Glycan Sequencing Service
Compared with proteins and nucleic acids, the structure of glycans is more complex and diverse. Their sequence information not only includes the composition of monosaccharides but also involves the type and position of glycosidic bonds. Therefore, sequencing is of great significance for a comprehensive understanding of glycan structures and functions. Glycan sequencing is the process of analyzing the types of monosaccharides, their order, linkage, and branching patterns in glycans through advanced analytical techniques. Common glycan sequencing methods include liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry (MS), capillary electrophoresis (CE), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), which can be combined to provide high-resolution structural information.
Glycan sequencing service has wide applications in multiple fields. In glycomics research, it can be used to reveal the roles of glycans in processes such as cell recognition, signal transduction, and immune regulation. In biopharmaceutical quality control, glycan sequencing ensures the stability and consistency of glycosylation patterns. In food science, it can be applied to analyze glycan structures in food, ensuring nutrition and quality standards. In plant and agricultural research, glycan sequencing helps elucidate the structure of plant polysaccharides, promoting crop improvement and functional studies.
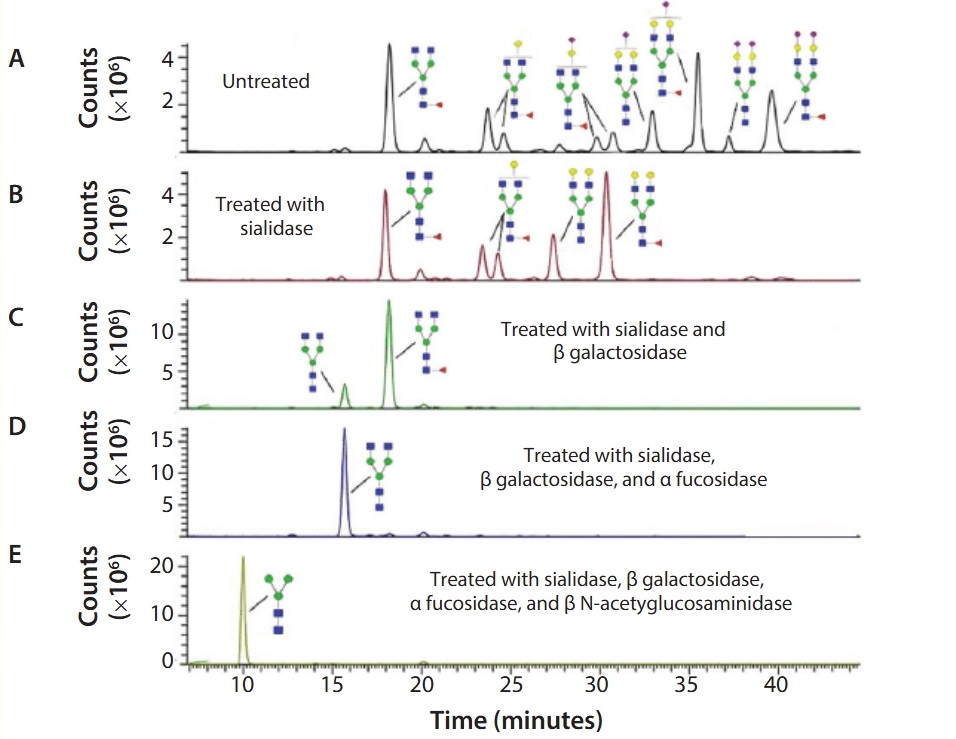
Guthrie, E P. et al. BioProcess International, 2016.
Figure 1. Sequencing of Enbrel Glycans.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced technology and analytical platforms, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the glycan sequencing service which enables precise sequencing of glycans from various samples. This service can analyze the monosaccharide composition, linkage types, branching patterns, and sequence characteristics of glycans, and provides both qualitative and quantitative data through bioinformatics approaches. The final results include sequence information, structural features, and distribution of glycans in different samples, offering reliable data support for glycosylation research, quality control, and functional studies.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Samples are pretreated to remove impurities and ensure the integrity of glycan structures, providing a high-quality basis for subsequent sequencing analysis.
2. Glycan Release and Purification
Glycans are released from glycoproteins, glycolipids, and other samples using glycosidases or chemical methods, followed by specific purification techniques to obtain target glycans.
3. Separation
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or capillary electrophoresis (CE) is used to achieve efficient separation of glycans, reducing interference and ensuring sequencing accuracy.
4. Mass Spectrometry and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Analysis
High-resolution mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are combined to precisely analyze glycan composition, linkages, branching patterns, and sequence characteristics.
5. Data Analysis and Report Generation
Bioinformatics tools are applied to integrate and interpret experimental data, generating detailed reports that provide glycan sequence and structural information.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Applicable to various glycan-containing biological samples, including glycoproteins, cell lysates, tissue extracts, serum, and plasma. Samples may be in liquid or solid form, and the integrity of glycan structures must be preserved.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended to remove proteins, lipids, and other impurities as much as possible to reduce interference with sequencing results. Complex samples may undergo preliminary impurity removal to improve analytical accuracy.
3. Sample Storage and Transportation
Samples should be stored and transported under low-temperature conditions. Liquid samples may be transported with ice packs or dry ice, while solid samples should be sealed and kept moisture-free. Freezing or chilled conditions should be maintained throughout the process to ensure glycan stability.
Service Advantages
1. High-Precision Sequencing
Relying on advanced mass spectrometry (MS) platforms, it can accurately analyze the monosaccharide sequence and linkage positions of glycans, ensuring highly accurate sequencing results.
2. Comprehensive Sequence Analysis
In addition to providing information on monosaccharide composition, it can also analyze branching structures, modification types, and sequence arrangements, fully presenting the structural characteristics of glycans.
3. Customized Sequencing Strategies
Personalized sequencing strategies are designed based on different sample characteristics and research needs to meet diverse scientific objectives.
4. One-Stop Service
From sample preparation, glycan release and separation, to sequencing detection and data analysis, a complete one-stop service is provided to simplify workflows and improve research efficiency.
Applications
1. Glycomics Research
Glycan sequencing service can be used to reveal the relationship between glycan sequence characteristics and functions, advancing studies of glycosylation in biological processes such as cell recognition and signal transduction.
2. Biopharmaceutical Quality Assessment
By analyzing glycan sequences in glycoproteins and glycolipids, the service ensures the consistency and stability of modifications, providing data support for biopharmaceutical quality control.
3. Food and Nutrition Science
This service can be applied to analyze glycan sequence characteristics in foods, assessing their effects on nutritional content, taste, and stability, supporting food research and optimization.
4. Plant and Agricultural Research
Glycan sequencing service can be used to study glycan sequence characteristics in plants, exploring their roles in plant growth, stress resistance, and metabolic regulation.
FAQ
Q1: Will the Sequencing Process Damage the Glycan Structure?
A1: No. Sequencing uses mild enzymatic digestion and derivatization methods combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry and chromatography technologies, allowing precise analysis while preserving glycan integrity.
Q2: Can Low-Abundance Glycans Be Sequenced?
A2: Yes. With high-sensitivity mass spectrometry platforms and optimized enrichment methods, low-abundance glycans can also be effectively detected and analyzed.
Related Services
Glycan Structure Analysis Service
Quantitative Glycomics Service
How to order?







