Polysaccharide Anomeric Configuration Identification Service
-
Raw analytical data from GC-MS, LC-MS, CD, or NMR platforms;
-
Processed result tables (Excel or CSV format);
-
Comprehensive analysis report (PDF format) including experimental details and result interpretation;
-
Graphical files (TIFF or PNG format) for visual presentation.
MtoZ Biolabs utilizes an advanced multi-platform analytical system, offers the polysaccharide anomeric configuration identification service which enables precise identification and analysis of α/β glycosidic bond configurations in polysaccharides and their monosaccharide residues. This service is widely applied in polysaccharide structure elucidation, natural product research, and biosynthetic mechanism studies, providing a solid data foundation for structure-activity relationship analysis and the advancement of glycochemistry.
Overview
Polysaccharide anomeric configuration refers to the stereochemical orientation of monosaccharide residues in polysaccharides during glycosidic bond formation, typically categorized as α- or β-type. This configuration directly influences the three-dimensional structure, physicochemical properties, and biological activity of polysaccharides, making it a key parameter in studying the relationship between structure and function. Polysaccharides with different anomeric configurations exhibit distinct solubility, stability, and molecular recognition characteristics; therefore, anomeric configuration identification plays an essential role in natural product analysis, polysaccharide-based drug development, and glycochemistry research.
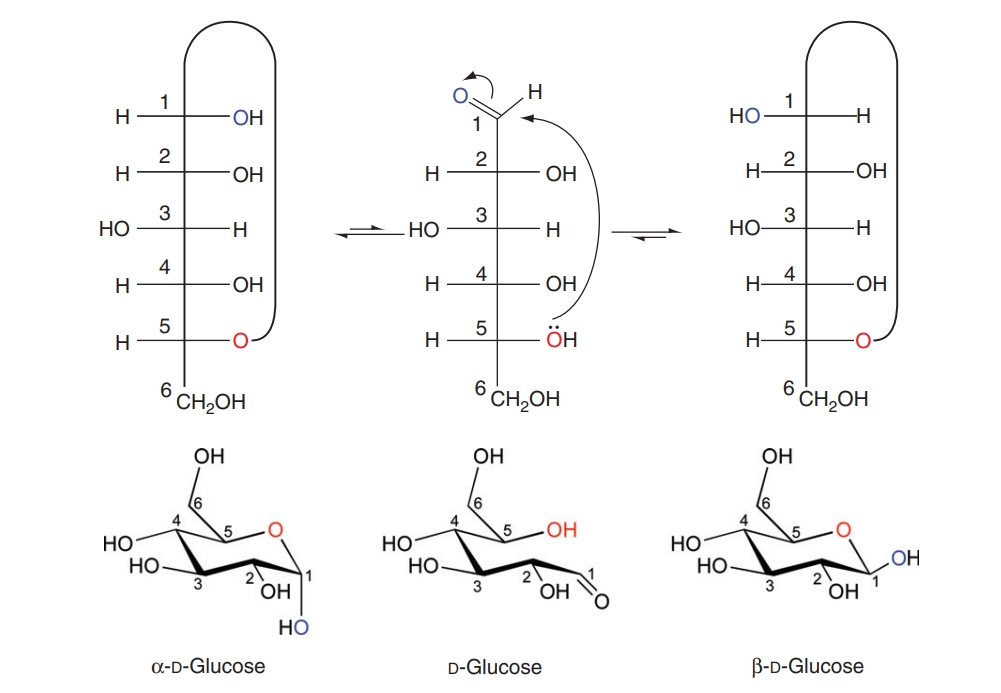
Crispin, M. et al. Comprehensive Biotechnology (Second Edition), 2011.
Figure 1. Chemistry of Anomer Interchange of D-Glucose.
Polysaccharide Anomeric Configuration Identification Service at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Anomeric Configuration Identification Based on Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
By derivatizing monosaccharides and analyzing their retention times and fragment ion characteristics, GC-MS enables accurate differentiation between α- and β-glycosidic configurations, suitable for various polysaccharide samples.
2. Anomeric Configuration Identification Based on Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
Combining efficient liquid-phase separation with high-resolution mass spectrometry detection, LC-MS allows sensitive detection and precise determination of anomeric carbon configurations.
3. Anomeric Configuration Identification Based on Circular Dichroism (CD)
By utilizing differences in optical responses of molecules with different configurations in circular dichroism spectra, CD provides rapid determination of polysaccharide chirality and configuration type.
4. Anomeric Configuration Identification Based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
Through analysis of chemical shifts and coupling constants, NMR directly identifies the α- or β-configuration of glycosidic bonds, providing intuitive and reliable results.
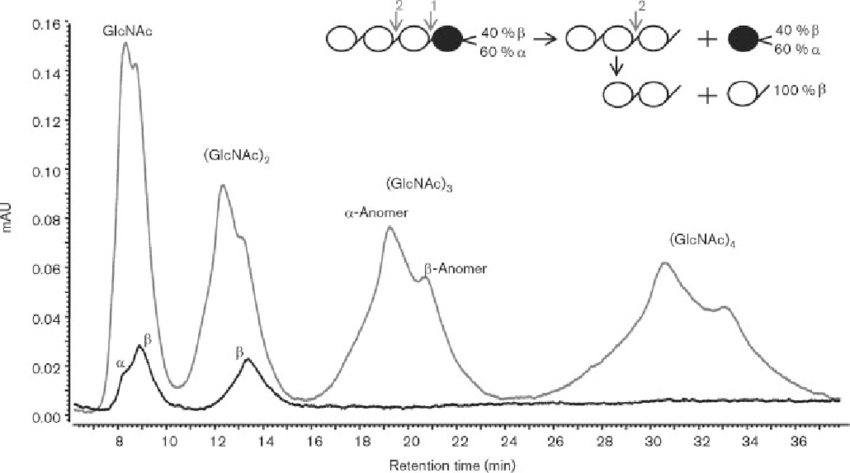
Munster, J V. et al. Microbiology, 2012.
Figure 2. HPLC Analysis of the Anomeric Configuration of Products from (GlcNAc) 4 Hydrolysis.
Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
✅ Multi-platform Integration: Integrates multiple analytical technologies to achieve precise determination of anomeric configurations.
✅ High-resolution Detection: Accurately distinguishes α/β configuration differences, enhancing the reliability of polysaccharide structure analysis.
✅ Standardized Workflow: A strict quality control system ensures experimental consistency and traceability.
✅ Comprehensive Data Interpretation: Provides detailed spectroscopic, chromatographic, and mass spectrometric reports to facilitate further research.
✅ Customized Analytical Solutions: Flexibly tailors analytical strategies based on sample characteristics and research objectives.
Applications of Polysaccharide Anomeric Configuration Identification Service
1. Polysaccharide Structure Analysis
Used to determine the α/β anomeric configurations of glycosidic bonds in polysaccharides, revealing their three-dimensional structural features and linkage patterns.
2. Biosynthesis and Metabolic Research
Analyzes configuration changes of polysaccharides during biosynthesis and degradation, supporting metabolic pathway elucidation.
3. Glycoconjugate and Glycoengineering Studies
Applied for configuration confirmation of glycoconjugates, glycoproteins, or glycosylated materials to ensure structural accuracy.
4. Biochemical and Molecular Research
Supports structural biology and glycoscience studies related to polysaccharides, facilitating the exploration of functional mechanisms.
5. Quality Control and Standardization Analysis
Used for batch consistency testing and structural standardization of polysaccharide products, improving product quality reliability.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Anomeric Configuration Identification Results
4. Spectroscopic, Mass Spectrometric, and Chromatographic Data
5. Comprehensive Analytical Report
6. Raw Data Files
FAQ
Q1: What types of samples are suitable?
A1: The polysaccharide anomeric configuration identification service provided by MtoZ Biolabs is suitable for a wide range of sample types, including natural polysaccharides, synthetic polysaccharides, glycoconjugates, and polysaccharide hydrolysates. To ensure accuracy, it is recommended that samples have high purity and be free from interfering impurities such as proteins, salts, and organic solvents.
Q2: What is the service general workflow?
A2:
Q3: What data formats are provided?
A3: MtoZ Biolabs offers standardized, multi-format data deliverables for convenient scientific analysis and presentation. Standard deliverables include:
If special analytical requirements exist, data formats can be customized according to project specifications.
Q4: How should I prepare my samples?
A4: To ensure analytical accuracy and reproducibility, MtoZ Biolabs recommends that clients follow these guidelines:
(1) Sample form: Powder or solution samples are acceptable;
(2) Purity requirements: Avoid residues of salts, surfactants, or organic solvents;
(3) Storage conditions: Store at -20℃ for short-term or -80℃ for long-term preservation;
(4) Transportation: Use dry ice cold-chain transportation with sealed, leak-proof containers;
(5) Additional information: Please specify sample origin, preparation method, and research objectives to optimize the testing strategy.
For more information, please refer to Sample Submission Guidelines for Proteomics, Sample Submission Guidelines for Metabolomics.
Start Your Project with MtoZ Biolabs
Contact us to discuss your experimental design or request a quote. Whether you are exploring the anomeric configuration characteristics of polysaccharides or investigating their roles in structure-function relationships, MtoZ Biolabs provides precise, professional analytical support and technical services to advance your research.
How to order?







