD63) and negative (e.g., Calnexin) markers. |
|||
|
Quantifies surface proteins and distinguishes subpopulations using fluorescent antibody labeling. |
|||
|
High-sensitivity single-particle analysis of exosome size, concentration, and surface marker expression. |
|||
|
Mass spectrometry-based profiling of exosomal proteins to reveal functional content and biomarkers. |
|||
|
Identifies low-molecular-weight metabolites in exosomes to explore their metabolic roles and signatures. |
|||
|
Comprehensive analysis of lipid species involved in membrane structure and signaling. |
|||
|
High-throughput sequencing of total RNA to reveal lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA content. |
|||
|
Fluorescent or functional labeling for exosome tracking and uptake studies. |
|||
|
Custom engineering of exosomes for targeted delivery to disease-specific tissues or cells. |
|||
|
Incorporates therapeutic cargos such as RNA, proteins, or small molecules into exosomes. |
|||
|
Exosome-Associated Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Vector Production |
Combines exosomes with AAV vectors to enhance gene delivery and targeting efficiency. |
||
|
Assesses cellular-level effects such as proliferation, migration, and immune modulation. |
|||
|
Evaluates biodistribution and biological activity of exosomes in animal models. |
|||
How to order?







