Parkinson's Disease Exosome Research Service
- Ultracentrifugation
- Microfluidic device
- Size exclusion chromatography (SEC)
- Polymer-based precipitation
- Immunoaffinity capture
- Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA)
- Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
- Western blotting
- Flow cytometry
- Fluorescent labeling
- Bioluminescence imaging (BLI)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Animal models
- Genetic engineering
- Sample Types: CSF, serum, plasma, brain tissue lysate, cell culture media, or other biological samples
- Volume Requirements: Minimum 500 μL for fluids, or 50 mg for tissue samples
- Storage and Transport: Store samples at −80°C and ship on dry ice; avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder primarily characterized by the selective loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. This neuronal degeneration is closely associated with the accumulation of misfolded and aggregated α-synuclein, which forms intracellular inclusions known as Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. These inclusions are widely recognized as the pathological hallmarks of PD. The resulting dopamine deficiency in the basal ganglia circuitry leads to the core motor symptoms of the disease, including bradykinesia, resting tremor, muscular rigidity, and postural instability. In addition to these motor impairments, patients frequently present with a range of non-motor symptoms, including hyposmia, constipation, REM sleep behavior disorder, depression, cognitive decline, and autonomic dysfunction.
Growing evidence indicates that exosomes are critical contributors to Parkinsonian pathology. Neuron- and glia-derived exosomes can transport pathogenic α-synuclein species between cells, thereby facilitating the spread of protein aggregates through connected brain regions. Exosomal cargos also modulate neuroinflammation, mitochondrial function, and synaptic integrity, influencing both neurodegenerative and compensatory processes. Because exosomes circulate in cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood, their molecular content holds promise for minimally invasive biomarkers that reflect disease stage and therapeutic response.
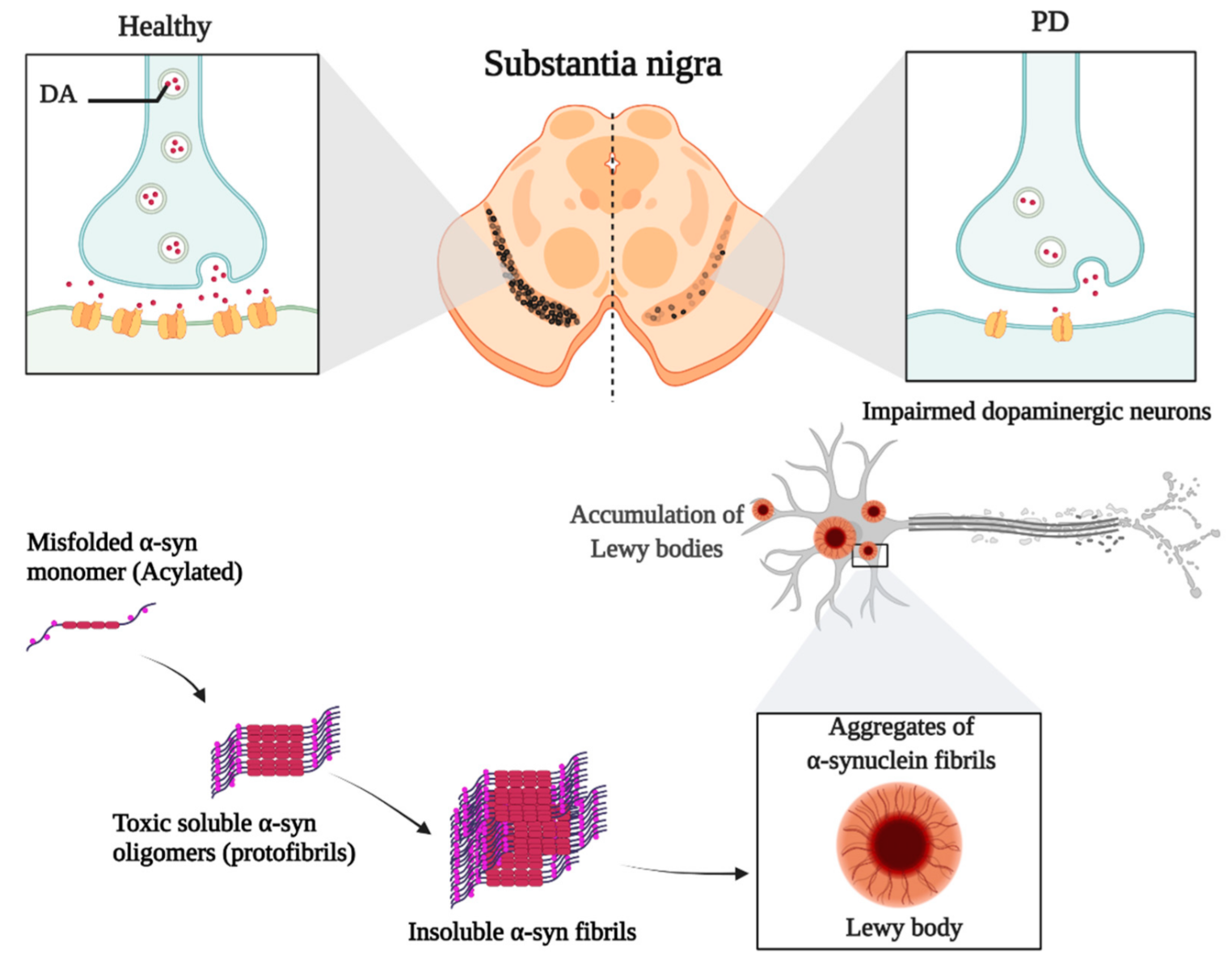
Figure 1. The Role of α-syn in the Development of PD
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
To support researchers in unlocking the mechanistic and diagnostic potential of exosomes in PD, MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive Parkinson's Disease Exosome Research Service. Our Parkinson's Disease Exosome Research Service integrates advanced exosome isolation, multi-omics profiling, molecular tracking, and functional analysis to facilitate biomarker discovery, mechanistic studies, and therapeutic innovation in Parkinson's research.
Our service portfolio includes:
💠Exosome isolation and purification from CSF, serum, plasma, brain tissue, or neural cell models
💠Structural and molecular characterization of exosomes
💠Quantitative and qualitative analysis of exosomal cargo (proteins, miRNA, lncRNA, lipids, etc.)
💠Labeling and real-time tracking of exosomes
💠In vitro and in vivo functional assays to study exosome-mediated cellular uptake, neuroinflammation, and dopaminergic signaling
Analysis Workflow

Service Advantages
☑️Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Parkinson's Disease Exosome Research Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
☑️Customizable Experimental Design: We provide flexible and tailored experimental strategies to meet specific research goals, from early biomarker discovery to mechanistic studies of α-synuclein propagation and exosome-mediated neurotoxicity.
☑️Expert Scientific Team: Our multidisciplinary team comprises specialists in neurodegeneration, extracellular vesicles, and molecular profiling, offering expert consultation and reliable data interpretation.
☑️Strict Quality Control: Each step of our workflow is governed by rigorous quality standards to guarantee reproducibility, sample integrity, and data traceability.
Applications
MtoZ Biolabs' Parkinson's Disease Exosome Research Service supports diverse research goals, including:
1️⃣Pathogenic Mechanism Elucidation: Uncovering how exosomes contribute to α-synuclein transmission, oxidative stress, or mitochondrial dysfunction.
2️⃣Early Biomarker Discovery: Identifying exosome-encapsulated miRNAs, proteins, or lipids that may signal PD onset.
3️⃣Therapeutic Target Validation: Investigating how exosome contents modulate dopaminergic neuron survival or immune response.
4️⃣Drug Delivery Research: Engineering exosomes as vehicles for targeted delivery of neuroprotective agents.
5️⃣Disease Stratification: Profiling patient-specific exosomal cargo to identify subtypes of PD with distinct molecular signatures.
Sample Submission Suggestions
To ensure optimal results, we recommend the following:
*Please consult us for tailored sample collection and storage protocols to maximize data quality.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive experimental details (materials, instruments, and methods)
2. Raw data
3. Processed omics data files
4. Quality control reports (NTA, Western blot, TEM images)
5. Functional assay results
6. Bioinformatics analysis
7. Customized report based on project requirements
To learn more or request a consultation, please contact us.
Related Services
Stroke Exosome Research Service
Huntington's Disease Exosome Research Service
Alzheimer's Disease Exosome Research Service
Exosomal Biogenesis and Identification Service
Exosomal Cargo and Loading Mechanism Service
Exosome-Based Drug Delivery Service
Exosome Antibody Development Service
How to order?







