Starch Phosphorylation Level Determination Service
Starch is one of the most abundant and versatile biopolymers in nature, widely used in food, pharmaceutical, and biomaterial industries. Its functional properties, including viscosity, gelatinization, solubility, and binding capacity, are largely influenced by its degree of phosphorylation. Starch phosphorylation refers to the introduction of phosphate groups to starch molecules, mainly at the C-3 and C-6 positions of glucose residues. These covalent modifications alter the physicochemical behavior of starch, enhancing its stability, thickening ability, and water-holding capacity. Accurate determination of the starch phosphorylation level is therefore essential for understanding its structure–function relationship, optimizing modification processes, and ensuring product quality in both native and industrially modified starches.
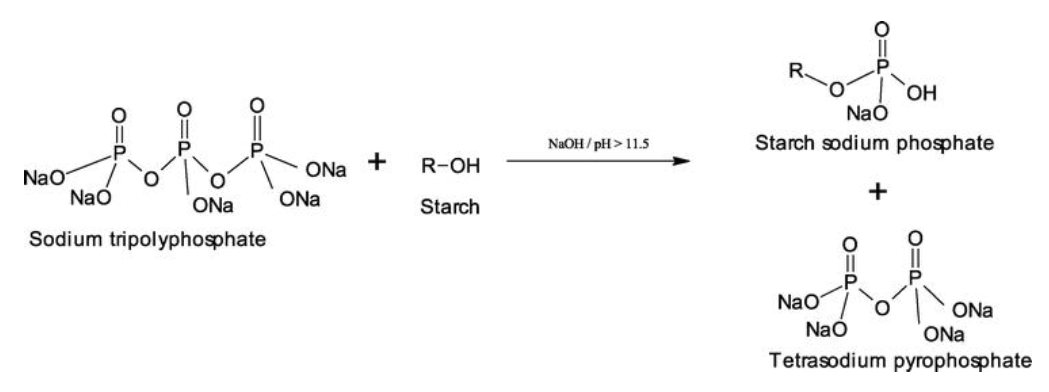
Omoregie Egharevba H. Chemical Properties of Starch. IntechOpen. 2020.
Figure 1. Phosphorylation of Starch with Sodium Tripolyphosphate
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers a specialized Starch Phosphorylation Level Determination Service that combines advanced chromatographic and spectrometric technologies with rigorous quantitative methods. By integrating ion chromatography (IC), HPLC, LC-MS/MS, and elemental analysis techniques, we provide precise measurement of phosphate ester content, distribution, and substitution degree in starch samples derived from various sources such as corn, potato, rice, and cassava. Our analytical expertise supports clients in food engineering, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and biomaterials to evaluate starch modification efficiency and functionality.
Technical Principles
Starch phosphorylation level determination relies on both chemical quantification and molecular analysis approaches to accurately measure phosphate content and its bonding characteristics.
🔸Chemical Quantification of Phosphorus
After acid digestion or enzymatic hydrolysis of the starch sample, inorganic phosphate is released and quantified using ion chromatography or colorimetric spectrophotometry. This provides an overall phosphate content, expressed as the degree of substitution (DS).
🔸Phosphate Ester Profiling by LC-MS/MS
For detailed structural information, phosphorylated glucose and oligosaccharides are detected using LC-MS/MS, enabling the identification of specific esterification sites and differentiating between mono- and di-phosphate substitutions.
🔸NMR Spectroscopy (Optional)
Nuclear magnetic resonance can complement mass spectrometry by providing direct insights into phosphate bonding environments and chemical shifts, verifying covalent linkage patterns within the starch backbone.
🔸Elemental and Gravimetric Analysis
Total phosphorus determination via ICP-OES or molybdenum blue assay further validates quantitative results, ensuring cross-method consistency and high analytical accuracy.
Together, these technologies allow comprehensive characterization of both the total and site-specific phosphorylation levels of starch, correlating structural data with functional performance metrics.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Precise weighing, defatting, and enzymatic or acid digestion of starch samples to release bound phosphate groups.
2. Chromatographic Separation
Separation of released phosphate or phosphorylated glucose using ion chromatography or HPLC under optimized mobile-phase gradients.
3. Detection and Quantification
Quantitative analysis using LC-MS/MS, spectrophotometric, or elemental methods to measure phosphate concentration and substitution degree.
4. Data Processing and Validation
Calibration with phosphate standards, peak integration, and comparison across methods to ensure data accuracy and repeatability.
5. Reporting
Comprehensive interpretation of results including degree of phosphorylation, phosphate ester distribution, and correlation with physicochemical properties.

Compart, J. et al. Plant Methods. 2024.
Figure 2. Schematic Representation of the Procedure for Analysing Phosphorylated Starches
Service Advantages
☑️High Accuracy and Reproducibility: Multiple complementary analytical methods ensure precise quantification of total and site-specific phosphate groups.
☑️Experienced Scientists: A professional team with extensive expertise in carbohydrate chemistry and analytical method development.
☑️Customizable Protocols: Tailored workflows depending on starch origin, modification type, and project objectives.
☑️End-to-End Data Support: From raw data acquisition to detailed interpretation, ensuring actionable scientific insight.
Applications
The starch phosphorylation level is a critical quality parameter for a wide range of research and industrial applications. MtoZ Biolabs supports clients in:
1. Food Science and Technology: Optimizing modified starches used as thickeners, stabilizers, and gelling agents in sauces, dairy products, and instant foods.
2. Agricultural Breeding: Evaluating natural variations in phosphorylated starch among plant cultivars to improve yield and functional traits.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry: Assessing starch excipients for drug formulation, ensuring controlled viscosity and tablet disintegration performance.
4. Biodegradable Materials: Characterizing phosphorylated starch used in biomaterial synthesis and coating applications.
5. Quality Control and Process Optimization: Monitoring phosphorylation degree in industrial modification processes such as wet-heat treatment or chemical esterification.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type: Starch powders or raw materials such as plant tissues, microbial biomass, or other starch-containing substances are acceptable. If raw materials are provided, starch extraction will be performed by MtoZ Biolabs prior to analysis.
2. Sample Quantity: At least 1 g of starch or 50 g of raw material is recommended; actual requirements may vary depending on starch content.
3. Replicates: We recommend submitting at least three biological replicates to ensure statistical reliability and data reproducibility.
4. Storage and Transport: Samples should be sealed in airtight containers, transported on dry ice or ice packs, and protected from repeated freeze–thaw cycles.
*Note: For special sample types or low-yield materials, please contact MtoZ Biolabs for customized preparation guidance.
How to order?







