Glycomic Profiling Service
Glycomics refers to the collection, analysis, and utilization of glycosidic biological data at the omics level. The profound biological effects of lipid and protein glycosylation make glycomics an important field in life sciences. N-glycome analysis (a comprehensive study of all glycans) is a complement to genomics and proteomics. Glycomics studies at the cellular or organismal level can provide a general overview of the overall glycosylation patterns of glycome, glycoprotein, lipid, or other type of biomolecules. Glycomics analysis can be used to compare differences between two glyco-engineered host strains in the production of therapeutic glycoproteins or to compare cancer data at different stages to discover new biomarkers.
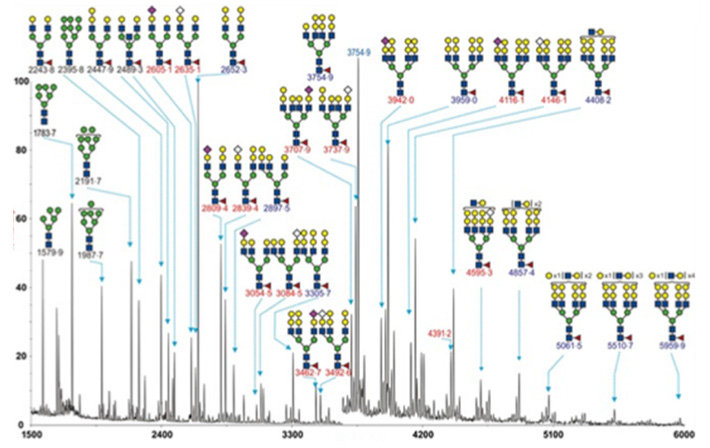
Figure 1. Glycomics Analysis Service
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
We can identify all N-glycans expressed by plasma/serum, cells, tissues, or organisms. All glycans linked to proteins will be digested and hydrolyzed by enzyme and separated by hydrophilic chromatography, followed by quantitative analysis by MALDI-TOF-MS.
Analysis Workflow
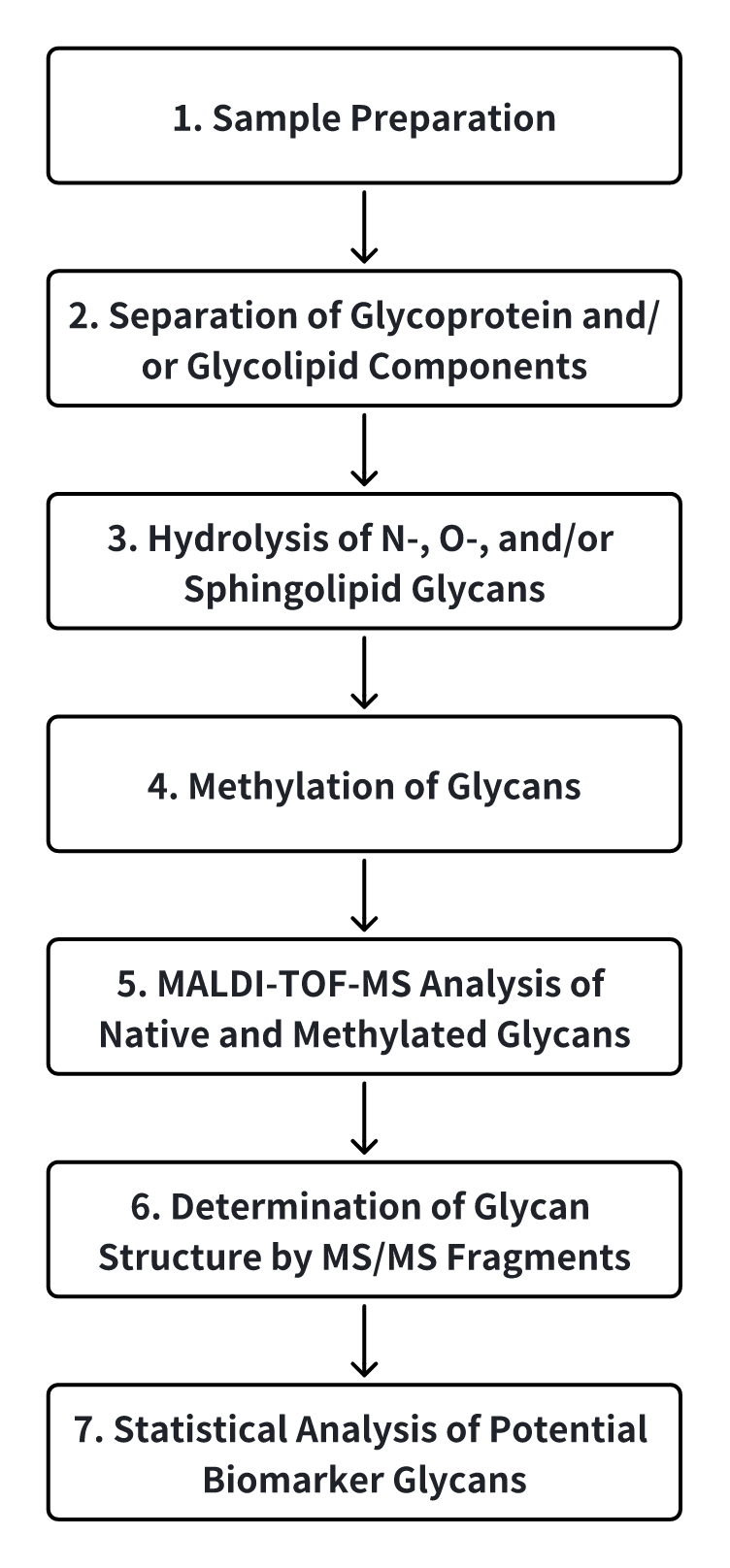
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Glycoprotein Analysis
2. Quantitative Glycoproteomics
3. N-glycan Analysis Service
4. O-glycan Analysis Service
5. N-glycosylation Site Analysis
6. O-glycosylation Site Analysis
7. N-glycan Modification and Modification Site Analysis Service
8. O-glycan Modification and Modification Site Analysis Service
9. HILIC-UHPLC Analysis of N-glycan Bonds
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Deep Phosphoproteomics Service
How to order?







