Exosome Cargo Loading Service
- Small RNAs (miRNA/siRNA): Electroporation is recommended for efficient loading without compromising exosome integrity.
- Proteins or large nucleic acids (mRNA/CRISPR components): Endogenous expression loading is preferred—express the target molecule within donor cells, which is then naturally packaged into secreted exosomes. This is ideal for complex or degradation-prone molecules.
- Small molecules/hydrophobic probes: Passive incubation or sonication can be used to facilitate membrane fusion or adsorption for effective loading.
Exosome Cargo Loading Service utilizes a variety of engineering strategies—including physical, chemical, and biological methods—to incorporate exogenous functional molecules (such as miRNA, siRNA, mRNA, proteins, compounds, probes, etc.) into exosomes. These engineered exosomes gain specific functional or targeting capabilities, making them suitable for applications in cell regulation, molecular therapy, imaging, signaling pathway research, and more.
Exosomes are membrane-bound vesicles secreted by various cell types, known for their excellent biocompatibility, low immunogenicity, and natural transmembrane delivery capacity. In recent years, exosomes have emerged as promising drug and molecule delivery vehicles in both basic research and translational medicine. Their native structure enables the encapsulation of various bioactive molecules, including nucleic acids, proteins, and small-molecule drugs, which can be precisely delivered to target cells via endocytosis and other mechanisms. To expand their utility in precision therapy, gene modulation, and functional studies, artificial methods are required to effectively load specific functional molecules into exosomes—giving rise to exosome cargo loading technologies. These techniques involve introducing target cargos either into the interior or onto the surface of exosomes using physical, chemical, or bioengineering approaches, leveraging the exosomes’ natural membrane structure and targeting properties to ensure stable delivery and cellular uptake of therapeutic or experimental molecules.
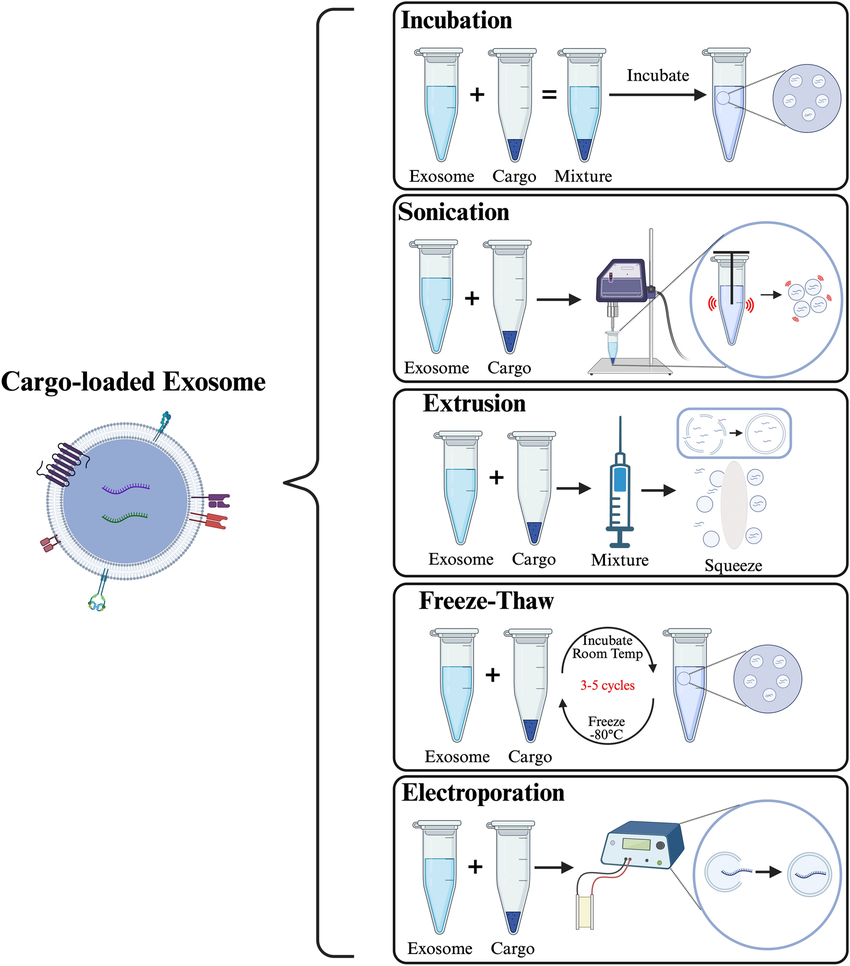
Al-Ani S A. et al. Molecular Biotechnology. 2024.
MtoZ Biolabs offers a professional Exosome Cargo Loading Service that enables the efficient encapsulation of various biomolecules—such as RNA, DNA, proteins, and small-molecule drugs—into exosomes. This service supports targeted delivery, functional release, and mechanistic studies across a wide range of research applications. Our service includes a full suite of capabilities: diverse loading strategies, customizable exosome sources, exosome purification, and cargo incorporation. Whether you're working on disease models, nanodrug development, or gene regulation, MtoZ Biolabs empowers your research with high-quality, application-ready exosome formulations.
Analysis Workflow
The Exosome Cargo Loading Service at MtoZ Biolabs follows a standardized and customizable workflow:
1. Exosome Source & Loading Strategy Planning
Recommend the optimal exosome source and loading strategy based on the type of cargo to be delivered.
2. Exosome Preparation & Purification
Obtain high-purity exosomes using methods such as ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), and ultrafiltration.
3. Cargo Loading
Introduce cargo into exosomes using electroporation, sonication, or transfection methods depending on molecular type and stability.
4. Quality Control & Validation
Exosome characterization: NTA (particle size), TEM (morphology), Western blot (marker verification).
Loading efficiency: qPCR, fluorescence labeling, spectrophotometry.
Functional validation: Cellular uptake assays, transfection efficiency analysis.
5. Delivery & Technical Support
Provide full experimental protocols, QC data, and practical recommendations for downstream applications.
Applications
RNA Delivery & Gene Modulation
Deliver siRNA, miRNA, CRISPR-Cas9 components, or mRNA via exosomes to regulate gene expression or edit genes, useful for mechanistic studies and pathway analysis.
Drug Delivery & Targeted Therapy
Load exosomes with anticancer drugs, antibiotics, or small-molecule inhibitors to enhance bioavailability and targeting specificity.
Protein Delivery & Functional Reprogramming
Deliver signaling proteins, transcription factors, or immune modulators to target cells to explore their role in cell fate decisions and functional modulation.
Molecular Imaging & Diagnostic Probe Delivery
Incorporate fluorescent dyes, MRI contrast agents, or radioisotopes into exosomes for targeted imaging and early disease detection.
Preclinical Disease Model Validation
Assess biodistribution, uptake, biological activity, and therapeutic efficacy of cargo-loaded exosomes in animal models.
FAQ
Q. Which cargo loading strategy is best suited for my molecule type?
The choice of strategy depends on the physicochemical properties of the cargo:
Q. How is cargo loading efficiency and stability assessed?
RNA cargo: Evaluate loading efficiency using qPCR, fluorescent labeling, or RNA quantification assays.
Protein/drug cargo: Use Western blot, ELISA, HPLC, or UV spectrophotometry for quantification.
Stability: Analyze particle size (NTA), morphology (TEM), and conduct functional release assays after storage. For leak-prone cargo, optimize buffer systems or use membrane stabilizers to improve retention and release profile.
Case Study
In this study, researchers used Exosome Cargo Loading technology to efficiently package mRNA encoding the epigenetic silencer ZPAMt (ZFP362-DNMT3A fusion protein) into exosomes. These engineered exosomes were produced by modified cells and delivered to HIV-1 latently infected cells, where they successfully induced DNA methylation at the viral promoter, stably repressing HIV-1 transcriptional activation. In a humanized mouse model, systemic delivery of these mRNA-loaded exosomes resulted in sustained HIV-1 silencing across multiple tissues, including bone marrow, spleen, and brain, demonstrating the potential of mRNA-loaded exosomes in epigenetic therapy for chronic viral infections.
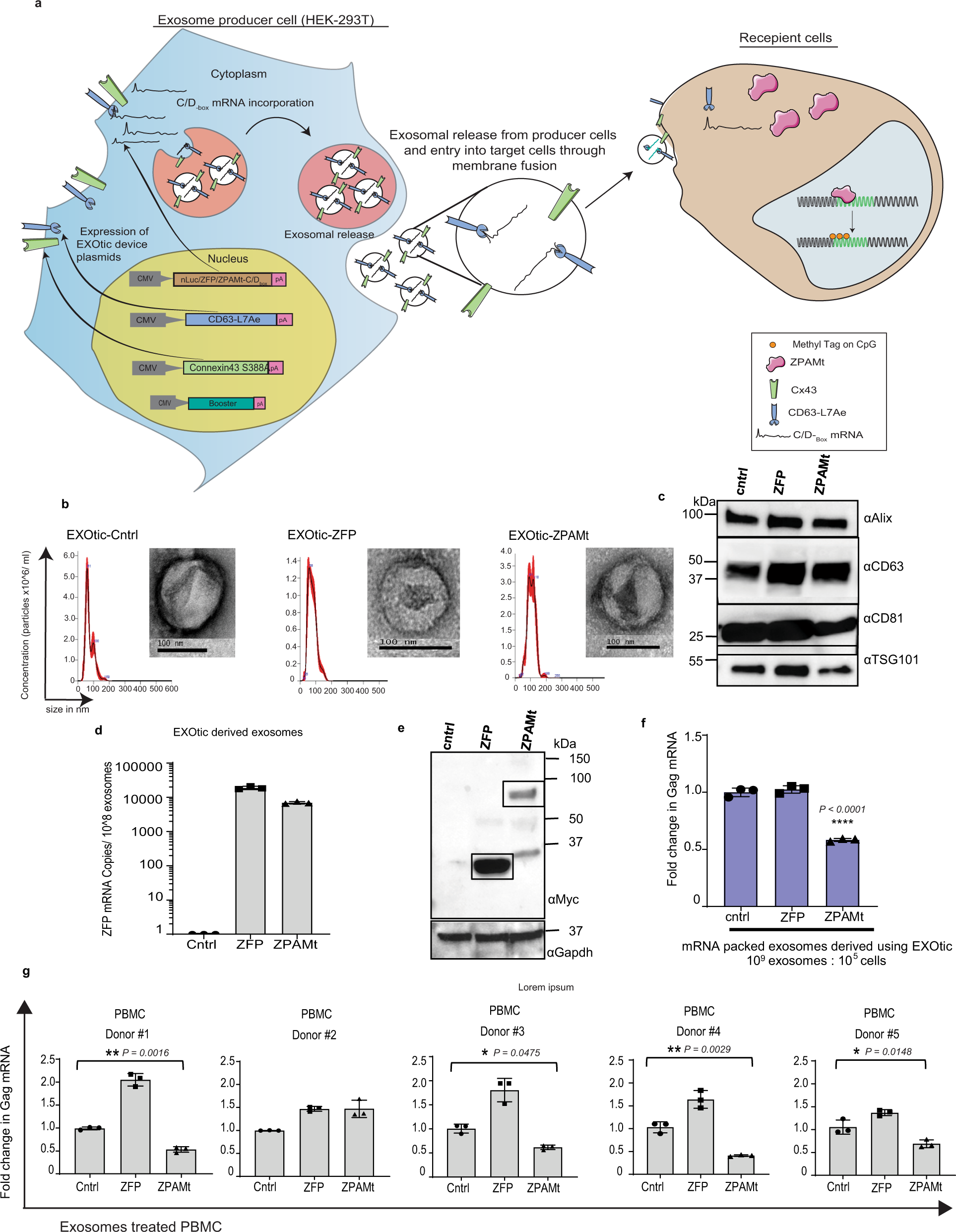
Shrivastava S. et al. Nature Communications. 2021.
How to order?







