Glycan Acetylation Modification Analysis Service
Acetylation is one of the common forms of glycan modification, in which an acetyl group (–COCH₃) is added to the hydroxyl (–OH) position on the glycan chain to alter its structure, function, and interaction properties with other molecules. Acetylation modification affects the role of glycans in biological processes such as cell recognition, signal transduction, and immune response. Therefore, analyzing acetylated glycans is of great significance. This service uses advanced technology to perform qualitative and quantitative analysis of acetylation modifications on glycans in samples, assessing their distribution and variation in different samples.
Glycan acetylation modification analysis service is widely applied in various fields, including exploring the impact of acetylation on glycan structure and function in glycomics research; analyzing changes in modification patterns and their relationship with tumors, infections, and metabolic disorders in disease research; evaluating modification consistency and stability during glycoprotein or vaccine production processes in biopharmaceutical quality control; and studying its effects on nutrient absorption and bioactivity in food and nutritional science.
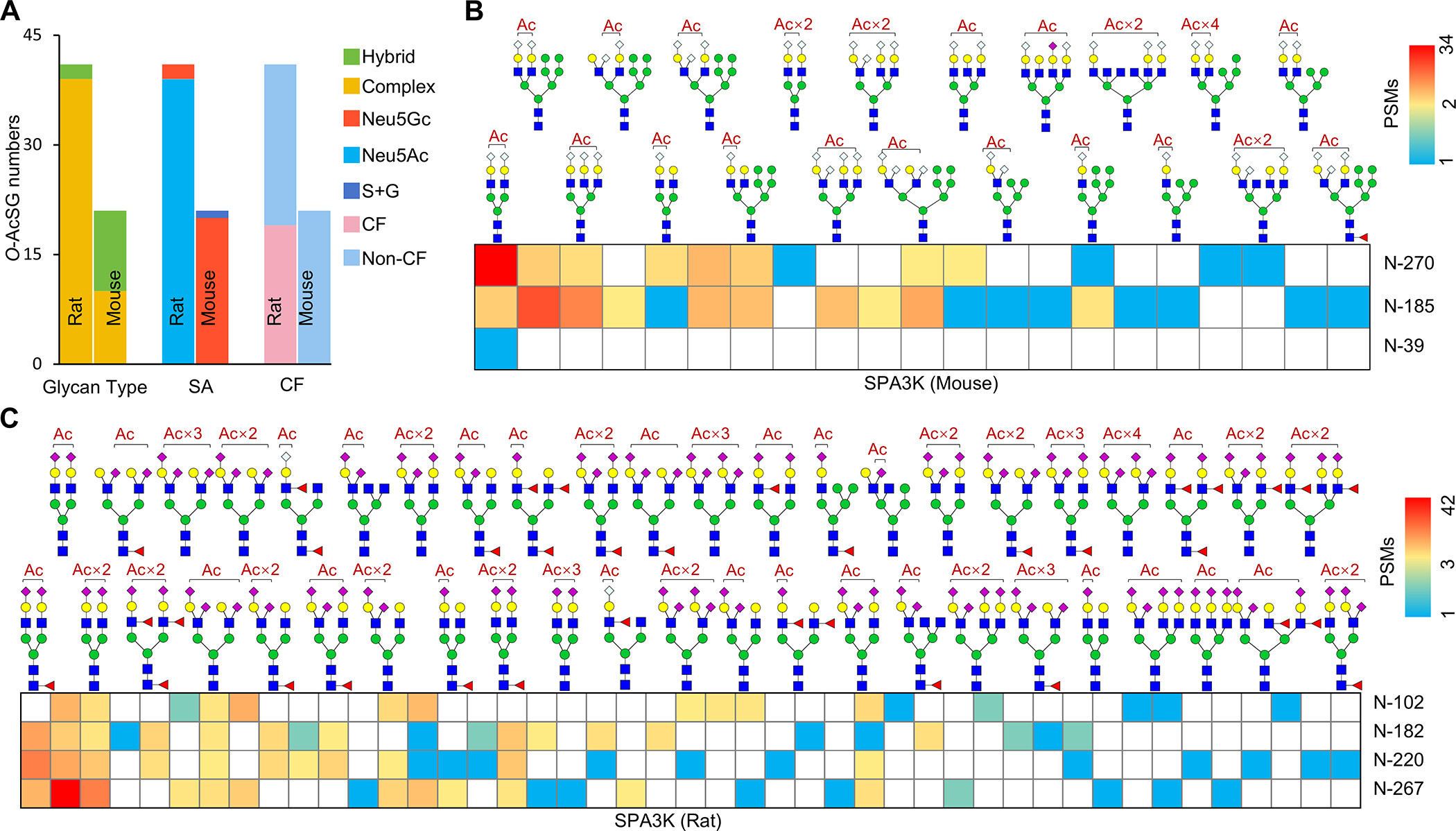
Liu, D D. et al. Journal of Proteome Research, 2024.
Figure 1. Differences of Site-Specific O-Acetylated N-Glycans on Glycoproteins in Rat and Mouse Sera.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on a high-resolution mass spectrometry platform combined with high-performance liquid chromatography, MtoZ Biolabs offers the glycan acetylation modification analysis service which enables precise identification and quantitative analysis of glycan acetylation modifications in glycoproteins, glycolipids, and various biological samples. This service can determine the modification sites, quantities, and distribution characteristics of acetylation, and, together with information on monosaccharide composition and linkage patterns, reveal the potential impact of these modifications on glycan structure and function. It provides high-quality structural and quantitative data to support disease mechanism studies, biopharmaceutical quality control, and glycomics research.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Pre-treatment
Remove impurities and interfering components to ensure the integrity and stability of glycan acetylation structures.
2. Glycan Extraction and Enrichment
Release glycans using enzymatic digestion or chemical methods, and employ specific enrichment techniques to obtain target glycans.
3. Chromatographic Separation
Use high-performance liquid chromatography to finely separate glycans, reducing co-elution interference and improving the accuracy of subsequent detection.
4. Mass Spectrometry Detection
Analyze the separated glycans with a high-resolution mass spectrometry platform for precise qualitative and quantitative characterization of acetylation modifications.
5. Data Analysis and Report Generation
Utilize bioinformatics tools to determine the modification sites, quantities, and distribution, and generate a complete report that can be directly applied to scientific research or applied studies.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Applicable to various biological samples containing glycan components, including glycoproteins, cell lysates, serum, and plasma. Samples can be in liquid or solid form, and the integrity of glycan components should be ensured.
2. Sample Purity
Glycans in the sample should be as purified as possible to reduce interference from proteins, lipids, and other impurities. For complex samples, impurity removal is recommended to ensure the accuracy of analysis results.
3. Sample Storage and Transportation
Samples should be transported at low temperatures. Liquid samples can be shipped with ice packs or dry ice, while solid samples should be sealed and kept moisture-free. To maintain sample quality, it is recommended to keep samples frozen or chilled during transportation.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Detection Platform
Leveraging advanced liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry to ensure precise identification and quantification of glycan acetylation modifications.
2. Comprehensive Analytical Capability
Capable of simultaneously analyzing acetylation sites, modification types, and distribution patterns of glycans, providing data support for in-depth studies on glycosylation regulation mechanisms.
3. Professional Team
A team composed of experienced glycomics and mass spectrometry experts offers integrated solutions from experimental design to data interpretation.
4. One-Stop Service
Provides full-process support from sample preparation, glycan extraction, and analytical detection to data analysis, simplifying experimental operations and improving research efficiency.
Applications
1. Basic Research in Glycomics
The glycan acetylation modification analysis service can be used to elucidate the role of glycan acetylation in cell signaling, molecular interactions, and structural stability, advancing in-depth glycomics research.
2. Biopharmaceutical Quality Control
By monitoring the types and ratios of acetylation modifications in biopharmaceuticals such as glycoproteins and glycolipids, product quality stability and consistency can be ensured.
3. Food and Nutrition Science
The glycan acetylation modification analysis service can be applied to evaluate the characteristics of glycan acetylation in food and nutritional products, as well as its impact on function, stability, and nutritional value.
4. Structural and Functional Studies
Investigating the effects of acetylation modifications on glycan spatial conformation and bioactivity, providing data support for related functional studies.
FAQ
Q1: Will the Analysis Process Alter the Glycan Structure?
A1: No. Our analysis workflow does not disrupt the natural structure of glycans, and acetylation modifications are fully preserved to ensure that the obtained data accurately reflect the original state of the sample.
Q2: What Is the Significance of Acetylation Modification in Glycan Research?
A2: Acetylation modifications can influence the spatial conformation, stability, and binding capabilities of glycans with other molecules. Studying these modification patterns helps in understanding the functional characteristics and biological roles of glycans.
Related Services
Glycan Modification Analysis Service
Glycan Sulfation Modification Analysis Service
How to order?







