Glycan Cross-linking Analysis Service
Glycan cross-linking refers to the covalent bond formation between sugar molecules and other biomolecules, such as proteins and lipids, through chemical or enzymatic reactions. By analyzing the cross-linking reactions between glycan chains and other molecules, it is possible to reveal how glycan chains influence cell recognition, signal transduction, and other biological interactions. This service relies on advanced cross-linking agents and high-resolution analytical platforms, providing precise glycan cross-linking patterns, cross-linking sites, and interactions between cross-linked molecules.
The glycan cross-linking analysis service has broad applications in various fields. In glycomics research, it helps to deepen the understanding of glycan chains' functions at the cellular and molecular levels. In drug development, it can assist in studying how glycan chains affect the binding and stability of drug targets, supporting the development of targeted therapies. In biopharmaceutical quality control, glycan cross-linking analysis helps monitor the consistency of glycan modifications, ensuring the quality and stability of the products.
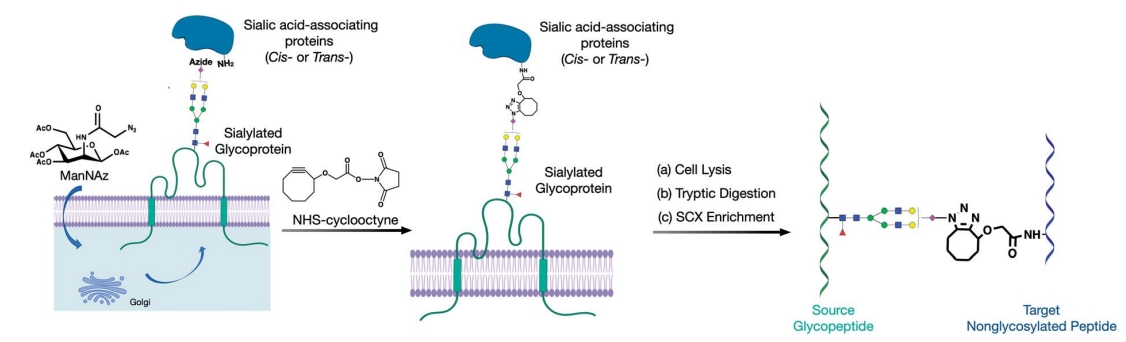
Xie, Y X. et al. Chemical Science, 2021.
Figure 1. Proposed Method for Producing and Implementing Glycan–Protein Cross-Linking on the Cell Membrane of Cell Lines.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced technology and platforms, MtoZ Biolabs' glycan cross-linking analysis service provides precise analysis of glycan cross-linking structures, functions, and their interactions with other molecules. Using optimized analytical methods, the service can detail the cross-linking sites, types, and efficiency of glycan chains. The analysis results include the types of cross-linked glycans, their concentrations, linkage modes, and distribution across different samples. This helps researchers gain deeper insights into the role of glycan cross-linking in biological processes.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
The sample is pretreated to remove impurities, ensuring the integrity of the glycan cross-linking components.
2. Glycan Cross-Linking Reaction
By adding cross-linking agents, glycan chains are induced to cross-link with other molecules, forming cross-linked glycans.
3. Glycan Extraction and Enrichment
Specific enzymatic or chemical methods are used to extract the cross-linked glycans, followed by enrichment techniques to isolate the target glycan chains.
4. Separation and Analysis
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or capillary electrophoresis (CE) is used to separate the cross-linked glycans, followed by precise qualitative and quantitative analysis using mass spectrometry (MS).
5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy Analysis
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is used to further analyze the structural features of glycan cross-linking, helping confirm the spatial conformation and cross-linking sites of the glycans.
6. Data Processing and Report Generation
Bioinformatics tools are applied to interpret the data, generating a report that provides detailed information on the types, sites, concentrations, and distribution characteristics of the glycan cross-links.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
This service is suitable for various biological samples containing glycan components, including glycoproteins, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, serum, plasma, etc. Samples can be in liquid or solid form, ensuring the integrity of the glycan chains.
2. Sample Purity
The glycan chains in the sample should be as purified as possible to reduce interference from impurities and improve the accuracy of the analysis. Complex samples should undergo preliminary impurity removal treatment.
3. Sample Storage and Transport
Samples must be transported at low temperatures. Liquid samples can be transported using ice packs or dry ice, while solid samples should be sealed and kept dry. To ensure sample quality, it is recommended that samples remain frozen or kept cold during transportation.
Service Advantages
1. High Precision Analysis
Based on advanced technologies such as mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), our service offers precise glycan cross-linking analysis, ensuring high accuracy and reliability of the data.
2. Comprehensive Data Support
We provide detailed analysis of glycan cross-linking types, locations, and degrees, along with the glycan's monosaccharide composition and linkage patterns, offering full support for in-depth understanding of glycosylation functions.
3. Customized Service
We offer tailored analysis plans based on the client's research goals and sample characteristics, providing flexibility to meet various glycosylation research needs.
4. One-Stop Service
We provide end-to-end support from sample preparation, glycan extraction, cross-linking analysis, to data interpretation, simplifying the process and improving research efficiency.
Applications
1. Cellular Mechanism and Glycomics Research
The glycan cross-linking analysis service can be used to study the impact of glycan cross-linking on glycosylation modifications, revealing its functions in cellular recognition, signal transduction, and other processes, promoting the advancement of glycomics research.
2. Biopharmaceutical Development and Monitoring
Through glycan cross-linking analysis, the consistency and stability of glycosylation modifications can be ensured, helping to improve the quality control of biopharmaceuticals like glycoproteins and glycosphingolipids.
3. Food Research and Quality Analysis
The glycan cross-linking analysis service can be used to assess the impact of glycan cross-linking on food texture, stability, and functionality, ensuring recipe standardization and supporting the development of nutritionally enhanced foods.
4. Plant Research and Agricultural Innovation
By analyzing glycan cross-linking in plants, its role in plant stress resistance, adaptability, and growth can be revealed, providing support for agricultural improvements and crop breeding.
FAQ
Q1: What Is the Sensitivity of Glycan Cross-Linking Analysis?
A1: Our glycan cross-linking analysis has high sensitivity and can detect low-abundance glycan cross-linking products, especially in complex biological samples. Through optimized extraction and separation techniques, we ensure effective analysis of trace glycan cross-links in complex samples.
Q2: How Does Glycan Cross-Linking Analysis Differ from Other Glycomics Analyses?
A2: Glycan cross-linking analysis primarily focuses on the cross-linking structures and modifications of glycans, while other glycomics analyses typically concentrate on glycan composition and modification types. Cross-linking analysis can reveal changes in glycan spatial conformation, stability, and interactions with other molecules, providing a unique perspective compared to traditional glycomics analyses.
Related Services
Glycan Structure Analysis Service
How to order?







