N-Glycan Modification and Site Analysis Service
Glycosylation modifications increase the complexity of protein molecular structure and the diversity of functions, not only affecting protein folding, structure, transportation, localization, and biological activity but also regulating various physiological processes such as cell growth, division, differentiation, recognition, and adhesion through specific recognition between sugars and proteins. Among these, N-glycosylated proteins are ubiquitously present on cell surfaces and various body fluids. Surface glycoproteins are considered key drug targets, for instance, glycoproteins in body fluids are major sources of biomarkers related to diseases. Proteomics of N-glycosylated proteins under various physiological and pathological conditions can elucidate the function of protein glycosylation. It is important for identifying new biomarkers in cancer prevention and diagnosis.
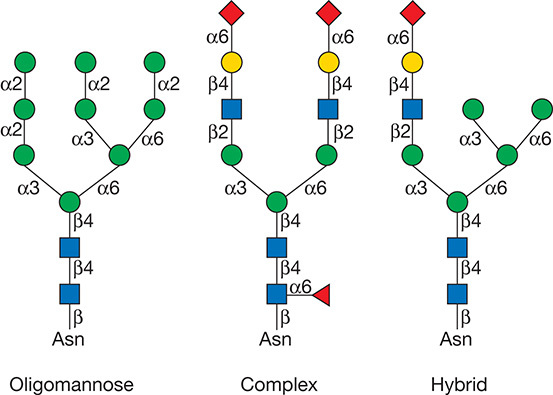
According to the substitutes of mannose residues, N-glycans can be roughly divided into three types: complex, high-mannose, and hybrid structures. The complex type includes fucose, sialic acid, and α-linked galactose. A branch of the high-mannose core structure contains multiple mannose residues. In the hybrid type, mannose is in one branch of the core structure, and another branch contains a lactosamine sequence. General N-glycan site analysis strategy: isolating and enriching glycoproteins/glycopeptides, then using enzyme or chemical methods to separate the sugar chains from the glycosylated peptides, and performing mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of the released sugar chains or deglycosylated peptides to achieve analysis of the overall expression and changes of sugar chains and/or glycoproteins in the test sample.
Varki A, et al. Current Cardiovascular Risk Reports. 2018.
Figure 1. Types of N-glycans
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers N-glycan modification and site analysis services, capable of identifying modification sites, specific glycan types, analyzing N-glycan modification types and locations, and resolving the structure and location of N-glycans, and can perform quantitative analysis of glycan modifications.
N-glycan chain analysis typically follows these steps:
1. Release of Attached Glycans by Enzyme
2. Derivatization of Released Glycans Through Reduction Amination by Aromatic Amine and Alkyl Amine or Permethylation
3. Analysis of Glycan
Service Advantages
1. Good Specificity and High Efficiency
2. High-throughput Identification Capable of Detecting up to 10,000 N-glycosylation Sites
3. High Sensitivity and Good Reproducibility
4. Relatively Short Project Time
Sample Submission Requirements
1. If you are providing tissue samples, please transport them on dry ice.
2. If you are providing protein samples, please transport protein extracted from normal tissues or cell lysis buffer.
Ensure sufficient dry ice for transportation and choose the fastest mailing method to minimize sample degradation during transport. If you have any questions about sample transportation, please contact us at any time.
MtoZ Biolabs has much analysis service experience in glycomics and can customize glycomics analysis service according to your specific needs.
Deliverables
1. Experimental Procedures
2. Mass Spectrometric Parameters
3. Mass Spectrometric Images
4. Raw Data
5. Results of N-glycan Modification and Site Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







