Isobaric Labeling Peptidomics Analysis Service
Isobaric labeling peptidomics analysis is a technique that uses isotope-labeled reagents to tag peptides and perform mass spectrometry analysis, widely applied for quantitative analysis of peptides in complex biological samples. This method utilizes isotope-labeled reagents, such as TMT or iTRAQ, which add identical mass tags to peptides from different samples, enabling the simultaneous analysis of multiple samples in a single mass spectrometry experiment, thus obtaining precise quantitative data.
The isobaric labeling peptidomics analysis service is extensively used in proteomics, disease mechanism research, drug development, and other fields. By quantitatively analyzing peptides from different samples, researchers can reveal protein expression differences, changes in post-translational modifications (PTM), and analyze their roles in physiological and pathological states. Additionally, this technique plays an important role in multi-omics studies, such as helping to discover biomarkers.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms, the isobaric labeling peptidomics analysis service provided by MtoZ Biolabs aims to achieve high-throughput, precise quantitative analysis of multiple samples. This service uses isotopic tags of the same mass (such as TMT or iTRAQ) to label peptides from different samples, enabling the simultaneous analysis of multiple samples in a single experiment. Through this service, researchers can perform both qualitative and quantitative analysis of peptides in complex samples, obtaining information such as peptide sequences, modification sites, and relative abundance, thus providing data support for further research in disease and other areas.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Process the peptide samples to be analyzed, ensuring they are suitable for isotope labeling and mass spectrometry analysis.
2. Isotope Labeling
Use isotopic labeling reagents such as TMT or iTRAQ to add identical mass tags to peptides from different samples, ensuring that multiple samples can be differentiated in the same mass spectrometry analysis.
3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
Labelled peptides are separated using liquid chromatography (LC) and analyzed with a high-resolution mass spectrometer (such as Orbitrap Fusion Lumos) to obtain peptide mass information.
4. Data Processing and Analysis
Use specialized software to process mass spectrometry data, perform quantitative analysis, and analyze post-translational modifications (PTM), generating data on peptide relative abundance, modification sites, etc.
5. Result Interpretation and Reporting
Combine the analysis results to generate a detailed report, providing qualitative and quantitative data on peptides as well as post-translational modification information to support subsequent research.
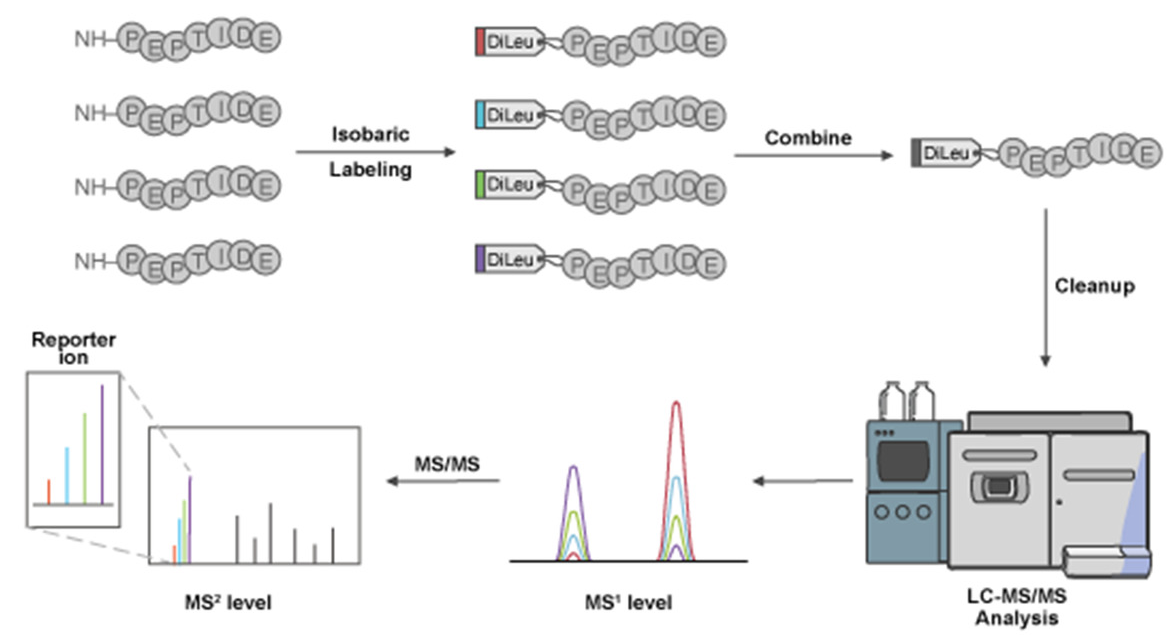
Sivanich, M K. et al. Proteomics, 2022.
Figure 1. Overview of Isobaric Tag Workflow.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Suitable for peptide samples from various sources, including but not limited to cells, tissues, serum, and urine. The samples should be purified peptides to ensure no significant impurities affect the analysis results.
2. Sample Transport
Samples should be stored at -20°C or lower and transported using dry ice to prevent degradation. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
3. Sample Submission
When submitting samples, please provide detailed information, including sample type, source, and storage conditions. It is recommended to include quality control data for the samples to ensure the accuracy of the analysis.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Platform
By utilizing high-resolution mass spectrometers, we provide highly sensitive and high-resolution data, ensuring the accuracy of the analysis results.
2. High-Throughput Analysis
With isotope labeling technology, multiple samples can be analyzed in a single experiment, significantly improving experimental efficiency while saving time and costs.
3. Customized Services
We offer flexible experimental designs and analysis plans tailored to the specific needs of our clients, ensuring that personalized research objectives are met.
4. One-Stop Service
MtoZ Biolabs provides a comprehensive service from sample preparation, isotope labeling, mass spectrometry analysis, to data interpretation, allowing clients to benefit from seamless and efficient services that simplify the research process.
Applications
1. Biomarker Discovery
By comparing peptide expression differences across various biological samples, this service helps identify biomarkers associated with specific physiological or pathological states, providing crucial data support for diagnosis and monitoring.
2. Post-Translational Modification (PTM) Research
The isobaric labeling peptidomics analysis service is applied to PTM analysis, revealing protein modification states and their significant roles in cellular functions, signal transduction, and protein interactions.
3. Protein Function Research
Through quantitative peptidomics analysis, this service explores changes in protein functions during cellular processes, helping to understand the roles of proteins in various biological processes.
4. Multi-Omics Research
By integrating data from other omics technologies, the isobaric labeling peptidomics analysis service provides a more comprehensive biological insight, supporting systems biology and integrated data analysis.
FAQ
Q1: What Are the Advantages of Isobaric Labeling Peptidomics Analysis?
A1: The advantages of this service include high-throughput analysis, precise quantification capabilities, and the ability to analyze multiple samples simultaneously. It is widely applied in protein expression, post-translational modification (PTM), and biomarker discovery, among other fields.
Q2: What Is the Difference between Isobaric Labeling and Isotope Labeling?
A2: Isobaric labeling uses the same mass tag to label multiple samples and differentiates them in mass spectrometry through specific methods, making it suitable for simultaneous analysis of multiple samples. Isotope labeling, on the other hand, uses different mass isotopic tags, making it suitable for comparing a small number of samples, typically used for single or few sample quantitative analysis. The main difference between the two lies in the labeling principle and applicable scenarios.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation
4. Bioinformatics Analysis
5. Raw Data Files
How to order?







