Interactomics Service
The interactomics service focuses on studying protein-protein interactions, enabling a deeper understanding of protein functions. Proteins exert their biological roles by interacting with other proteins or compounds, forming macromolecular complexes. The principle of protein interactomics service is based on protein interaction analysis techniques such as immunoprecipitation (IP), co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), or GST pull-down assays. After isolating target proteins through these methods, mass spectrometry is employed for analysis, identification, and quantification. This approach facilitates the characterization of interacting proteins, thereby advancing the functional analysis of proteins.
1. Immunoprecipitation (IP)
Immunoprecipitation is an affinity purification technique that utilizes specific antibodies immobilized on solid-phase supports such as magnetic beads or agarose resin to isolate target antigens.
Taking the magnetic bead-based immunoprecipitation (IP) method as an example, this technique is developed based on the specific binding between an antigen and its corresponding antibody, as well as the affinity of Protein A/G for the Fc fragment of antibodies. The principle involves leveraging the antigen-antibody specificity by adding the antibody into the solution to precipitate the target antigen, forming an antigen-antibody complex. Subsequently, magnetic beads conjugated with Protein A/G are used to capture this antigen-antibody complex, forming a magnetic bead-Protein A/G-antibody-antigen complex, which is then separated from the mixture via magnetic precipitation. Finally, the target protein is eluted from the magnetic beads and analyzed using techniques such as SDS-PAGE and Western blot, allowing for further characterization of the purified protein.
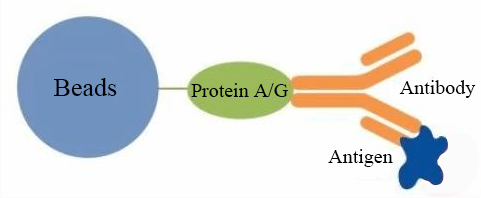
Figure 1. Immunoprecipitation Process.
2. Pull-Down Assay
The pull-down assay, also known as an in vitro protein-binding assay, is used to determine the interaction between a known bait protein and unknown interacting proteins. In this method, the bait protein is labeled with tags such as biotin, PolyHis, or GST and then immobilized on a solid-phase support with affinity for the tag, serving as the bait. The immobilized bait protein is then incubated with protein samples or cell/tissue lysates, allowing for the capture of proteins that interact with the bait protein (target proteins). Subsequently, washing or elution steps are performed to remove nonspecific components, and the captured proteins are then recovered and analyzed using Western blot (WB) or mass spectrometry (MS) to characterize the interactions.
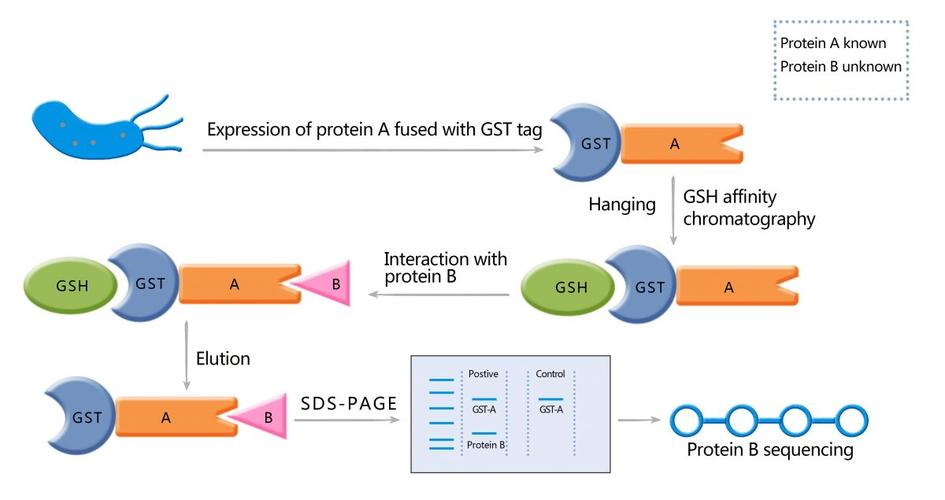
Figure 2. Pull Down Process.
3. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) is an extension of immunoprecipitation (IP) and is primarily used to detect specific interactions between two protein molecules. The principle of this method is that if two proteins specifically interact in an in vitro system, then when an antibody against one protein is used for immunoprecipitation, the interacting protein will also be co-precipitated.
Using the magnetic bead method as an example, antigen A (target protein/bait protein) binds to protein B (interacting protein). An antibody specific to antigen A is then used to precipitate antigen A. Pre-purified Protein A/G is pre-conjugated to magnetic beads, which then react with the antigen-containing solution and the antibody. The Protein A/G on the magnetic beads binds to the antibody, thereby capturing the complex of antigen A and interacting protein B. Through a series of steps including centrifugation, enrichment, washing, and elution, the target interacting protein B is obtained. The detection of interacting protein B allows for the acquisition of information about protein-protein interactions.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced analytical instruments, MtoZ Biolabs has established a protein interactomics service platform. We can analyze protein samples from your protein interaction experiments, or you can directly send your samples to us. We provide a one-stop analysis and detection service, covering all subsequent project procedures, including sample preprocessing, protein interaction experiments (IP, Co-IP, GST Pull-down), mass spectrometry analysis, and raw data analysis, ensuring a seamless and comprehensive workflow.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analytical Platform
MtoZ Biolabs has developed a cutting-edge protein interactomics Service Platform, ensuring reliable, rapid, and high-precision analytical services.
2. Transparent Pricing
Our pricing structure is transparent, with no hidden or additional fees.
3. High-Quality Data
We provide in-depth data coverage with rigorous quality control, delivering comprehensive and high-accuracy reports to our clients.
4. Customized Research Solutions
MtoZ Biolabs offers tailored services to address your specific research questions and experimental requirements.
Applications
1. Disease Mechanism Research
By studying protein-protein interactions, the molecular mechanisms underlying disease development can be uncovered. For example, abnormal interactions between certain proteins may contribute to the onset and progression of diseases. By analyzing these interaction relationships, new targets and strategies for disease diagnosis and treatment can be identified.
2. Drug Development
Protein interactomics service plays a crucial role in drug discovery and development. Understanding protein interactions enables the design of small-molecule inhibitors or agonists targeting specific protein-protein interactions, which can be used for therapeutic intervention. Additionally, protein interaction analysis aids in identifying new drug targets, accelerating the development of novel therapeutics.
3. Biotechnology
In biotechnology, protein interaction studies help elucidate cellular signaling pathways and metabolic processes. By analyzing the composition and function of protein complexes, researchers can optimize biological reactions and enhance production efficiency. Furthermore, protein interaction research is valuable in gene editing and gene therapy applications.
4. Fundamental Biological Research
In basic biological research, protein interactomics service facilitates the understanding of protein function and regulatory mechanisms within cells. By mapping protein interaction networks, scientists can gain insights into cellular physiology and metabolic pathways, advancing our fundamental knowledge of life sciences.
Case Study
1. Disruption of TIGAR-TAK1 Alleviates Immune Pathology in a Mice Sepsis Model
Macrophage TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) is upregulated in a mouse sepsis model. Knockout of TIGAR significantly improves septic inflammation in mice. Studies have shown that TIGAR promotes TRAF6-mediated ubiquitination of TAK1 through E3 ligase activity. A mutation in the key TIGAR residues (152-161), which disrupts the TIGAR-TAK1 interaction, has been demonstrated to eliminate sepsis symptoms in mice in vivo. This suggests a potential therapeutic approach for treating sepsis by targeting and disrupting the TIGAR-TAK1 interaction.
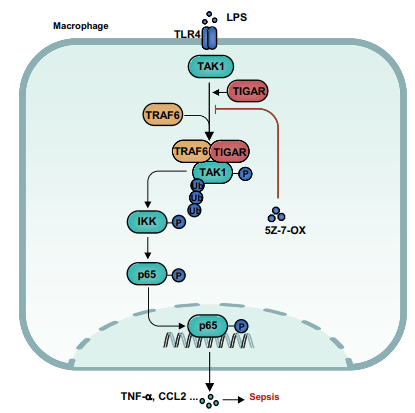
Wang, D D. et al. Nature Communications, 2024.
Figure 3. Schematic Diagram of the Mechanism of TIGAR in Sepsis.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation
4. Raw Data Files
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. Free project evaluation, welcome to learn more details!
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







