Isomaltose Analysis Service
- Liquid samples: ≥ 2 mL
- Solid samples: ≥ 2 g
- Complex matrices (e.g., plant tissues, fermented samples): ≥ 5 g (depending on moisture and matrix complexity)
Isomaltose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose units linked by an α-1,6-glycosidic bond. It occurs naturally in starch hydrolysates, malt extracts, and fermentation broths and is also produced during enzymatic modification of polysaccharides. Owing to its low sweetness, high stability, and prebiotic properties, isomaltose plays an increasingly important role in the food, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries. Accurate quantification and structural characterization of isomaltose are essential for understanding carbohydrate metabolism, evaluating enzymatic conversion efficiency, and ensuring product quality during manufacturing and formulation.
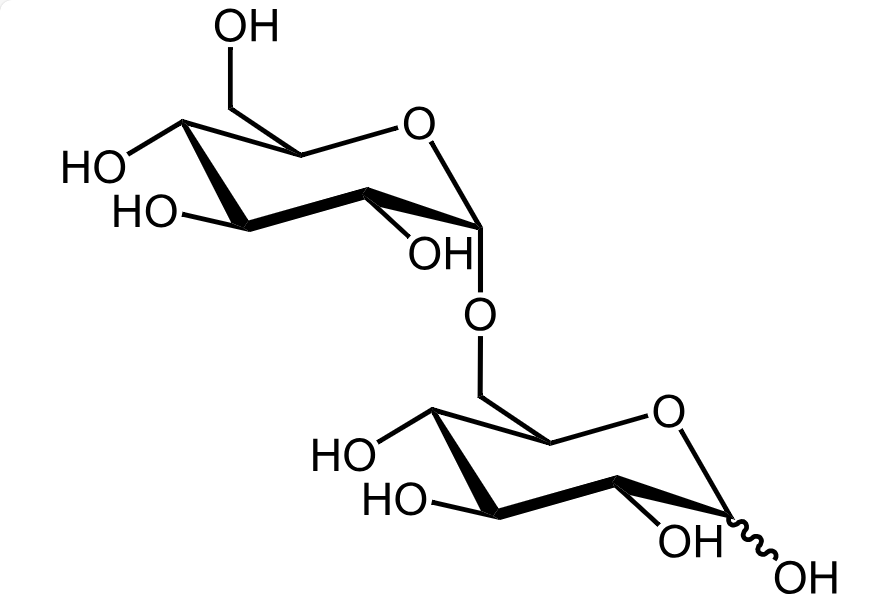
Source: Wikipedia
Figure 1. Structure of Isomaltose
MtoZ Biolabs provides professional Isomaltose Analysis Service covering quantitative determination, purity analysis, structural elucidation, stability evaluation, and metabolic profiling. Equipped with advanced chromatographic and spectrometric platforms including High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Gas Chromatography (GC), Ion Chromatography with Pulsed Amperometric Detection (IC-PAD), Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC), and Capillary Electrophoresis (CE), MtoZ Biolabs delivers high-precision, reproducible, and publication-ready analytical data that support research and industrial applications.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
💠Content Determination
Accurate quantification of isomaltose concentration using HPLC or IC-PAD, with detection limits down to 0.05 µg/mL.
💠Purity Analysis
Assessment of isomaltose purity and detection of co-existing sugars such as maltose, glucose, and trehalose to ensure compositional integrity.
💠Structural Analysis
Determination of molecular structure and linkage type through GC and CE-based profiling to confirm α-1,6 glycosidic bonds.
💠Stability Evaluation
Monitoring of isomaltose stability under various pH and temperature conditions using accelerated degradation models.
💠Metabolic Research
Quantitative assessment of isomaltose metabolism in biological systems to study carbohydrate utilization and enzymatic pathways.
Analytical Platforms
🔸HPLC separates sugars based on polarity and molecular interactions, enabling accurate quantification and purity determination. Refractive index (RI), evaporative light scattering (ELSD), or UV detectors are commonly used for reliable sugar analysis.
🔸GC analyzes derivatized isomaltose compounds, offering high separation efficiency and mass-based identification for compositional and structural studies.
🔸IC-PAD detects monosaccharides and disaccharides with high sensitivity without derivatization, particularly useful for complex biological or fermentation samples.
🔸TLC provides a rapid qualitative assessment of sugar composition and sample purity through visual comparison against standards.
🔸CE separates ionic sugar molecules under an electric field, allowing rapid and efficient resolution of isomers and charged sugar derivatives.
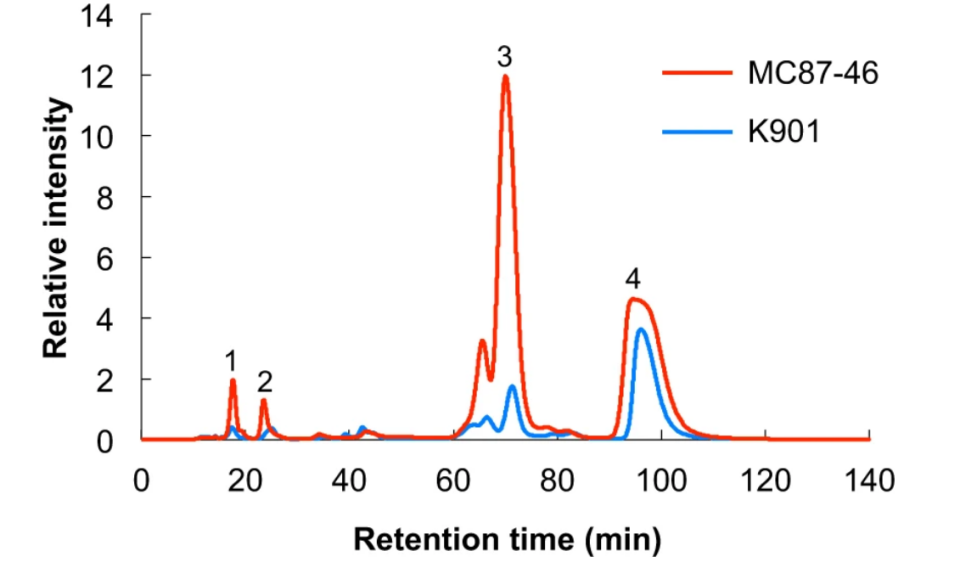
Tsutsumi, S. et al. Sci Rep. 2019.
Figure 2. HPLC Analysis of Sugars in Sake Fermented by Saccharomyces cerevisiae (MC87-46 and K901). Peak 3 is Isomaltose.
Service Advantages
☑️High Accuracy and Reliability: All analyses follow strict quality control procedures with internal standards and calibration curves to ensure precision and reproducibility.
☑️Customizable Analytical Solutions: Methods are tailored to specific research or production needs, supporting studies in purity verification, degradation kinetics, and metabolic pathways.
☑️Rapid and Professional Reporting: Results are delivered promptly with clear data interpretation, visual outputs, and conclusions suitable for publication or regulatory submission.
☑️Expert Technical Support: Our experienced scientists provide consultation throughout the project, ensuring each client receives the most appropriate analytical approach for their goals.
Applications
1. Food and Beverage Industry: Evaluation of isomaltose content in starch-derived syrups, malt extracts, and low-sugar sweeteners.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry: Quality control of excipients, bioactive carbohydrate formulations, and prebiotic agents.
3. Biotechnology and Fermentation Research: Monitoring of enzymatic hydrolysis products, carbohydrate metabolism, and fermentation by-products.
4. Agricultural and Plant Research: Investigation of carbohydrate biosynthesis and modification during plant growth or stress responses.
5. Clinical and Nutritional Studies: Analysis of carbohydrate metabolism and isomaltose utilization in physiological samples.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types: Biological extracts, fermentation media, plant tissues, food products, syrups, and other sample types.
2. Recommended Quantity:
3. Storage and Transport: Store at –20°C for short term or –80°C for long term. Ship samples on dry ice or with ice packs to prevent degradation.
*Note: For samples with limited availability or specific handling requirements, please contact MtoZ Biolabs for customized sample preparation instructions.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
At MtoZ Biolabs, we are committed to providing reliable, reproducible, and publication-quality carbohydrate analysis services. Our Isomaltose Analysis Service supports food science, biochemistry, pharmaceutical, and industrial research, offering precision-driven solutions to meet the growing demands of sugar analysis worldwide. Free project evaluation, welcome to learn more details!
How to order?







