Polysaccharide Composition Analysis Service
Based on high-resolution HPLC, LC-MS and GC-MS platforms, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the polysaccharide composition analysis service which enables systematic analysis of monosaccharide composition, molar ratio, and relative content in polysaccharide samples. Through acid hydrolysis, derivatization, and high-sensitivity detection, this service accurately identifies various monosaccharides such as glucose, galactose, mannose, arabinose, and rhamnose. By combining standard calibration and quantitative calculation, detailed quantitative data and compositional profiles of polysaccharides can be obtained, providing reliable data support for further polysaccharide research.
Overview
Polysaccharides are macromolecular carbohydrates composed of multiple monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds. They are widely distributed in living organisms and play essential roles in energy storage, structural support, and signal transduction. Polysaccharide composition refers to the types and proportions of monosaccharides contained within a polysaccharide, which determine its physicochemical properties, biological activities, and functional characteristics. This analysis is widely applied in food science, pharmaceutical development, natural product research, microbial metabolism, and biomaterials, providing critical insights for structural elucidation, quality control, and functional studies of polysaccharides.
Analysis Workflow
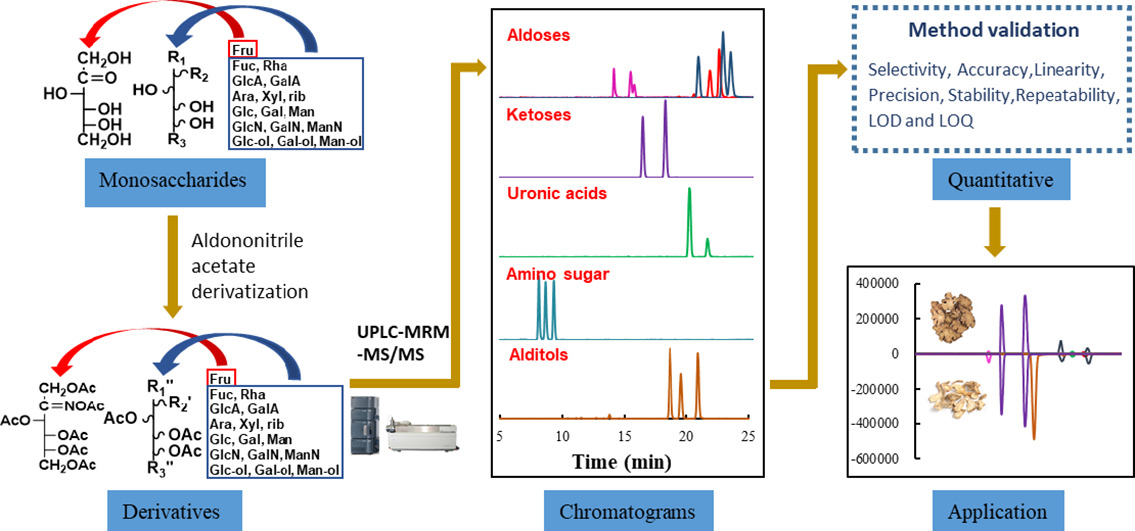
1. Sample Pretreatment
Polysaccharide samples are desalted, deproteinized, and purified to remove interfering substances and ensure analytical accuracy.
2. Acid Hydrolysis
Appropriate acid hydrolysis conditions are applied to decompose polysaccharides into monosaccharide units, ensuring complete component release.
3. Derivatization
The generated monosaccharides undergo chemical derivatization to improve volatility and detection sensitivity, facilitating subsequent separation and analysis.
4. Chromatographic Detection
High-performance HPLC, LC-MS or GC-MS systems are used to separate and detect monosaccharide components.
5. Data Analysis and Result Output
By comparing with standards and calculating peak areas, the types and relative contents of monosaccharides are determined, and a quantitative report of polysaccharide composition is generated.
LI, Y. et al.Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021.
Figure 1. Characterization of Monosaccharide Composition in Plant-Derived Polysaccharides.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Acceptable samples include plant tissues, microorganisms, pharmaceutical formulations, and purified polysaccharides, available in powder, solution, or lyophilized forms.
2. Sample Storage
Samples should be stored in a dry, sealed environment to prevent moisture absorption, oxidation, and microbial contamination. Liquid samples are recommended to be kept at -20°C for short-term storage and at -80°C for long-term preservation.
3. Sample Transportation
Lyophilized samples can be shipped at ambient temperature for short periods, while liquid samples should be transported under low-temperature cold chain conditions to prevent degradation and compositional changes.
Service Advantages
1. High-Sensitivity Analytical Platform
Utilizing advanced analytical systems to achieve high-precision qualitative and quantitative analysis of trace monosaccharide components in polysaccharides.
2. Comprehensive Monosaccharide Coverage
Capable of detecting both common and rare monosaccharides, including neutral sugars, amino sugars, and deoxy sugars, with broad analytical coverage.
3. Standardized Analytical Workflow
A strictly quality-controlled process from sample preparation to data interpretation ensures reproducible and reliable results.
4. Customized Research Solutions
Research plans can be tailored according to sample origin and study objectives to meet diverse experimental requirements.
Applications
1. Pharmaceutical Polysaccharide Development
Analyzing polysaccharide components in natural medicinal materials or fermentation products helps reveal the relationship between structural features and biological activity.
2. Biopharmaceutical Quality Control
Polysaccharide composition analysis service can be applied to evaluate the consistency of glycan components in vaccines, glycoproteins, or polysaccharide-based drugs.
3. Plant and Microbial Research
By characterizing the composition of plant cell wall and microbial extracellular polysaccharides, this service supports studies in structural biology and metabolic engineering.
4. Industrial and Fermentation Process Monitoring
Polysaccharide composition analysis service enables real-time monitoring of polysaccharide synthesis and degradation dynamics during fermentation processes.
FAQ
Q1: Can Samples Contain Proteins or Lipids?
A1: It is not recommended. Proteins, lipids, and inorganic salts can interfere with hydrolysis and signal detection, and should be removed as much as possible to ensure analytical accuracy.
Q2: Do Samples from Different Sources Require Different Pretreatment Methods?
A2: Yes. Plant samples usually require alcohol extraction to remove pigments, while fermentation broth samples should be centrifuged to eliminate impurities, ensuring polysaccharide purity and analytical accuracy.
Q3: Can the Analysis Distinguish Polysaccharide Branching Structures?
A3: Basic composition analysis mainly reflects monosaccharide types and ratios. For detailed branching structure analysis, methylation analysis or NMR detection can be combined.
Related Services
How to order?







