Starch Digestibility Testing Service
- Evaluation of starch-based ingredients for glycemic index reduction.
- Optimization of functional foods designed for diabetic or weight management.
- Quality assessment of processed foods to ensure consistent digestibility profiles.
- Characterization of starch excipients used in controlled-release formulations.
-
Evaluation of digestion-resistant starch for prebiotic or gut health products.
- Screening of starch digestibility among plant varieties for breeding programs.
- Understanding structural variations in cereal, tuber, and legume starches.
- Assessing enzymatic degradability of starch-based biopolymers, films, and packaging materials.
- Supporting sustainability research through controlled biodegradability studies.
- Exploring the molecular basis of starch digestion and metabolism.
- Studying the effects of chemical, enzymatic, or physical modification on starch digestibility.
Starch is the principal carbohydrate reserve in plants and one of the most important energy sources for humans. It is composed of two polysaccharides: amylose, a linear polymer of α-1,4-linked glucose units, and amylopectin, a highly branched polymer with both α-1,4 and α-1,6 glycosidic linkages. The digestibility of starch depends on its molecular structure, crystalline organization, granule morphology, and the presence of non-starch components such as lipids, proteins, and fibers.
During digestion, starch undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis by α-amylase and other carbohydrases, producing maltose, maltotriose, and ultimately glucose. However, not all starch fractions are equally digestible. Based on digestion rate, starch is classified into three fractions:
1. Rapidly Digestible Starch (RDS): Hydrolyzed quickly in the small intestine, causing a fast increase in blood glucose levels.
2. Slowly Digestible Starch (SDS): Broken down gradually, providing sustained energy release and promoting stable blood sugar response.
3. Resistant Starch (RS): Escapes digestion in the small intestine and reaches the colon, where it functions as dietary fiber with prebiotic and metabolic benefits.
Starch digestibility is a critical parameter that determines the nutritional quality, functional behavior, and physiological impact of starch-containing foods. It reflects how rapidly and efficiently starch is hydrolyzed into glucose during digestion, influencing postprandial glycemic response, energy availability, and overall health outcomes. As the global food, nutrition, and biomaterial industries shift toward functional and sustainable starch-based formulations, accurate assessment of starch digestibility has become essential for both product development and nutritional evaluation.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs provides a professional Starch Digestibility Testing Service based on advanced enzymatic hydrolysis methods. Our Starch Digestibility Testing Service delivers quantitative analysis of rapidly digestible starch (RDS), slowly digestible starch (SDS), and resistant starch (RS) fractions. By simulating physiological digestion conditions using a precise enzymatic approach, we help clients evaluate starch nutritional properties, processing effects, and functional characteristics across diverse applications in food science, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and biomaterials.
With a team of experienced analytical scientists and high-precision instrumentation, MtoZ Biolabs ensures accurate, reproducible, and regulatory-compliant starch digestibility data. Our testing platform supports product optimization, functional claims validation, and scientific research, providing the data foundation for innovation in starch-based solutions.
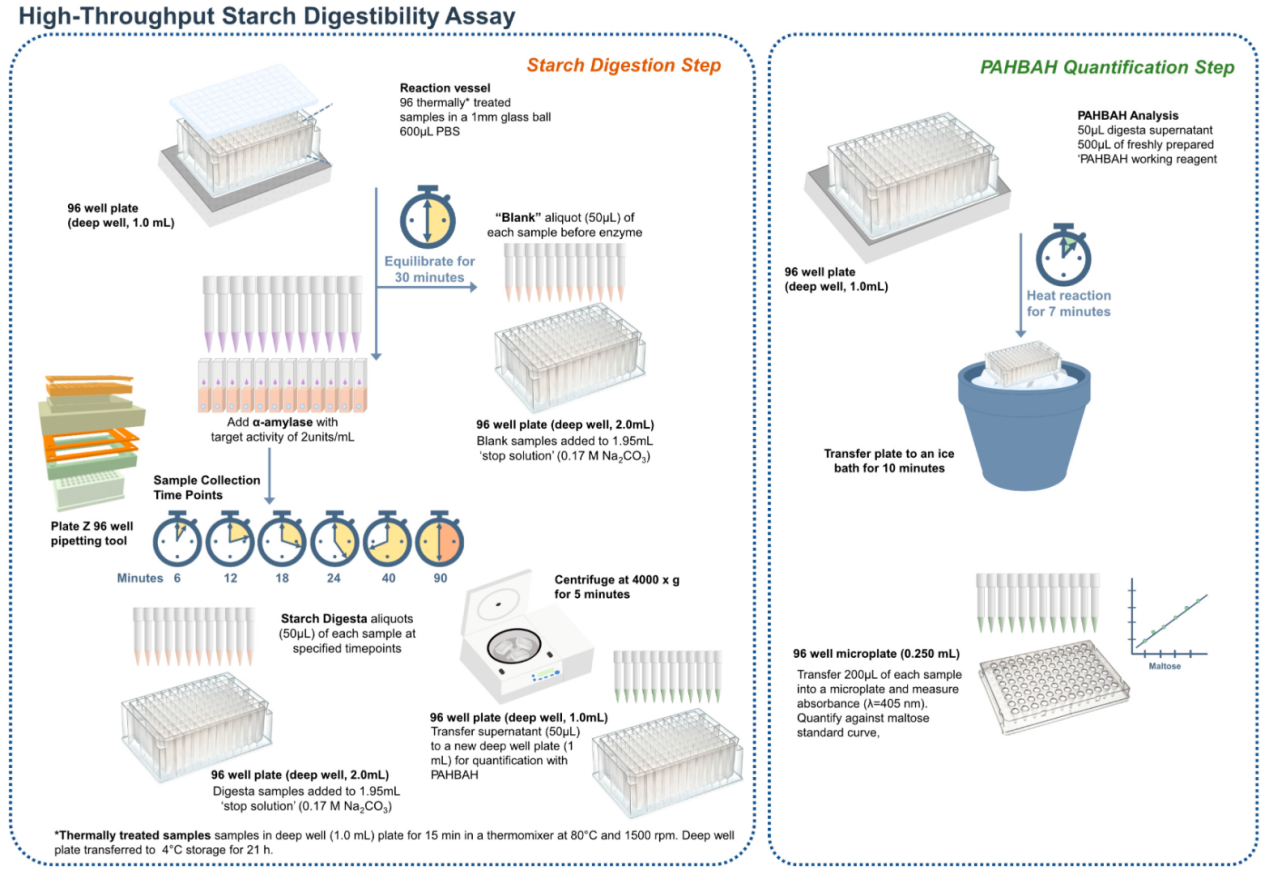
Zafeiriou, P. et al. Foods. 2023.
Figure 1. Principle of the High-Throughput In Vitro Starch Digestibility Assay Using a Single Enzyme System
Service Advantages
✔️Advanced Enzymatic Testing Platform
MtoZ Biolabs utilizes validated in vitro enzymatic digestion protocols that accurately simulate human gastrointestinal conditions.
✔️High Analytical Accuracy and Reproducibility
Controlled enzymatic conditions and precision glucose quantification ensure reliable and consistent results.
✔️Customizable Assay Conditions
Parameters such as enzyme concentration, pH, temperature, and digestion time can be tailored to fit specific sample types or research goals.
✔️Scientific Expertise and Technical Support
Our multidisciplinary team provides detailed data interpretation and recommendations for starch optimization and functional food formulation.
✔️Fast Turnaround and Standardized Reporting
Efficient workflows guarantee quick delivery of results with clear, detailed documentation suitable for publication or regulatory use.
Applications
The Starch Digestibility Testing Service provided by MtoZ Biolabs has broad applicability across scientific research and industrial sectors.
1. Food and Nutrition Industry
2. Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Industry
3. Agriculture and Crop Science
4. Material and Biomaterial Development
5. Academic and Research Institutions
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type: Purified starch powders or raw materials containing starch from plant, microbial, or synthetic sources. If raw materials are provided, starch extraction will be performed by MtoZ Biolabs prior to analysis.
2. Sample Quantity: At least 10 g of starch or 60 g of fresh raw material; actual requirements depend on starch purity and experimental conditions.
3. Replicates: We recommend three or more biological replicates to ensure statistical reliability.
4. Packaging and Transport: Samples should be sealed in airtight containers, protected from moisture and contamination.
*Note: For samples with limited availability or specific handling requirements, please contact MtoZ Biolabs for customized submission instructions.
How to order?







