Exosome Labeling Service
Exosome labeling is a technique for labeling exosomes to enable dynamic tracking and functional studies. This is achieved by labeling exosomes with fluorescent dyes, protein fusions, magnetic nanoparticles, or radioactive isotopes, making them visible and traceable under microscopy, flow cytometry, or in vivo imaging systems. The principle of this service is based on the conjugation of labeling agents to exosomal membrane lipids or membrane proteins, thereby allowing precise monitoring of exosome distribution, targeting characteristics, and uptake pathways within cells, tissues, or live animals.
Exosome labeling service is widely applied in areas such as tumor metastasis mechanism research, stem cell-derived exosome homing validation, drug delivery evaluation, and immune regulation analysis. By accurately labeling exosomes, this service facilitates the study of their dynamic behavior in intercellular communication, disease progression, and therapeutic response, serving as a critical tool for advancing both in-depth functional research and clinical translation of exosome applications.
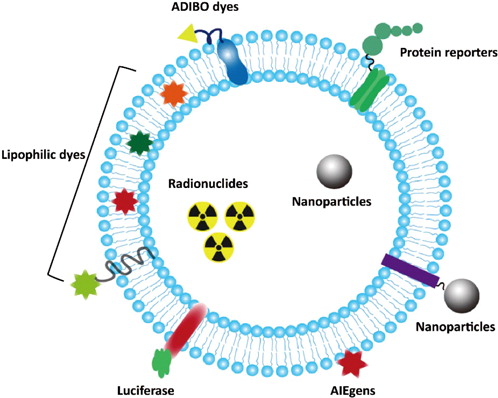
Ma, N. et al. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences, 2021.
Figure 1. Different Strategies for Exosome Labeling.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced platforms such as flow cytometry and imaging systems, and incorporating multiple techniques including fluorescent dyes and magnetic nanoparticles, the exosome labeling service provided by MtoZ Biolabs can efficiently label exosomes. The service includes exosome isolation, labeling, purification, and verification of labeling efficiency, ensuring high signal intensity, strong specificity, and excellent reproducibility of the visual tracking data. This robust workflow supports subsequent in vitro and in vivo functional studies and quantitative analyses.
Service Advantages
1. Multiple Labeling Options Available
A variety of labeling strategies are provided, including fluorescent dyes, protein fusions, nanoparticles, and radioisotopes, to support both in vitro and in vivo imaging needs across different research goals and sample types.
2. High Sensitivity and Specificity
By integrating flow cytometry, confocal microscopy, and in vivo imaging systems, the service enables high-resolution imaging and quantitative analysis of labeled exosomes, ensuring high sensitivity, strong specificity, and low background in experimental data.
3. Standardized Workflow
A comprehensive one-stop workflow covering exosome isolation, labeling, purification, and validation has been established to ensure high experimental consistency and stable labeling performance.
4. Customized Solutions
MtoZ Biolabs is supported by a team of experienced researchers who can tailor labeling strategies based on specific research goals, thereby enhancing experimental efficiency and data reliability.
Applications
1. In Vivo Homing and Distribution Studies of Exosomes
The exosome labeling service can be used to trace the dynamic in vivo distribution and tissue accumulation of exosomes, revealing their targeting behavior and homing characteristics. It is widely applied in studies involving the tumor microenvironment and organ-specific targeting.
2. Drug Delivery System Development
In the development of engineered exosomes as drug carriers, labeling services are essential for evaluating in vivo delivery efficiency, targeting specificity, and biosafety, providing experimental support for the advancement of novel nano drug delivery systems.
3. Functional Validation of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes
The exosome labeling service enables the tracking of stem cell-derived exosomes in processes such as tissue repair and immune regulation, supporting studies in regenerative medicine and functional localization.
4. Investigation of Intercellular Communication Mechanisms
By labeling exosomes and combining with uptake assays, this service facilitates analysis of interactions between exosomes and recipient cells, helping to uncover the roles of exosomes in cell-to-cell communication, inflammatory responses, and related biological processes.
5. Exploration of Tumor Metastasis and Immune Evasion Mechanisms
The exosome labeling service can be used to track tumor-derived exosomes across various organs, providing insights into their roles in promoting metastasis, modulating immune responses, and driving disease progression.
Case Study
1. Covalently Labeled Fluorescent Exosomes for In Vitro and In Vivo Applications
This study aimed to develop a covalent labeling strategy for preparing exosomes with stable fluorescent signals, enabling long-term tracking and functional research in both in vitro and in vivo settings. The research focused on exosomes derived from various sources, including tumor and stem cells. Researchers employed NHS ester reactions to covalently attach fluorescent dyes to amino groups on the exosome surface, resulting in highly stable fluorescently labeled exosomes. The labeling efficiency was validated using confocal microscopy and flow cytometry, with results showing strong signal intensity and notable stability, making the method suitable for long-term culture and repeated imaging. In a mouse model, the labeled exosomes were effectively tracked and displayed distinct distribution patterns and tissue accumulation. The study concludes that this covalent labeling method offers a reliable tool for exosome tracking, cellular uptake studies, and delivery system development, thereby advancing both basic research and preclinical applications of exosomes.
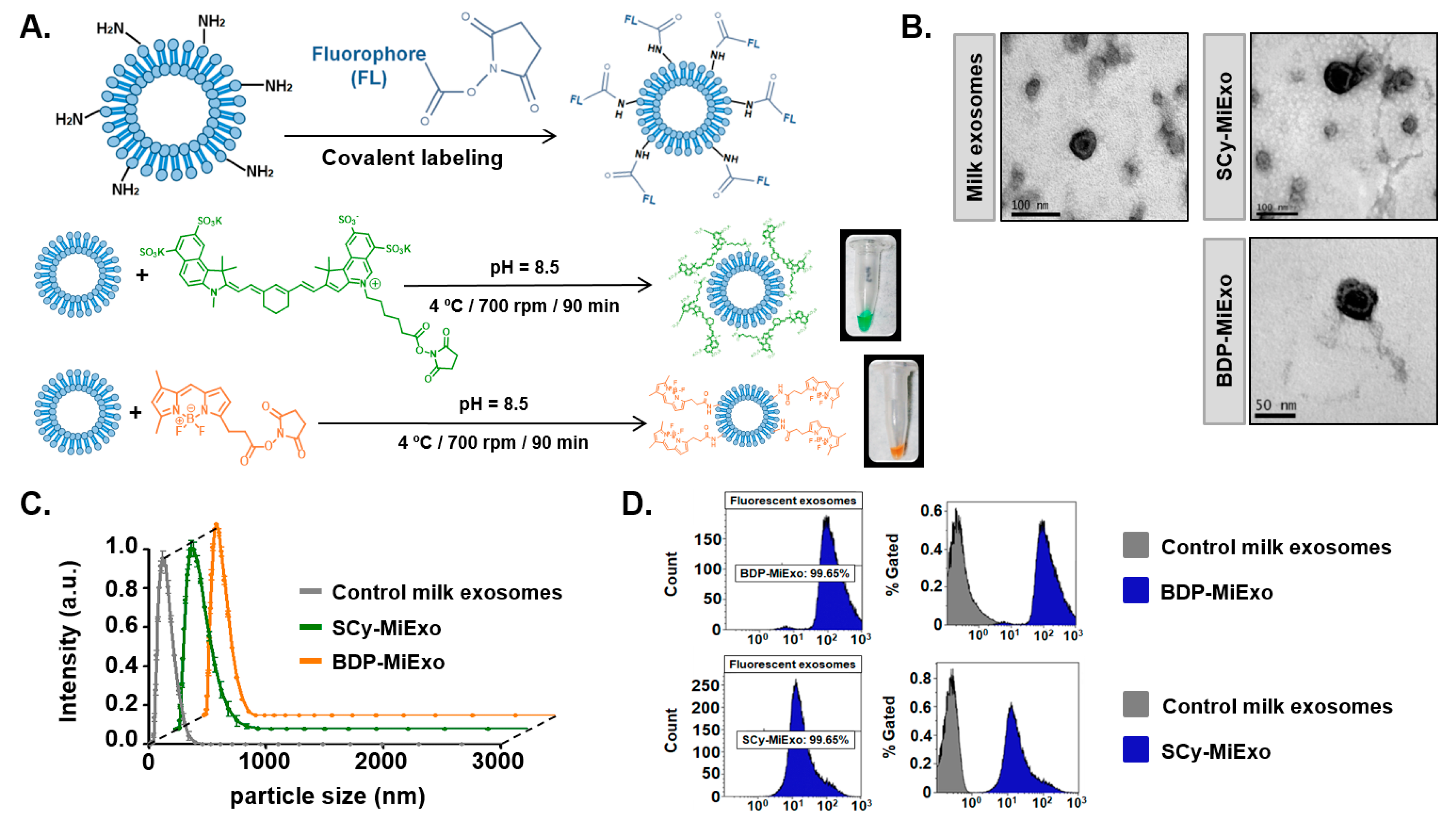
González, M I. et al. Biomedicines, 2021.
Figure 2. Optical Labeling and Physicochemical Characterization of Control and Fluorescence-Labeled Milk Exosomes.
FAQ
Q1: What Sources of Exosomes Can Be Used for Labeling?
A1: We support exosomes derived from various sources, including cell culture supernatants, serum, plasma, urine, saliva, and cerebrospinal fluid. As long as the samples are pre-cleared by low-speed centrifugation to remove debris and cell fragments, subsequent isolation and labeling can be performed.
Q2: Does the Labeling Process Affect the Biological Function of Exosomes?
A2: We have optimized the labeling conditions by carefully controlling dye concentration, reaction time, and washing steps to ensure high labeling efficiency while preserving the structural integrity and biological activity of exosomes. For sensitive applications, we also offer mild labeling options upon request.
How to order?







