Trace Elemental Analysis Service
- Biological samples should be stored at low temperature, protected from light, and are recommended to be transported on dry ice.
- Pharmaceutical and excipient samples should be sealed in clean containers to prevent moisture absorption and secondary contamination.
Trace Elemental Analysis Service is a high-sensitivity elemental detection service that focuses on the qualitative and quantitative analysis of trace and ultra-trace metals or impurity elements in samples.
Trace elements are typically defined as components present in the range of 1-100 ppm, while ultra-trace elements are present at concentrations below the ppm level. Even at extremely low concentrations, metals or impurity elements can significantly impact drug quality, biological system functions, and material performance. For example, in pharmaceutical production, active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients may compromise efficacy and safety if impurity metals exceed acceptable limits. In biological samples such as blood or tissue, variations in trace metal levels are often closely associated with the onset and progression of disease. Therefore, accurate monitoring and strict control of trace and ultra-trace elements are critical in pharmaceuticals, life sciences, and quality regulation.
Technical Principles
The basic principle of trace elemental analysis is to detect the characteristic signals of elements using high-sensitivity spectroscopic and mass spectrometric techniques. Common methods include:
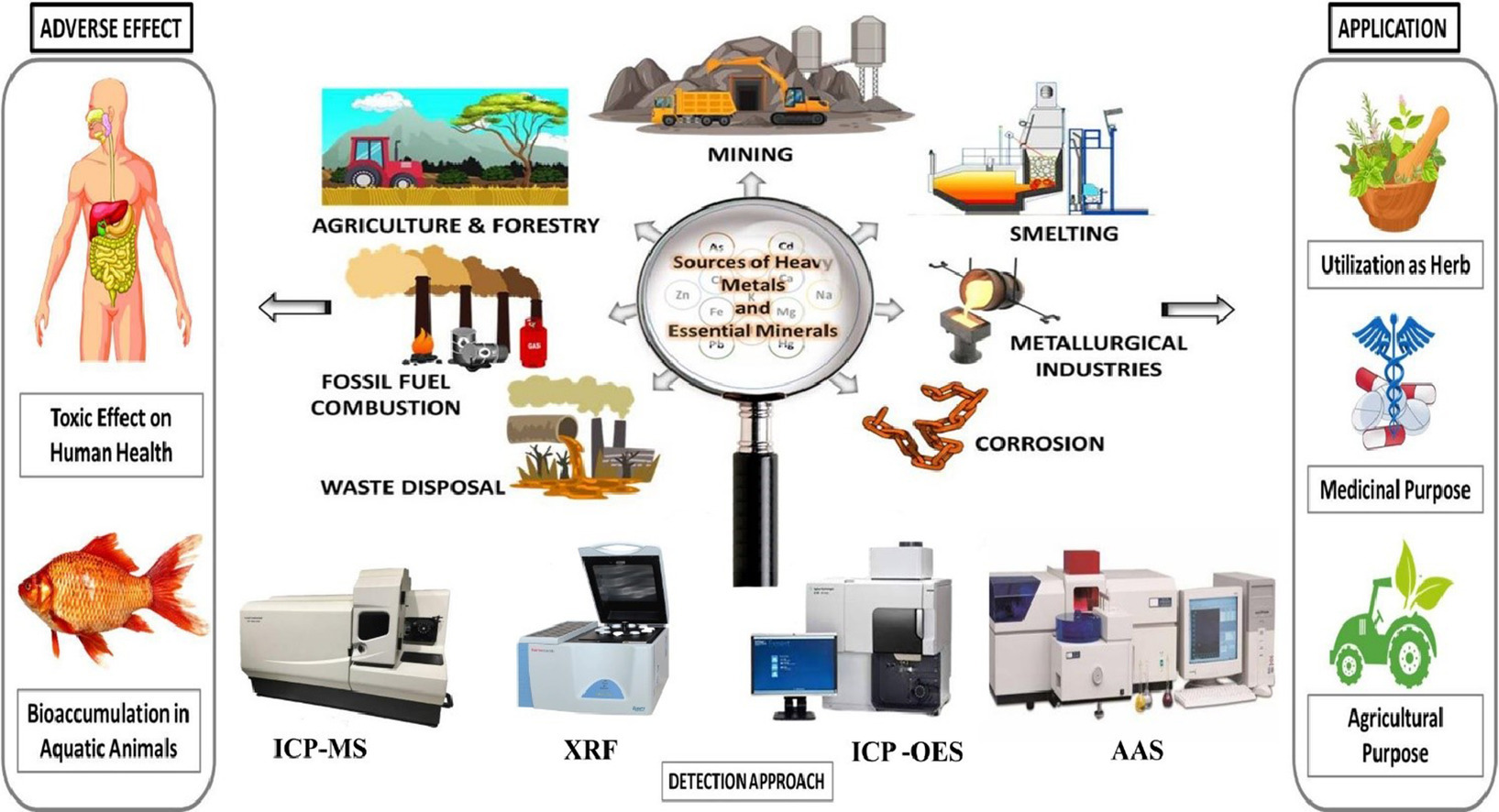
ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry): This method uses high-temperature plasma to atomize and ionize the sample, with mass spectrometry enabling precise quantification of trace metals. Detection limits can reach ppb or even ppt levels.
ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy): By measuring the characteristic light emitted by excited atoms and ions in the plasma, this method provides rapid and accurate multi-element quantification.
XRF/TXRF (X-ray Fluorescence/Total Reflection X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy): This approach relies on X-rays to excite the sample and generate element-specific fluorescence signals, making it suitable for fast screening and semi-quantitative analysis.
AAS (Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy): By measuring the absorption of light at characteristic wavelengths of elements, this method is well-suited for routine heavy metal detection.
SIMS (Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry): A high-energy ion beam bombards the sample surface, sputtering secondary ions that are then analyzed by mass spectrometry. This enables trace and ultra-trace detection of surface elements and isotopes, as well as depth profiling studies.
Each of these methods offers distinct advantages, and the choice often depends on the sample type, concentration range, and analytical goals. In many cases, they are combined to achieve comprehensive and reliable results.
Rawat H. et al. Talanta Open. 2024.
Analysis Workflow
The general workflow of Trace Elemental Analysis Service is as follows:
1. Sample Pretreatment
Solid samples are converted into homogeneous solutions through acid digestion or microwave digestion. Liquid and biological samples may undergo dilution, desalting, or matrix separation treatments.
2. Sample Introduction and Detection
The prepared samples are transformed into detectable signal sources through nebulization, optical excitation, or ionization.
3. Signal Acquisition
Spectrometers or mass spectrometers record the characteristic light emissions or mass-to-charge ratio signals of the target elements.
4. Data Analysis
The signals are compared with standards to obtain qualitative and quantitative results of the elements.
5. Result Validation and Reporting
Blank samples, quality control samples, and reference standards are used to ensure data accuracy, and a complete standardized analysis report is generated.
Service Advantages
Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Trace Elemental Analysis Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
High Sensitivity and Wide Coverage: Capable of achieving detection at ppm, ppb, and even ppt levels, allowing precise quantification of a broad range of metals and impurity elements.
Complex Matrix Handling: Optimized pretreatment methods are developed for biological samples such as blood and tissue, as well as pharmaceutical matrices, to minimize matrix interferences.
Rapid Response and Customization: Analytical schemes can be tailored to client requirements, supporting both scientific research and industrial regulation needs.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs, leveraging advanced platforms such as ICP-MS、ICP-OES、XRF, and AAS, provides Trace Elemental Analysis Service that focuses on the qualitative and quantitative detection of trace and ultra-trace metals as well as impurity elements in samples. Our service covers impurity element limit control in active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients, monitoring of trace metals in biological samples such as blood and tissue, and heavy metal residue detection and compliance evaluation in pharmaceuticals. Through standardized workflows combined with customized solutions, we deliver highly sensitive, reliable, and regulatory-compliant analytical data to support pharmaceutical development, quality control, and biomedical research.
Sample Submission Suggestions
Sample Types
Acceptable samples include active pharmaceutical ingredients, excipients, formulations, blood, tissue, and other liquid or solid samples.
Storage and Transportation
It is recommended to contact our technical support team before submitting samples to confirm their suitability and to receive tailored submission guidance.
Applications
Pharmaceutical Development and Quality Control: Used for controlling the limits of metal impurities in active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients.
Biomedical Research: Enables monitoring of trace metals in biological samples such as blood and tissue, helping to reveal their roles in metabolic processes, disease onset and progression, and toxicological mechanisms.
Extended Applications: Can also be applied to fields such as food testing, environmental monitoring, and materials analysis.
How to order?







