Starch Gel Consistency Determination Service
Starch is one of the most essential biopolymers in food science, agriculture, and biomaterial engineering. Its functional properties, such as gelatinization, viscosity, and gel consistency, play a decisive role in determining product quality, stability, and consumer acceptance. Among these, starch gel consistency is a key index reflecting the texture, elasticity, and retrogradation characteristics of starch after gelatinization and cooling. It serves as an important indicator of cooking quality, particularly in rice, cereals, and other starchy materials.
The measurement of starch gel consistency helps characterize how starch pastes behave upon cooling, providing insights into internal molecular structure, amylose content, and the interactions between amylose and amylopectin. This analysis is vital for understanding starch behavior during food processing, formulation of modified starches, and optimization of industrial applications where starch texture is critical.
MtoZ Biolabs offers a professional Starch Gel Consistency Determination Service to accurately quantify the consistency of gelatinized starch pastes under standardized conditions. By combining precise laboratory instrumentation with optimized analytical protocols, MtoZ Biolabs provides highly reproducible data that support both academic research and industrial development in food, agriculture, and material science.
Technical Principles
The determination of starch gel consistency is based on the flow behavior of gelatinized starch paste after cooling under controlled conditions. The test reflects the strength of the starch gel network and the degree of re-association of amylose molecules during cooling.
1. Gelatinization and Cooling Process
Starch suspensions are heated in a boiling water bath to induce complete gelatinization. During this process, starch granules absorb water, swell, and lose their crystalline structure, forming a viscous paste. The paste is then cooled to allow gel formation.
2. Gel Flow Measurement
Once the paste has cooled and solidified into a gel, the consistency is evaluated by measuring the distance that the gel flows in a standardized test tube when placed horizontally. The greater the flow, the softer the gel and the lower its consistency.
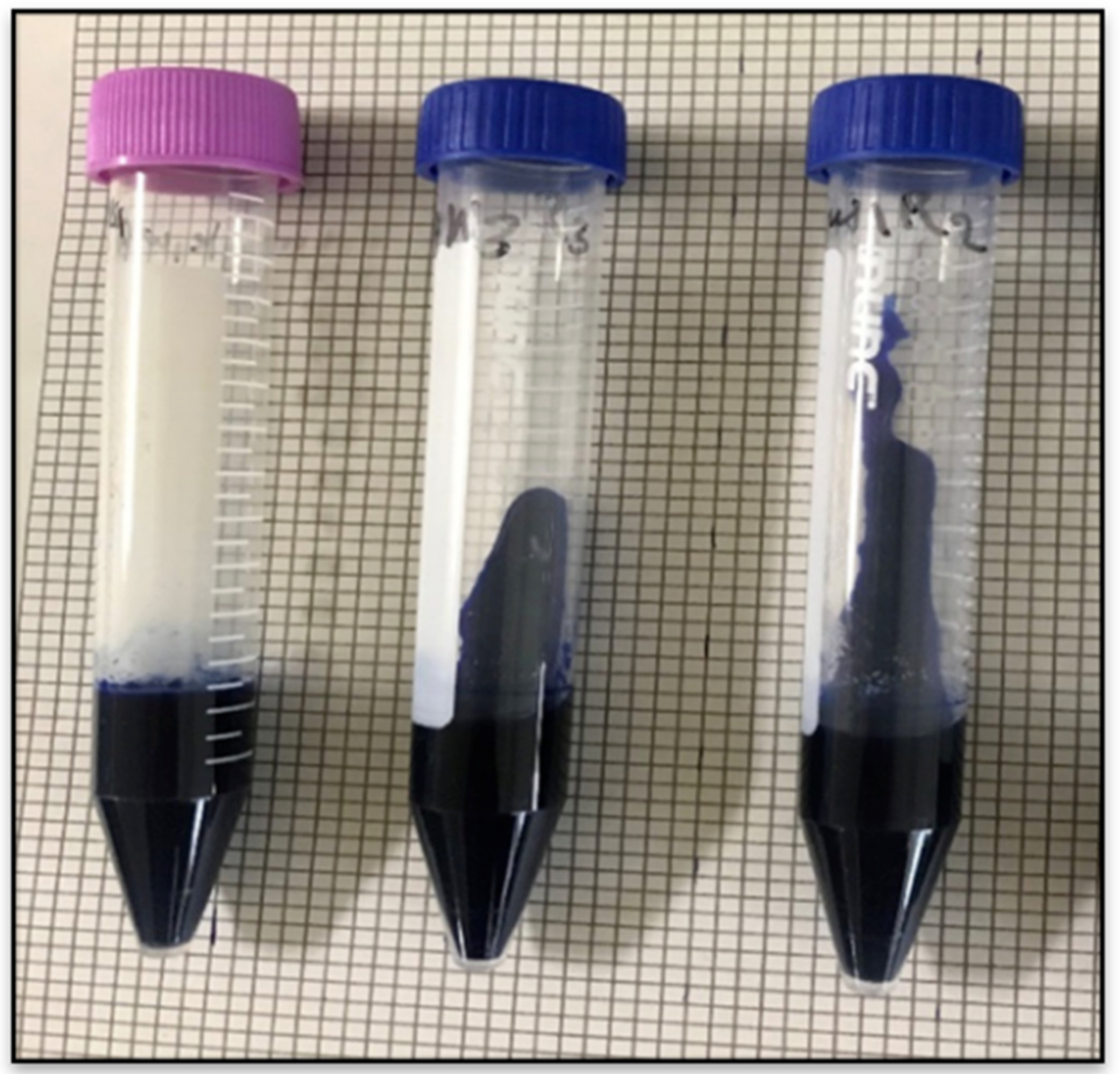
Rayee, R. et al. Agriculture. 2021.
Figure 1. Gel Consistency of the Samples
3. Relation to Amylose Content
Starches with higher amylose content tend to produce firmer gels with lower flow distances, while those with lower amylose content form softer gels with higher flow distances. Thus, gel consistency indirectly reflects the amylose–amylopectin ratio and the internal molecular organization of starch.
4. Temperature and Shear Sensitivity
The consistency is also influenced by temperature control, mechanical shearing during preparation, and the rate of cooling. MtoZ Biolabs performs all analyses under rigorously standardized conditions to ensure reproducibility and comparability between samples.
Analysis Workflow
Service Advantages
✔️High Precision and Reproducibility
Standardized conditions and precise control of temperature and time ensure reliable and comparable results.
✔️Comprehensive Texture Evaluation
Integrates with other starch analyses (gelatinization, viscosity, swelling power) for a complete understanding of physical properties.
✔️Applicable to Various Starch Sources
Suitable for cereals, tubers, legumes, and modified starches with different amylose–amylopectin ratios.
✔️Rapid Turnaround and Detailed Reporting
Efficient processing workflow and structured data presentation facilitate research and industrial decision-making.
✔️Expert Support and Consultation
Our technical team provides interpretation of results and guidance for improving starch formulation or product performance.
Applications
The Starch Gel Consistency Determination Service supports a wide range of applications across the food, agricultural, and biomaterial industries.
1. Food and Beverage Industry
Evaluate starch quality for rice, noodles, baked goods, and sauces. Gel consistency correlates strongly with textural properties such as firmness, stickiness, and mouthfeel.
2. Cereal Breeding and Crop Improvement
Used as a standard index in rice breeding programs to classify varieties by cooking quality, complementing amylose content and gelatinization temperature data.
3. Modified Starch and Additive Development
Assess the impact of chemical or physical modification on gel strength and structure, guiding formulation for thickening or gelling agents.
4. Pharmaceutical and Biopolymer Research
Determine gelation characteristics of starch excipients in tablet coatings, capsules, or biodegradable films.
5. Industrial Process Optimization
Aid in controlling processing conditions such as heating, cooling, and mixing in food or biomaterial production lines.
6. Quality Assurance and Product Standardization
Ensure batch-to-batch consistency of starch-based ingredients and monitor product performance over storage or formulation changes.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types: Native starch, modified starch, or raw materials for starch extraction.
2. Recommended Quantity: Minimum 1 g of dry starch or 2 g of raw material for extraction.
3. Replicates: At least three biological replicates are recommended for statistical reliability.
4. Storage: Samples should be kept in sealed, dry containers and protected from moisture absorption.
*Note: For special sample types or low-yield materials, please contact MtoZ Biolabs for customized preparation guidance.
How to order?







