Starch Thermal Stability Determination Service
Starch is a naturally occurring biopolymer composed primarily of amylose and amylopectin arranged within semi-crystalline granules. Its physicochemical properties are influenced by botanical source, molecular structure, degree of crystallinity, and chemical modification. When subjected to heat, starch undergoes a series of physical and chemical transformations, including gelatinization, retrogradation, and thermal decomposition.
Thermal stability describes the resistance of starch to structural breakdown and weight loss when exposed to elevated temperatures. This property determines the processing temperature limits for starch-based materials and influences their shelf stability, texture, and mechanical strength. Native starches typically degrade at lower temperatures due to their high moisture content and weak crystalline organization, while chemically or physically modified starches often display improved stability. Evaluating the thermal stability of starch provides vital information for process optimization, formulation design, and quality assurance. It also helps in selecting the appropriate starch type or modification strategy for specific industrial applications.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers a professional Starch Thermal Stability Determination Service to help researchers and industrial partners evaluate the heat resistance and degradation characteristics of native and modified starches. Using advanced Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), our Starch Thermal Stability Determination Service quantifies mass loss, degradation stages, and thermal transition profiles, providing precise data that support quality control, process optimization, and material design. Our scientific team combines years of experience in polysaccharide analysis with precise instrumentation to deliver reliable, reproducible, and actionable results.
Technical Principles
The Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) technique is a precise thermal analytical method used to assess material stability by measuring weight change as a function of temperature or time under a controlled atmosphere. For starch analysis, TGA detects moisture loss, thermal decomposition, and residue formation during gradual heating.
In a typical TGA experiment, a small amount of starch sample (usually 5–10 mg) is placed in a platinum pan and heated at a constant rate under either nitrogen or air atmosphere. As the temperature increases, the instrument continuously records the sample’s mass change. The resulting thermogram, or TGA curve, displays distinct weight loss steps corresponding to different thermal events:
🔸Initial Stage (25–120°C): Evaporation of surface and bound water.
🔸Intermediate Stage (250–350°C): Main decomposition phase involving cleavage of glycosidic linkages and depolymerization of starch chains.
🔸Final Stage (above 400°C): Formation of carbonaceous residue and ash.
The Derivative Thermogravimetry (DTG) curve, obtained by differentiating the TGA data, identifies the temperature at which maximum decomposition rate occurs, allowing precise comparison of thermal resistance between samples. Together, TGA and DTG provide quantitative and qualitative insights into starch degradation kinetics, oxidation resistance, and modification effects.
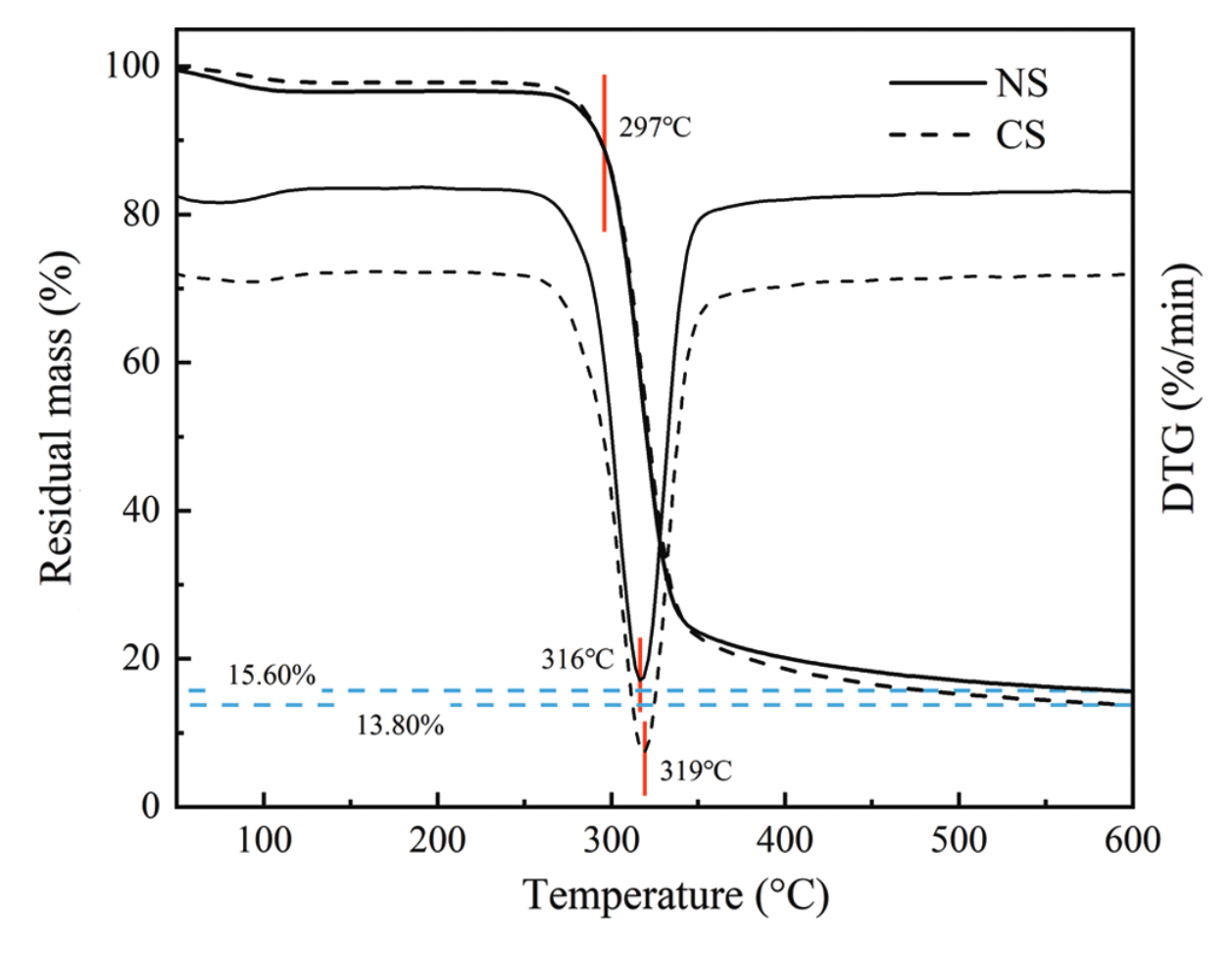
Chen, X. et al. J Renew Mater. 2021.
Figure 1. TGA of Cassava Starch and Corn Starch
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation: Samples are weighed precisely and pre-conditioned to remove excessive moisture. Homogeneity is ensured for consistent results.
2. Instrument Setup: Starch samples are placed in platinum or alumina pans within a high-sensitivity TGA instrument under controlled gas flow (nitrogen or air).
3. Temperature Programming: Heating is conducted at a predetermined rate (commonly 10°C per minute) from ambient temperature up to 600°C or higher, depending on sample type.
4. Data Acquisition: Continuous recording of sample mass and derivative mass loss yields TGA and DTG curves representing thermal events.
5. Data Analysis: Key parameters such as onset degradation temperature, peak temperature, total mass loss percentage, and residual content are extracted.
6. Report Generation: Results are compiled into comprehensive reports with graphical representations, comparative analyses, and technical commentary.
Service Advantages
✔️High Analytical Precision
Our state-of-the-art TGA systems deliver high sensitivity and reproducibility for accurate assessment of starch degradation behavior.
✔️Customizable Analytical Conditions
Temperature range, heating rate, and atmosphere can be tailored to specific sample types and research goals.
✔️Expert Data Interpretation
Our scientific team integrates TGA results with compositional and structural data, providing actionable insights for formulation and process design.
✔️Wide Applicability
Suitable for native and modified starches, composite materials, food powders, and biopolymers.
✔️Reliable Quality Assurance
Strict adherence to international analytical standards ensures high confidence in results.
Applications
MtoZ Biolabs' Starch Thermal Stability Determination Service supports a wide range of applications in academic research, product development, and industrial production:
1. Food Industry
Thermal stability data guide processing parameters such as cooking temperature, extrusion conditions, and drying profiles for starch-based foods. It ensures that starch functionality, viscosity, and texture remain stable during thermal processing.
2. Pharmaceutical Formulation
In drug development, starch and its derivatives are used as binders, fillers, and disintegrants. Evaluating thermal stability ensures that these materials maintain integrity during drying, granulation, or tablet compression.
3. Biomaterials and Packaging
Thermal analysis helps assess the heat resistance and degradation profiles of starch-based biodegradable films, adhesives, and composites, supporting material innovation and environmental sustainability.
4. Chemical and Industrial Processing
Modified starches used as thickeners, stabilizers, or binders require high thermal tolerance for industrial applications such as paper coating, textile sizing, and polymer blending.
5. Agricultural and Botanical Research
Comparative thermal stability studies of starches from different plant sources provide valuable insights into genetic and compositional variability, supporting crop improvement and functional characterization.
6. Quality Control and Product Standardization
Regular thermal stability testing ensures consistent product quality, particularly for modified starches, pregelatinized formulations, and industrial additives.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types: Native starch, modified starch, or raw materials for starch extraction.
2. Recommended Quantity: Minimum 1 g of dry starch or 50 g of raw material for extraction.
3. Replicates: At least three biological replicates are recommended for statistical reliability.
4. Storage: Samples should be kept in sealed, dry containers and protected from moisture absorption.
*Note: For special sample types or low-yield materials, please contact MtoZ Biolabs for customized preparation guidance.
How to order?







