Mannan Oligosaccharides Analysis Service
Mannan oligosaccharides (MOS) are a class of functional oligosaccharides composed of mannose units linked by glycosidic bonds and are mainly classified into two types: α-mannan oligosaccharides and β-mannan oligosaccharides. The α-type is primarily derived from yeast cell walls and exhibits strong immunomodulatory and anti-adhesive properties against pathogens, while the β-type is commonly found as a hydrolysis product of plant-derived mannans and is effective in improving intestinal health and promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. As a natural prebiotic, mannan oligosaccharides have broad application value in animal nutrition, intestinal microecological regulation, and the development of functional oligosaccharide products.
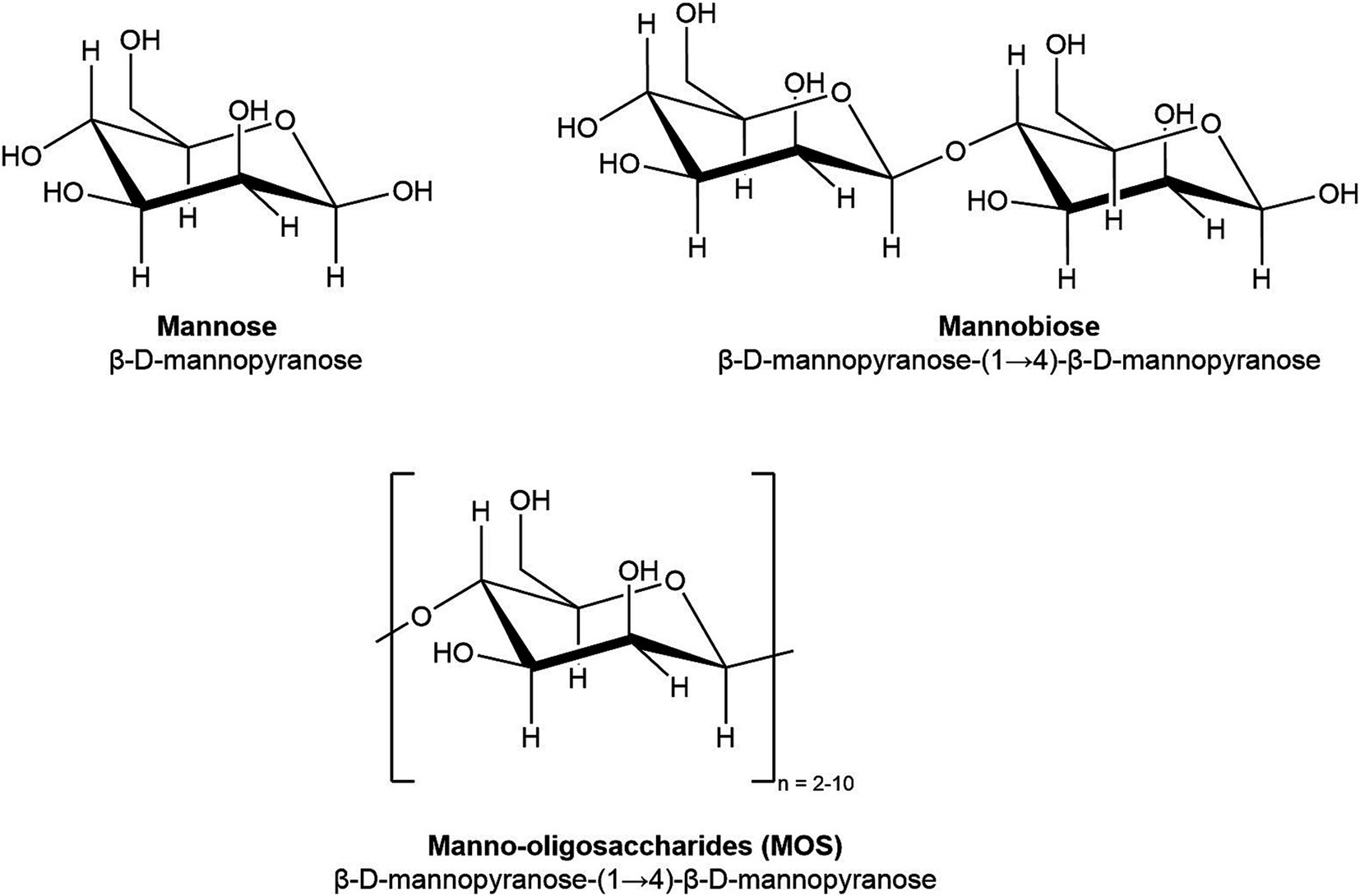
Mano, M C R. et al. Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018.
Figure 1. Chemical Structure of Mannose (DP 1), Mannobiose (DP 2), and Manno-Oligosaccharides (DP 2-10).
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on a high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis platform, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the mannan oligosaccharides analysis service which enables precise qualitative and quantitative analysis of mannan oligosaccharides in various samples. Through efficient separation and high-sensitivity detection, this service provides comprehensive analysis of the composition types, degree of polymerization (DP) distribution, and structural characteristics of mannan oligosaccharides. The resulting data can be used to evaluate the purity and content of mannan oligosaccharides, reveal molecular structural differences, and determine their distribution characteristics in different biological systems, providing reliable data support for feed nutrition research, microecological function assessment, and functional oligosaccharide development. MtoZ Biolabs offers services including but not limited to the following:
1. Quantitative Analysis
Using HPLC or LC-MS/MS techniques, the content of mannan oligosaccharides in samples is accurately determined to ensure data precision and reliability.
2. Purity and Content Analysis
Through high-resolution separation and detection, the purity and potential impurities of mannan oligosaccharides are assessed, providing a basis for quality control and component identification.
3. Structural Characterization
High-resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are applied to elucidate the molecular structure, linkage types, and terminal modifications of mannan oligosaccharides.
4. Degree of Polymerization (DP) Distribution
Using chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis, the distribution of mannan oligosaccharides with different degrees of polymerization is determined, revealing their compositional characteristics and biological functional differences.
5. Stability Evaluation
The changes in structure and content of mannan oligosaccharides under different temperatures, pH levels, and storage conditions are examined to assess their physicochemical stability and suitability for application.
6. Metabolic Analysis
By integrating metabolomic strategies, the metabolic distribution and dynamic changes of mannan oligosaccharides in biological systems are investigated to support microecological and functional mechanism studies.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Various types of samples are accepted, including plant extracts, yeast or fungal cell wall samples, fermentation liquids, and purified mannan oligosaccharide formulations. Liquid, powder, and lyophilized forms are all supported.
Note: Samples should be free from high salt, protein, or organic solvent residues to avoid interference with analytical results.
2. Sample Storage
Samples should be sealed and protected from light. For short-term storage, samples can be kept at -20°C, while long-term storage is recommended at -80°C. Repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided to prevent oligosaccharide degradation.
3. Sample Transportation
Liquid samples are recommended to be transported on dry ice through a cold chain system. Lyophilized samples may be shipped at ambient temperature for short durations but must be protected from moisture, high temperatures, and light to ensure the stability of mannan oligosaccharides.
Service Advantages
1. Multidimensional Data Analysis
Covers multiple analytical aspects including content, purity, structure, and degree of polymerization, providing a comprehensive overview of mannan oligosaccharide characteristics.
2. Customized Service Solutions
Flexible detection and data analysis plans are designed according to sample type and research objectives.
3. Strict Quality Control System
Standard calibration and quality control monitoring are applied to ensure accuracy and reliability of results.
4. One-Stop Service Delivery
Includes sample testing, data analysis, and report generation, offering clients an efficient and convenient analytical experience.
Applications
1. Plant and Microbial Metabolism Research
By analyzing the production and distribution of mannan oligosaccharides in plant or microbial systems, their roles in carbon metabolism and energy utilization can be elucidated.
2. Fermentation Process Monitoring
The mannan oligosaccharides analysis service can be applied to monitor the dynamic changes of mannan oligosaccharides during fermentation, assessing production efficiency and pathway optimization.
3. Functional Oligosaccharide Product Development
By verifying the purity, structure, and bioactivity of mannan oligosaccharides from different sources or processing conditions, this service provides data support for product improvement.
4. Biomedical and Immunological Research
The mannan oligosaccharides analysis service can be used to explore the potential applications of mannan oligosaccharides in immune regulation, anti-inflammatory responses, and prebiotic mechanisms.
FAQ
Q1: Can Mannan Oligosaccharide Analysis Distinguish between Different types (α-Type and β-Type)?
A1: Yes. The high-resolution high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) system at MtoZ Biolabs can differentiate and quantify α- and β-mannan oligosaccharides based on retention time, molecular ion peaks, and characteristic fragment ions. By comparing with standard references, the structural type and linkage pattern can be further verified.
Q2: Do Samples from Different Sources (Plants, Microorganisms, Feed, etc.) Require Different Pretreatment Methods?
A2: Yes. The impurities present in different matrices vary significantly. Plant samples generally require decolorization and polyphenol removal, microbial fermentation liquids need centrifugation to remove debris, and feed samples require enzymatic hydrolysis or extraction treatment. MtoZ Biolabs designs optimized pretreatment protocols according to the sample type to ensure detection sensitivity and accuracy.
How to order?







