Polysaccharide Isolation and Purification Service
Polysaccharides are natural macromolecules composed of multiple monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds and are widely found in plants, microorganisms, algae, and animal tissues. Polysaccharide isolation and purification is a critical process for extracting and obtaining high-purity target polysaccharides from complex biological samples, typically involving steps such as degreasing, deproteinization, precipitation, desalting, and chromatographic purification. This process serves as a key prerequisite for functional studies and structural identification, providing a foundation for subsequent physicochemical property determination, bioactivity analysis, and product development.
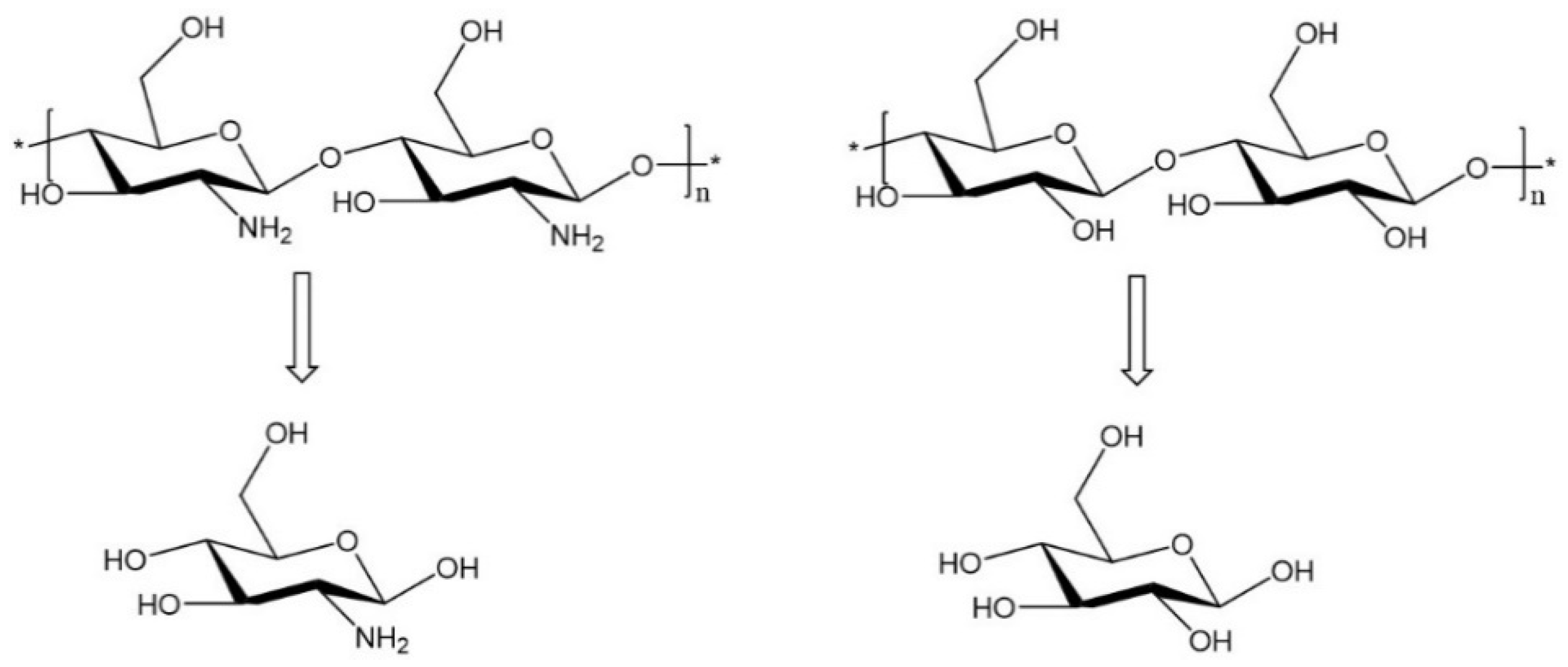
Ren, Y. et al. Molecules, 2019.
Figure 1. Structures of Animal and Plant Polysaccharides
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on multiple separation and purification platforms, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), and ion exchange chromatography (IEC), MtoZ Biolabs has launched the polysaccharide isolation and purification service, which enables efficient extraction, impurity removal, and purity enhancement of polysaccharides from various sample sources. By precisely controlling separation parameters and analytical conditions, we provide high-purity polysaccharide samples with well-defined components, establishing a solid foundation for subsequent structural identification and functional studies.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Pretreatment
The samples are subjected to degreasing, deproteinization, and impurity removal to ensure that the polysaccharide components are in an extractable state.
2. Crude Extraction and Preliminary Separation
Hot water extraction, alcohol precipitation, or enzymatic hydrolysis is used to obtain crude polysaccharide solutions, followed by centrifugation or filtration to remove insoluble impurities.
3. Purification and Fractionation
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC), ion exchange chromatography (IEC), or ultrafiltration systems are employed to fractionate and purify polysaccharides, improving purity and component resolution.
4. Purity Verification
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or ultraviolet detection is applied to evaluate purification efficiency and confirm the integrity and purity of the isolated polysaccharides.
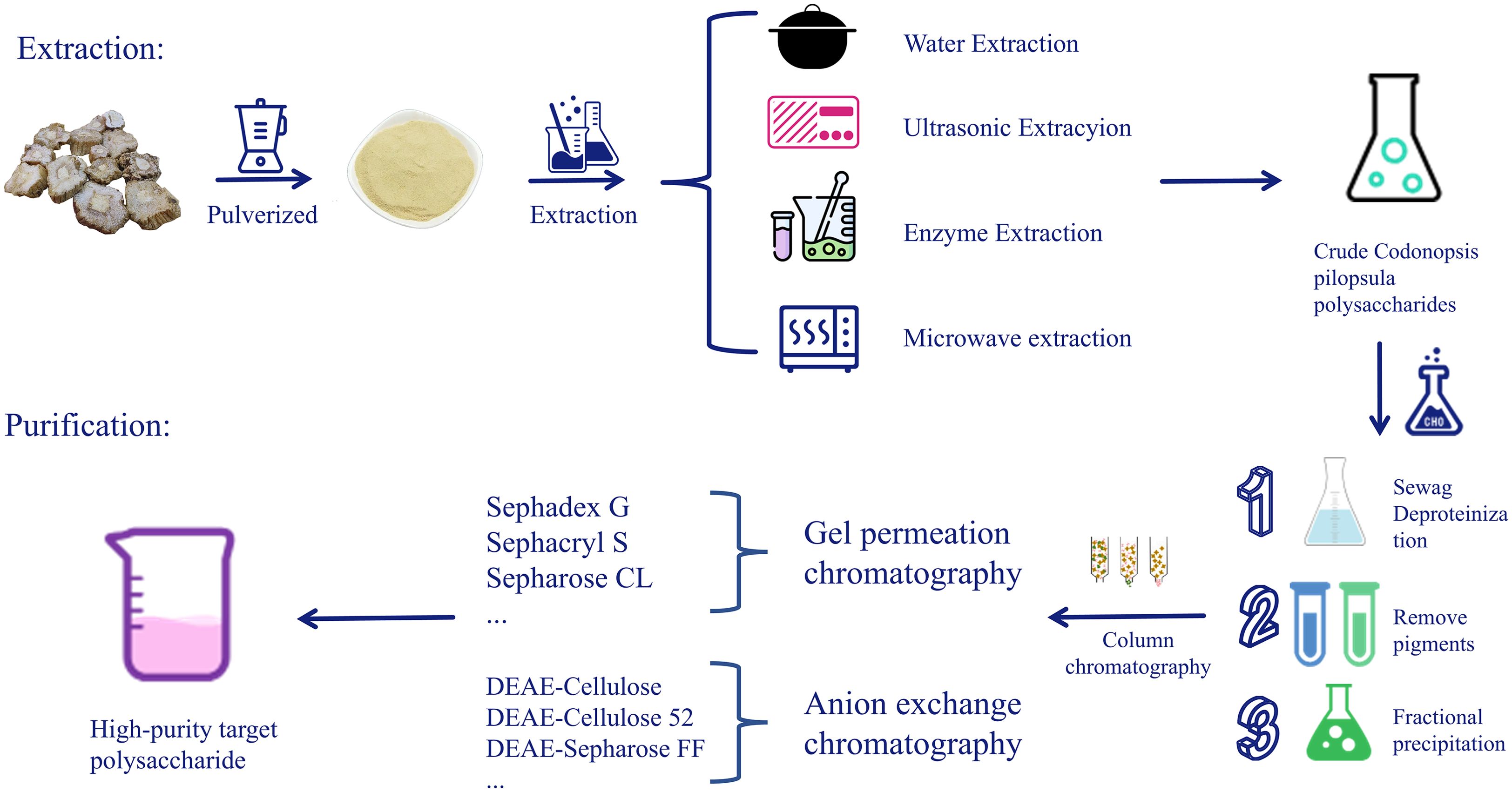
Pan, M T. et al. Frontiers in Immunology, 2025.
Figure 2. Extraction, Separation, and Purification Process of C. pilosula Polysaccharides
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Plant tissues, algae, biological extracts, fermentation broths, and microbial cultures are all acceptable sample types. Crude polysaccharides or partially extracted samples can also be processed.
2. Sample Storage
Solid samples should be sealed and stored in a light-protected environment at 4°C or −20°C. Liquid samples should be kept refrigerated to prevent degradation and avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles.
3. Sample Transportation
Samples should be shipped in sealed, moisture-proof packaging. Liquid samples require cold-chain transportation, while solid samples can be shipped at ambient temperature for short periods, avoiding exposure to heat and humidity.
Service Advantages
1. Standardized Operating Procedures
Strictly follows quality control guidelines to ensure the stability and reproducibility of separation results.
2. Multiple Separation Modes Available
Offers a variety of polysaccharide separation methods suitable for different types of samples.
3. Experienced Technical Support
The technical team has extensive experience handling complex polysaccharide samples and can adjust purification strategies based on sample characteristics.
4. Customized Purification Solutions
Provides flexible separation routes and purification strategies tailored to sample properties and research requirements.
Applications
1. Functional Polysaccharide Research
The polysaccharide isolation and purification service can support studies on bioactive polysaccharides with antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties.
2. Environmental and Ecological Sample Research
By extracting and separating natural polysaccharides from soil, algae, or biofilm samples, this service facilitates ecological function analysis.
3. Natural Active Ingredient Enrichment
Used for enriching polysaccharide-based active components from medicinal plants or natural products to support pharmaceutical research.
4. Preprocessing for Structural and Physicochemical Analysis
The polysaccharide isolation and purification service provides high-purity samples for subsequent molecular weight, structural, and physicochemical characterization.
FAQ
Q1: Is Sample Pretreatment Required?
A1: It is recommended to perform initial defatting, deproteinization, or impurity removal to improve purification efficiency. If pretreatment is not possible, MtoZ Biolabs can provide professional sample preprocessing services.
Q2: Will the Polysaccharide Structure Be Altered during Purification?
A2: We use mild processing conditions and appropriate solvent systems to minimize glycosidic bond cleavage or side-chain loss, ensuring the structural integrity of the polysaccharides.
Q3: What Level of Purity Can Be Achieved after Purification?
A3: The achievable purity depends on sample complexity and the purification method used. In most cases, polysaccharide fractions with over 90% purity can be obtained, accompanied by detailed purity verification data.
Related Services
How to order?







