Glycan Release Service
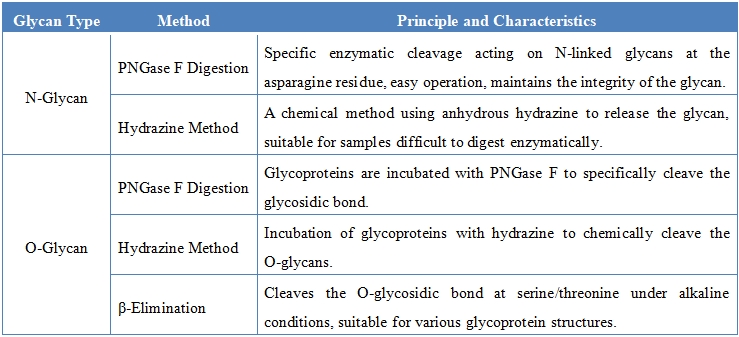
Glycan release refers to the process of cleaving and releasing glycans from glycoproteins, glycolipids, and other complex molecules through enzymatic or chemical methods. Glycans are typically attached to proteins or lipids in an N-linked or O-linked manner, and their release is a prerequisite for structural analysis, quantitative analysis, and functional studies of glycans. Common methods for glycan release include the use of PNGase F enzyme for releasing N-linked glycans, as well as chemical or specific enzymatic methods for releasing O-linked glycans. Through advanced technical platforms, the released glycans can be separated, detected, and characterized, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the results.
Glycan release service has broad applications in multiple fields. In glycomics research, it is an essential step for studying glycan composition, modification, and function; in biopharmaceutical quality control, it can be used to monitor glycosylation consistency in glycoproteins or vaccine production; in food and nutritional sciences, it helps analyze glycan components and their changes in food; and in plant and agricultural research, it can be used to study the glycan structures in plant cell walls or polysaccharides, providing support for crop improvement and functional research.
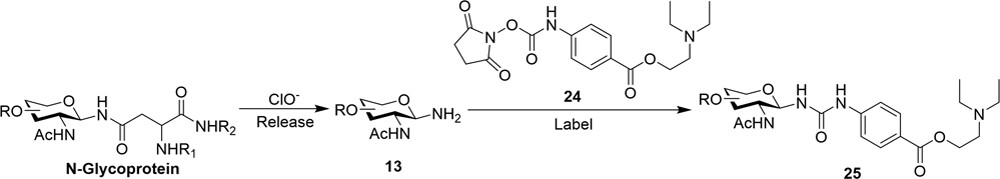
Zhang, Q. et al. Analytical Chemistry, 2024.
Figure 1. Glycoprotein N-Glycan Oxidative Release and Specific Labeling Reaction.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced technologies and analytical platforms, MtoZ Biolabs offers glycan release service that efficiently and accurately release and analyze glycans from biological samples. This service uses enzymatic or chemical methods to release N-linked and O-linked glycans, and combines purification and separation techniques to ensure the integrity of the glycans and the sensitivity of detection. Ultimately, the service provides detailed data on the type, composition, linkage, and distribution of the glycans, laying a solid foundation for subsequent glycan structure analysis, quantitative research, and functional studies. The methods for glycan release include, but are not limited to, the following:
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Preprocess the sample to remove impurities and ensure the integrity of the glycan components.
2. Glycan Extraction
Release glycans from glycoproteins, glycolipids, and other samples through enzymatic or chemical methods.
3. Glycan Enrichment
Use specific enrichment techniques to extract target glycans, ensuring the purity and analytical accuracy of the glycan components.
4. Glycan Release
Release glycans completely from proteins or lipids using specific enzymes (such as PNGase F) or chemical methods (such as hydrazinolysis).
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Applicable to various biological samples containing glycan components, including glycoproteins, tissues, cell lysates, serum, plasma, etc. Samples can be in liquid or solid form, and their glycan integrity must be ensured.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended to remove impurities as much as possible to reduce interference and improve analytical accuracy. For complex samples, initial impurity removal is suggested to ensure the reliability of the data.
3. Sample Storage and Transport
Samples should be transported at low temperatures. Liquid samples can be transported using ice packs or dry ice, while solid samples should be sealed and protected from moisture. To ensure sample quality, it is recommended to keep samples frozen or cold during transportation.
Service Advantages
1. High-Efficiency Glycan Release
Through optimized enzymatic and chemical methods, we can efficiently release glycans, ensuring their integrity and the accuracy of the analysis.
2. Diverse Methods
We use a variety of glycan release methods, such as enzymatic methods and chemical methods, to ensure the ability to handle different types of glycans, adapting to various samples and research needs.
3. Optimized Experimental Process
By combining advanced technologies with optimized experimental workflows, we minimize side reactions and ensure that the glycan release process is efficient and precise.
4. Customized Services
Based on the client's research objectives and sample characteristics, we offer personalized glycan release and analysis solutions to ensure flexibility and efficiency in the research process
Applications
1. Glycosylation Mechanism Research
The Glycan release service can be used to study the role of glycans in cell functions and interactions, revealing the impact of glycosylation modifications on biological processes, and advancing research in the field of glycomics.
2. Biological Product Analysis
In the development of glycoproteins, glycolipids, and other biological products, this service provides glycan release technology to ensure the consistency and reliability of glycan modifications, supporting the quality evaluation of biological products.
3. Food Safety and Quality Control
The Glycan release service can be used to analyze the glycan composition in food, monitor changes in glycans, and ensure product quality and stability, especially for the development and testing of functional foods and nutritional products.
4. Plant Research and Agricultural Improvement
By analyzing glycans in plant samples, this service helps reveal the impact of glycosylation on plant growth, development, and stress resistance, supporting crop improvement and advancements in agricultural research.
FAQ
Q1: How Is the Efficiency of Glycan Release Ensured?
A1: By optimizing enzymatic and chemical methods, we can efficiently release glycans, ensuring efficient extraction of glycan components even from complex biological samples, minimizing glycan loss to the greatest extent.
Q2: What Further Analyses Can Be Performed on the Released Glycans?
A2: Released glycans can undergo structural analysis, modification feature characterization, and functional studies, helping to uncover the important roles glycans play in biological processes and supporting glycosylation research and exploration in other related fields.
Related Services
Glycan Structure Analysis Service
Glycan Separation and Purification Services
How to order?







