Glycan Derivatization Service
Glycan derivatization is a technique that modifies glycan chains through chemical reactions to enhance their detectability and sensitivity in analysis. By reacting with derivatization reagents, glycan chains can be converted into derivatives with enhanced optical properties (such as fluorescence, UV absorption, etc.). This derivatization process makes glycan detection more efficient in instruments like liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS), particularly in complex samples, improving analysis sensitivity, accuracy, and separation performance. Glycan derivatization is of great significance in fields such as glycomics, protein modifications, and bioanalysis.
The glycan derivatization service is widely applied across multiple fields. In glycomics research, derivatization helps reveal the structural characteristics and functional changes of glycan chains; in biopharmaceutical quality control, derivatization techniques improve the sensitivity of glycan analysis; in the food industry, derivatization is used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of carbohydrate components. Through this service, researchers can obtain more precise glycan data, providing strong support for glycan research and various types of analysis.
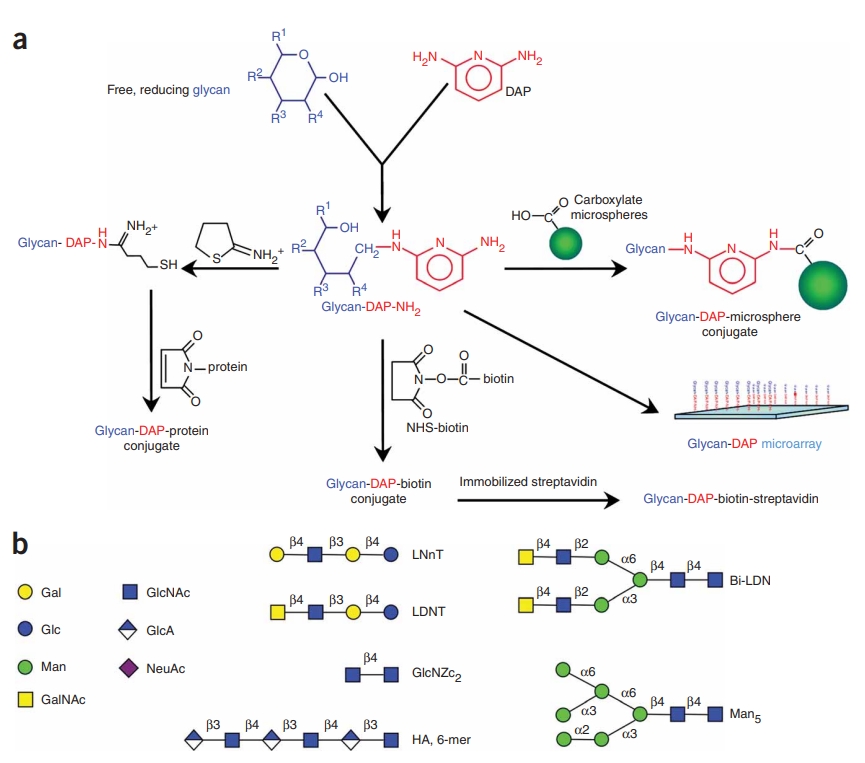
Xia, B Y. et al. Nature Methods, 2005.
Figure 1. The Derivatization of Free Glycans with 2,6-Diaminopyridine (DAP).
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced chemical derivatization techniques, MtoZ Biolabs offers the glycan derivatization service which can derivatize glycan chains in samples such as glycoproteins and glycolipids, improving their separation efficiency and quantitative accuracy in complex samples. This technique enhances the detectability and sensitivity of glycan chains on analytical platforms such as liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS), allowing for the detailed composition and structural information of glycans in samples, including the types of glycans, their concentration, and distribution. The Glycan Derivatization technology provided by MtoZ Biolabs includes, but is not limited to, the following methods:
1. Fluorescent Derivatization
This method involves reacting glycan chains with fluorescent reagents to enhance their fluorescence characteristics, improving the detection sensitivity of low-abundance glycans. It is commonly used in liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection.
2. Methylation Derivatization
Methylation derivatization involves adding methyl groups to glycan chains to enhance their stability and separation performance. This technique is commonly used in gas chromatography analysis and enhances glycan detection sensitivity.
3. Acetylation Derivatization
Using acetylation reagents to modify glycan chains increases their stability and sensitivity, making it suitable for glycan analysis in complex samples.
4. Amino Derivatization
By reacting with amino reagents, this method enhances the ultraviolet absorption or fluorescence properties of glycan chains, commonly used in liquid chromatography analysis to improve glycan detection sensitivity.
5. Reducing End Modification
This modification targets the reducing end of glycan chains, enhancing their stability and increasing the signal in mass spectrometry analysis.
6. One-pot Derivatization Strategy
The one-pot derivatization strategy performs glycan derivatization in a single reaction system, improving reaction efficiency and saving time, particularly suitable for high-throughput analysis of large sample volumes.
7. Ionic Liquid-Based Derivatization
Ionic liquid-based derivatization uses ionic liquids as reaction mediums, improving the solubility and stability of glycan chains, enhancing separation efficiency in complex samples, and is commonly used in glycomics research.
8. Linker-Based Derivatization
This method attaches chemical labels or linkers to glycan chains, facilitating their interaction with other molecules, and is applied in studies of glycan interactions and modifications.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
This service is suitable for various samples containing carbohydrate components, including glycoproteins, glycolipids, cell lysates, serum, plasma, etc. Samples can be in liquid or solid form, and it is essential to ensure the integrity of the glycan components.
2. Sample Purity
The glycan components in the sample should be purified as much as possible to reduce interference from proteins, lipids, and other substances. For complex samples, it is recommended to perform preliminary impurity removal to ensure the accuracy of the analysis.
3. Sample Storage and Transportation
Samples should be transported under low-temperature conditions. Liquid samples can be transported using ice packs or dry ice, while solid samples must be securely sealed and protected from moisture. To ensure sample quality, it is recommended that samples remain frozen or cold during transportation.
Service Advantages
1. High Sensitivity
Through derivatization, the detectability and sensitivity of glycan chains in analysis are significantly improved, making it particularly suitable for the precise analysis of low-abundance glycans.
2. Strong Analytical Accuracy
Derivatization technology enhances the stability of glycan chains and optimizes separation, improving the accuracy and reproducibility of liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS) analysis.
3. Simplified Experimental Process
By optimizing the derivatization process, the experimental operation is simplified, saving time and improving efficiency, helping clients quickly obtain high-quality analysis results.
4. Customized Analytical Solutions
Based on the characteristics of the client's samples and research objectives, personalized derivatization analysis solutions are provided to ensure accurate and comprehensive analysis results.
Applications
1. Glycomics Research
The glycan derivatization service helps researchers deeply analyze the structure and function of glycan chains, revealing the important roles of glycosylation in biological processes such as cell recognition and signal transduction, advancing the field of glycomics.
2. Biopharmaceutical Quality Control
In the production of glycoproteins, glycolipids, and other biopharmaceuticals, derivatization technology enhances the sensitivity of glycan analysis, ensuring the consistency and stability of glycan composition in the product, supporting quality control.
3. Food Analysis
The glycan derivatization service can be used to analyze carbohydrate components in food, ensuring the standardization and quality of carbohydrate formulations, especially in the development of functional foods and analysis of nutritional content.
4. Environmental and Agricultural Research
By derivatization analysis of carbohydrate components in plant or environmental samples, this service helps reveal the key roles of carbohydrates in plant growth, development, and stress resistance, supporting agricultural research and environmental protection.
FAQ
Q1: Will the Derivatization Process Damage the Glycan Chain?
A1: Our derivatization process uses mild chemical reagents to ensure that the glycan chain structure is not damaged. The goal of derivatization is to enhance the detectability and stability of the glycan chains, not to alter their basic structure, thus maintaining their biological function.
Q2: How Should the Samples Be Handled and Stored After Derivatization?
A2: Derivatized samples should be stored under low-temperature conditions to prevent degradation of the glycan components. Liquid samples can be transported using ice packs or dry ice, while solid samples should be securely sealed and protected from moisture. We recommend keeping the samples frozen or cold during transportation to ensure sample quality.
Q3: What Is the Impact of the Derivatization Process on the Glycan Chain?
A3: The derivatization process enhances the stability and detectability of glycan chains without altering their basic structure. It increases the signal strength of the glycan chains during analysis, improving detection sensitivity and ensuring high precision in the analysis.
Related Services
How to order?







