N-Glycan Liberation Service
N-glycans are oligosaccharide chains covalently linked to the asparagine (Asn) residues of glycoproteins through N-glycosidic bonds, typically at Asn-X-Ser/Thr consensus sequences (where X is any amino acid except proline). As one of the most common post-translational modifications, N-glycosylation occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus and is essential for protein folding, stability, cellular recognition, and signal transduction.
Releasing N-glycans from glycoproteins enables in-depth analysis of glycan structures, identification of glycosylation patterns, and discovery of disease-associated biomarkers. This step is critical for investigating glycosylation function, understanding disease mechanisms, and ensuring product consistency in biopharmaceutical development. Aberrant N-glycosylation has been linked to cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and other pathological conditions, highlighting the importance of N-glycan analysis in both basic research and precision medicine.
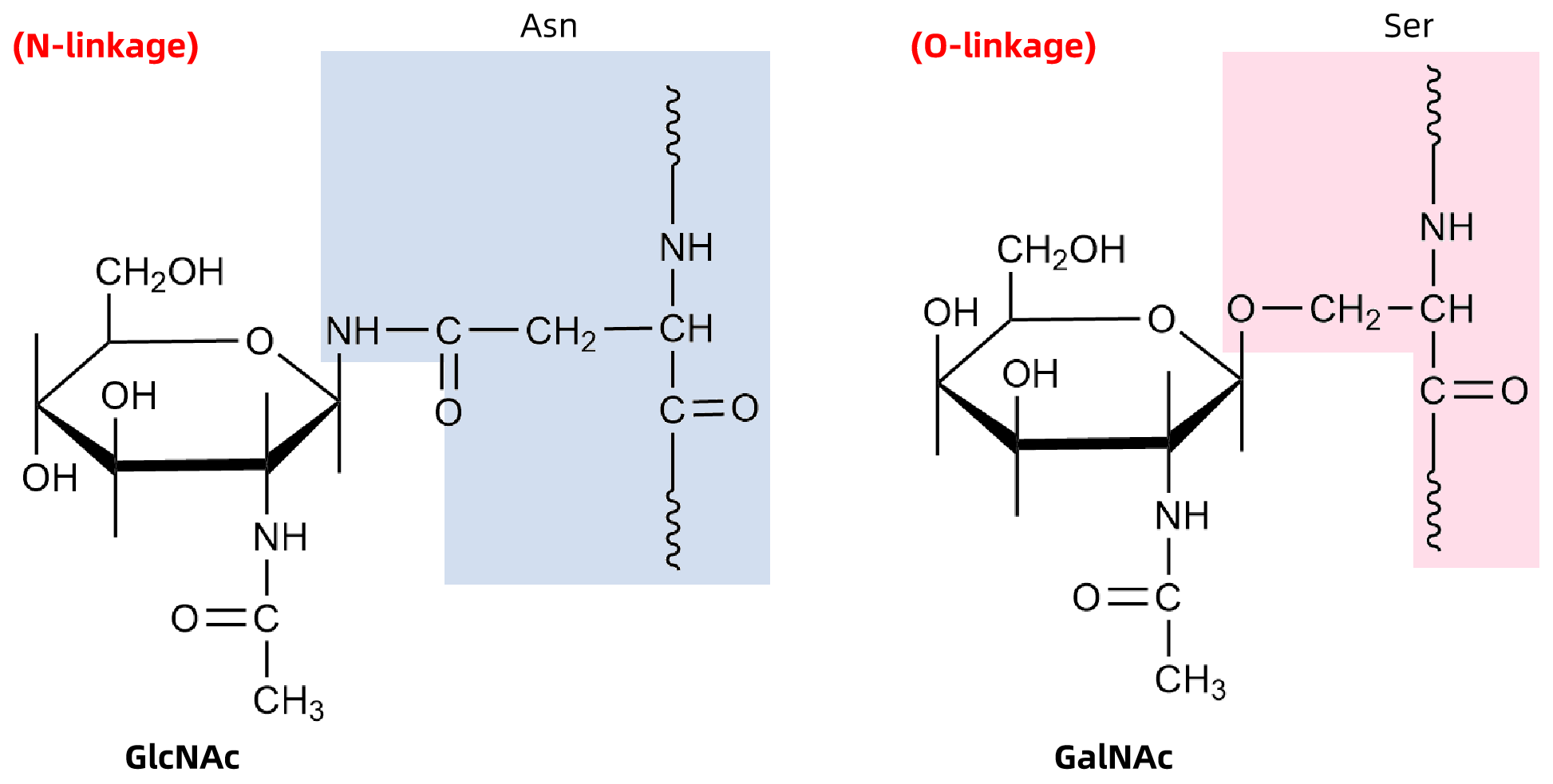
Figure 1. Comparison of N- and O-Glycan Linkages
MtoZ Biolabs offers N-glycan Liberation Service utilizing a range of separation techniques to effectively release N-glycans from glycoproteins. Combined with our high resolution mass spectrometry platforms including Thermo Fisher’s Q Exactive HF and Orbitrap Fusion Lumos systems and nano-LC technology, we provide high sensitivity and high resolution detection of a broad variety of N-glycan structures, supporting both basic research and biopharmaceutical development.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers N-Glycan Liberation Service using multiple enzymatic and chemical strategies tailored to sample characteristics and analytical goals, ensuring optimal release performance and structural fidelity.
· Enzymatic Method: Specific Release Using PNGase F
We primarily use Peptide-N-Glycosidase F (PNGase F) for N-glycan release. This enzyme specifically recognizes the Asn-X-Ser/Thr sequence and cleaves the amide bond between the innermost GlcNAc and the Asn residue, releasing the intact N-glycan with minimal side reactions.
Mechanism: Enzyme selectively targets N-glycosylation sites for glycan release.
Advantages: High specificity, excellent structural integrity, suitable for most glycoproteins.
· Chemical Method: Hydrazinolysis
For glycoproteins resistant to enzymatic cleavage or with non-canonical structures, we offer hydrazinolysis. This method uses anhydrous hydrazine to cleave amide bonds and efficiently release N-glycans.
Mechanism: Hydrazine reacts with amide bonds to break the linkage between glycan and Asn.
Advantages: Broad applicability for complex glycoproteins.
For structurally diverse or heavily modified samples, we can implement a combined enzymatic-chemical approach to maximize release efficiency while preserving glycan integrity.
Analysis Workflow
1. Technical Evaluation and Customization
Selection of optimal release strategy based on sample background and research goals.
2. Sample Preparation
Includes protein concentration, desalting, and removal of terminal modifications to enhance efficiency.
3. N-Glycan Release
N-Using PNGase F, hydrazinolysis, or a hybrid approach to release target glycans.
4. Glycan Purification and Derivatization
Glycans are purified using magnetic beads or solid-phase extraction. Optional fluorescent or isotopic labeling is available.
5. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
High-resolution MS is used to identify and characterize released glycans.
6. Data Analysis and Report Delivery
Includes structural annotation, glycoform distribution, quantitative results, and spectrum interpretation.
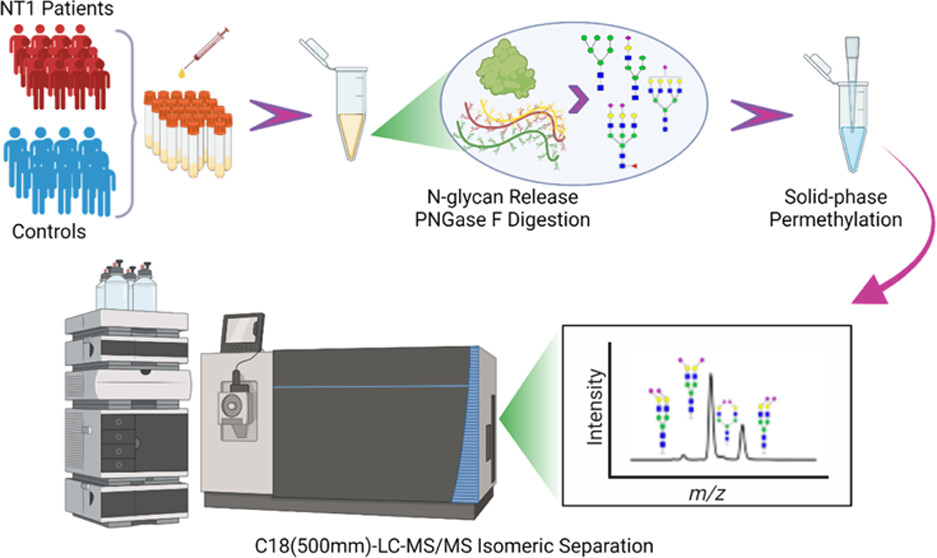
Sanni, A. et al. ACS Omega. 2024.
Figure 2. N-Glycan Release and Analysis Workflow
Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
✅ High-Specificity Release Protocols: Flexible combination of enzymatic and chemical methods to meet various analytical needs.
✅ Advanced Analysis Platform: Equipped with Orbitrap Fusion Lumos and Nano-LC systems for high-resolution, high-sensitivity detection of glycan isomers and trace-level species.
✅ Customizable Service Integration: Supports upstream and downstream services, including N-glycan enrichment, glycopeptide enrichment, and glycoprotein identification.
✅ One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
Sample Submission Suggestions
|
Sample Type |
Minimum Recommended Amount |
|
Serum/Plasma |
≥ 50 µL |
|
Cell Culture Supernatant |
≥ 1 mL |
|
Tissue Homogenate |
≥ 10 mg |
For other sample types or limited quantities, please contact us for detailed handling recommendations.
Complete and efficient release of N-glycans is a critical prerequisite for accurate glycosylation analysis, disease mechanism studies, and biopharmaceutical quality assessment. MtoZ Biolabs’s N-Glycan Liberation Service integrates optimized enzymatic and chemical strategies to ensure high-yield release while preserving structural integrity and functional relevance. When coupled with downstream high-resolution mass spectrometry, our service enables in-depth profiling of glycan composition and distribution, supporting both basic research and applied biopharmaceutical development. Contact us today to advance your glycoscience research with confidence.
FAQ
Q1: Does N-glycan release affect other protein modifications?
Enzymatic methods like PNGase F operate under mild conditions and do not significantly disrupt other post-translational modifications. We can optimize reaction conditions as needed to preserve your target structures.
Related Services
How to order?







