Western Blotting based Exosome Characterization Service
Western blotting-based exosome characterization is a specialized service that utilizes Western Blot technology to detect and validate protein markers within exosomes. Western Blot separates exosomal proteins using SDS-PAGE, followed by their transfer onto a membrane and detection using antibodies specific to exosome markers, thereby confirming the presence, purity, and origin of exosomes. This method offers high sensitivity and specificity, effectively identifying both membrane and internal proteins of exosomes to validate the success of exosome isolation.
Western blotting-based exosome characterization service is widely applied in exosome-related basic research, disease mechanism studies, and the development of novel drug delivery systems across fields such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and immune disorders. By detecting specific proteins in exosomes via Western Blot, researchers can assess the efficiency of exosome isolation, functional modifications, and drug loading capacity. It is a commonly used and essential quality verification tool in exosome research.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on high-performance protein electrophoresis transfer systems and chemiluminescence imaging systems, MtoZ Biolabs' western blotting-based exosome characterization service enables the detection of signature proteins in exosome samples. The service includes exosomal protein extraction, SDS-PAGE separation, membrane transfer, specific antibody incubation, and imaging analysis, ensuring high-resolution and highly specific protein band images that clearly display the expression of exosome marker proteins. A detailed analysis report is provided to verify the presence and purity of exosomes.
Analysis Workflow
1. Exosome Isolation and Purification
Exosomes are isolated and purified from blood, urine, or cell culture media using ultracentrifugation, density gradient centrifugation, or immunoaffinity methods to ensure high-purity samples.
2. Protein Extraction and Quantification
Proteins are extracted from purified exosomes by lysis, followed by concentration quantification using methods such as BCA assay to ensure accurate downstream analysis.
3. Protein Electrophoresis Separation
The extracted protein samples are separated using SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis technology, resolving protein bands according to their molecular weights.
4. Protein Transfer and Antibody Incubation
The electrophoretically separated proteins are transferred onto PVDF or nitrocellulose membranes, followed by incubation with antibodies specific to exosomal markers.
5. Detection, Imaging, and Data Analysis
Protein bands are visualized using a chemiluminescence imaging system, generating images of exosomal marker expression. Semi-quantitative analysis and definitive exosome identification results are provided through image analysis software.
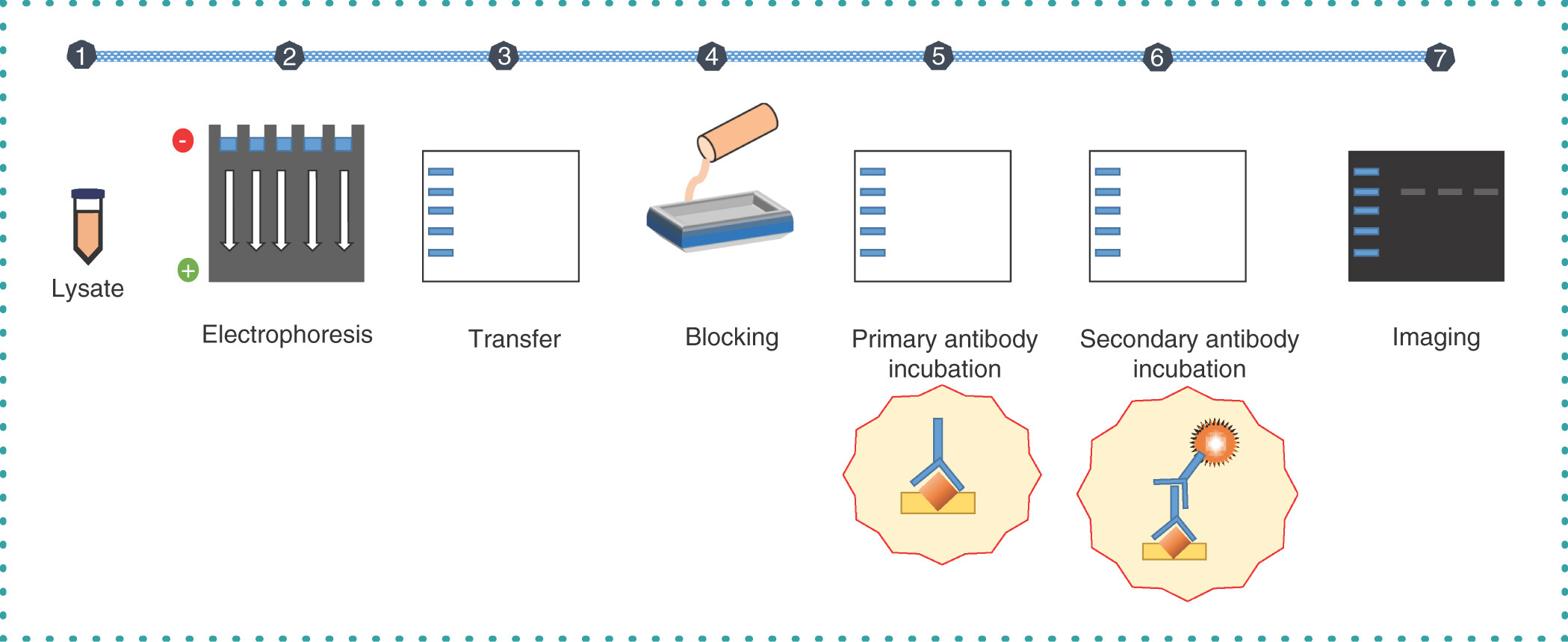
Begum, H. et al. Taylor & Francis, 2022.
Figure 1. Overview of the Multistep Western Blotting Technique.
Service Advantages
1. High Sensitivity
Advanced chemiluminescence imaging systems enable the detection of low-abundance exosomal proteins, providing clear and reliable data.
2. One-Time-Charge
Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. High-Data-Quality
Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all western blotting analysis data, providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
4. Flexible Customization
MtoZ Biolabs offers customizable exosomal protein marker panels based on client needs, meeting the personalized requirements of diverse research projects.
Applications
1. Exosome Purity Verification
Western blotting based exosome characterization service helps confirm the purity of exosomes isolated from blood, urine, cell culture supernatants, and other biological samples, excluding contamination from other vesicles or impurities.
2. Disease Mechanism Research
Western blotting can be used to analyze the expression changes of exosomal marker proteins under various disease conditions (such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases), supporting studies on disease mechanisms.
3. Engineering Exosome Validation
Western blotting based exosome characterization service can be used to detect and confirm the successful loading of drugs or biomolecules onto exosomes, supporting the development of drug delivery systems.
4. Quality Control and Standardization
Provides essential protein expression data for preclinical research or exosome product development, ensuring experimental reliability and reproducibility.
Case Study
1. Hypoxia-Treated Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Exosomes Enhance the Therapeutic Effects on Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Mice
This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects of hypoxia-treated adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell (ADSC)-derived exosomes on renal injury in unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) mice and to characterize the exosomes using Western blotting. The study focused on exosomes secreted by ADSCs cultured under hypoxic conditions. Methods included isolating exosomes by ultracentrifugation, followed by Western blot analysis to detect exosome-specific markers (such as CD63, CD81, and TSG101) to confirm the purity and quality of exosomes. Western blot results showed that hypoxia-treated ADSC-derived exosomes strongly expressed these exosome-specific proteins, validating the successful isolation and high purity of exosomes. Furthermore, the study found that hypoxia-treated ADSC-derived exosomes more effectively alleviated renal fibrosis and inflammatory injury in the UUO model. The study concluded that Western blotting effectively characterized the quality and identity of exosomes, supporting that hypoxia preconditioning enhances the therapeutic potential of ADSC-derived exosomes.
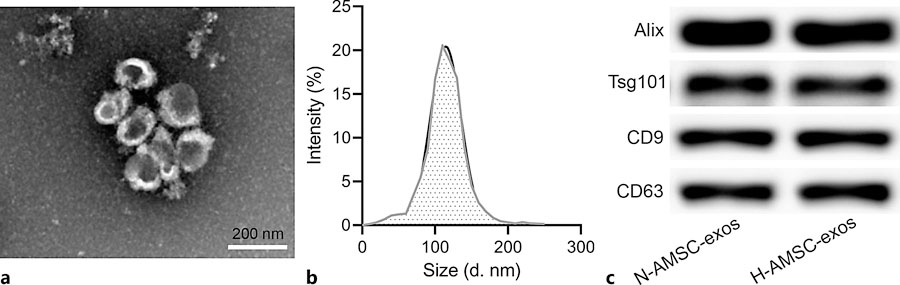
Zhang, C. et al. Pharmacology, 2024.
Figure 2. Identification of AMSC-Derived Exosomes.
2. Role of Tear Exosomes in the Spread of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 in Recurrent Herpes Simplex Keratitis
This study aimed to investigate the role of tear-derived exosomes in the spread of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) in recurrent herpes simplex keratitis (HSK) and to characterize exosomes using Western blotting. The study focused on a recurrent HSK mouse model, and methods included collecting tear fluid from diseased mice, isolating exosomes by ultracentrifugation, and detecting exosome markers (such as CD9, CD63, CD81) and viral proteins using Western blotting. The results showed that Western blotting successfully confirmed the presence of typical exosome markers in tear exosomes, indicating high purity of isolated exosomes; moreover, HSV-1-specific viral proteins were clearly detected, suggesting that exosomes effectively carry viral particles. The study concluded that tear-derived exosomes serve as critical carriers for HSV-1 dissemination, and Western blot characterization provided essential molecular evidence for exosome-mediated viral transmission, offering new insights into the diagnosis and treatment of HSK.
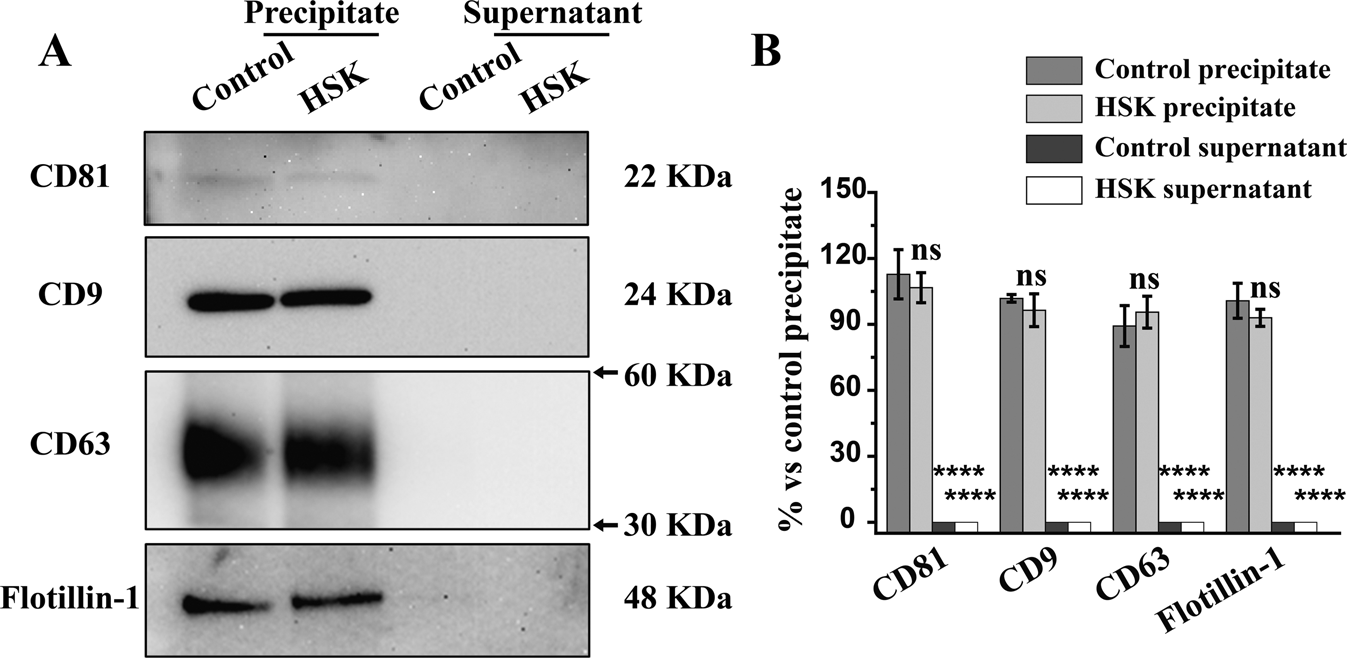
Huang, H Y. et al. Eye, 2023.
Figure 3. Identification of Exosome Biomarkers in Precipitate and Supernatant Isolated from Tear Fluids.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Western Blot Imaging and Quality Control Assessment
4. Data Analysis and Quantification
5. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
FAQ
Q1: What Are the Advantages of Western Blotting in Exosome Characterization?
A1: Western blotting offers high specificity and strong reliability in exosome characterization, enabling direct detection of specific proteins within exosomes and their relative expression levels. Moreover, by targeting well-established exosomal markers, Western blotting ensures the purity and integrity of isolated exosomes, making it an essential quality control method in exosome research.
Q2: How Is the Reproducibility and Reliability of Western Blot Analysis Ensured?
A2: We follow a rigorous standardized workflow, including precise protein quantification, consistent sample loading amounts, inclusion of positive and negative controls, use of internal reference proteins, and standardized antibody incubation conditions, to ensure high reproducibility and reliability of the experiments. In addition, parallel experiments and multiple repetitions are performed to validate the consistency of the results.
How to order?







