DIA Proteomics Service
DIA proteomics is an advanced mass spectrometry-based technique designed to provide comprehensive and systematic identification and quantification of proteins within complex biological samples. The core principle of DIA proteomics involves the simultaneous fragmentation and detection of all peptides within predefined mass-to-charge (m/z) windows, rather than selectively targeting specific peptide ions as in traditional Data-Dependent Acquisition (DDA) methods. In a typical DIA workflow, the mass spectrometer sequentially scans across the entire m/z range, fragmenting all peptides within each narrow window during each scan cycle. This approach ensures that every peptide present in the sample is analyzed, generating extensive and consistent MS/MS data sets. By capturing information on all peptides within each window, DIA minimizes the bias inherent in DDA, where only the most abundant peptide ions are selected for fragmentation. This comprehensive data acquisition allows for more accurate and reproducible quantification of proteins, including those of low abundance that might be overlooked by DDA methods.
Doerr, A. Nat Methods. 2015.
Figure 1. The Principle of DIA
When compared to DDA proteomics, DIA proteomics offers several significant advantages and strengths that address the limitations of traditional approaches. Firstly, DIA provides enhanced quantitative accuracy and reproducibility, as its systematic and unbiased sampling strategy ensures consistent detection of peptides across multiple runs. This is particularly beneficial for studies requiring precise quantification, such as biomarker discovery and validation. Secondly, DIA achieves broader protein coverage, enabling the identification and quantification of a larger number of proteins within complex samples, which is essential for comprehensive proteomic profiling. Additionally, the data generated by DIA are more comprehensive and consistent, facilitating robust downstream data analysis and integration with multi-omics datasets. This consistency also improves the reproducibility of results across different experiments and laboratories. DIA proteomics effectively addresses the challenges associated with DDA, such as the stochastic nature of peptide selection and the difficulty in reproducibly quantifying low-abundance proteins. By ensuring that all peptides within each m/z window are systematically analyzed, DIA enhances the depth and reliability of proteomic studies.
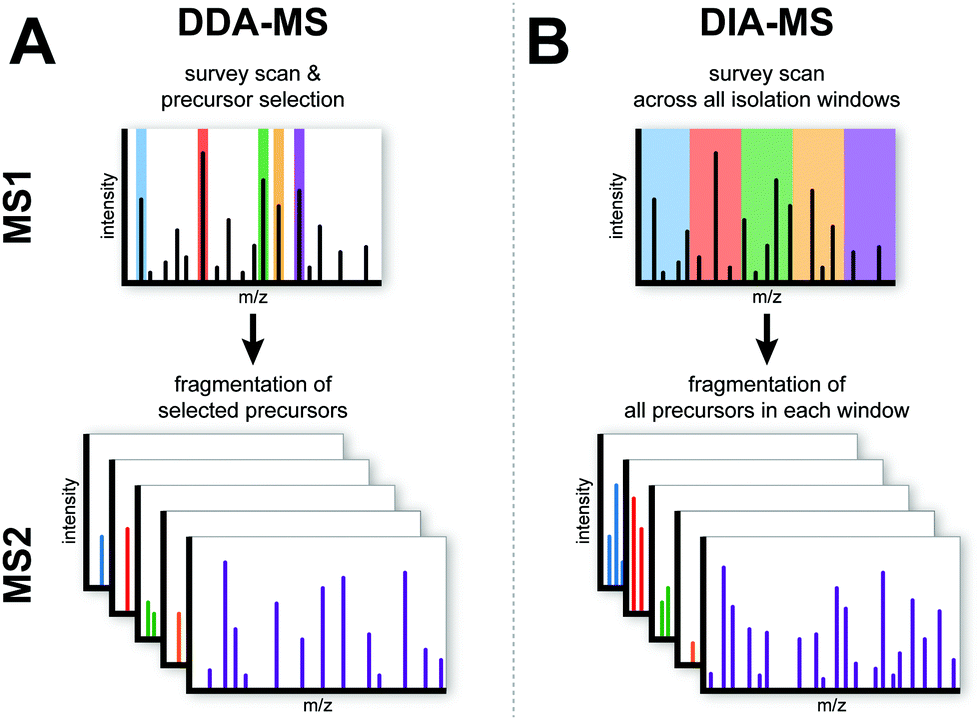
Krasny L, et al. Mol Omics. 2021.
Figure 2. Comparision Between DIA and DDA
However, broader adoption of DIA still requires the development of robust data analysis tools to handle the complex MS/MS spectra generated, as multiple peptides are fragmented simultaneously within each window. As these analytical challenges are overcome, DIA proteomics is poised to become a cornerstone technique in proteomics, enabling researchers to tackle more intricate biological questions with greater confidence and precision.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. We have established a powerful and professional DIA proteomics platform, which includes Thermo Fisher Q Exactive HF and Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass analyzer system, coupled with Nano-LC system. Our DIA proteomics service can be used for protein identification, quantification, and PTM analysis, providing the most comprehensive support for our clients. If you are interested in our service, please contact us freely.
Analysis Workflow
DIA Proteomics begins with protein extraction and enzymatic digestion of the sample, where proteins are broken down into peptides. These peptides are then ionized and introduced into the mass spectrometer. During Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA), the mass spectrometer systematically scans the entire mass-to-charge (m/z) range using predefined m/z windows and simultaneously fragments all precursor ions within each window. This process generates complex MS/MS spectra that contain detailed information about all peptides present in the sample. To accurately interpret these complex spectra and identify specific peptides, DIA Proteomics relies on the assistance of spectral libraries. A spectral library contains mass spectrometric and chromatographic parameters for each peptide, such as precursor and fragment m/z values, fragment types, charge states, and elution times. This information is used to match and deconvolute the experimental data, enabling precise identification and quantification of proteins.
Figure 3. The Workflow of DIA Proteomics
In recent years, the establishment and publication of comprehensive reference spectral libraries for multiple organisms have significantly enhanced the efficiency and reproducibility of this technology. By utilizing these extensive spectral libraries, DIA Proteomics not only resolves issues related to protein coverage and quantitative consistency but also greatly improves analysis efficiency and the reliability of results. This makes DIA Proteomics highly promising for large-scale proteomic studies, including the exploration of disease mechanisms and the discovery of biomarkers. The widespread availability of comprehensive spectral libraries has expanded the application prospects of DIA Proteomics, enabling more reliable and in-depth protein expression analysis across various research fields.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Mass Spectrometers
MtoZ Biolabs utilizes high-resolution Quadrupole Time-of-Flight (QTOF) or hybrid Quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometers ensures efficient capture of all peptide information in complex biological samples, providing high-quality data.
2. Efficient Data Processing
With advanced bioinformatics tools and a professional data analysis team, MtoZ Biolabs efficiently handles complex MS/MS data, providing reliable quantitative results and in-depth protein expression analysis.
3. Suitable for Large-Scale Proteomic Studies
MtoZ Biolabs' DIA proteomics support biomarker discovery, disease mechanism research, and drug target validation, meeting the demands of large-scale, high-throughput studies and facilitating breakthrough advancements in research projects.
4. Professional Technical Support
Providing comprehensive technical support from experimental design to data interpretation, MtoZ Biolabs ensures that clients’ research progresses smoothly and achieves high-quality scientific outcomes.
Applications
1. DIA Proteomics Advances Clinical and Biological Research
Fröhlich, K. et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024.
2. Common Applications of DIA Proteomics in Oncology
Krasny L, et al. Mol Omics. 2021.
FAQ
Q1: Are DIA Proteomics and SWATH Proteomics the Same? What Are Their Differences or Relationship?
Answer: DIA is a mass spectrometry strategy used in proteomics research, contrasting with DDA, which is a more traditional mass spectrometry approach. A key characteristic of DIA is that during the mass spectrometry analysis, it performs full-scan acquisitions across predefined window widths rather than selecting specific precursor ions for analysis based on their predicted abundance, which enables DIA to achieve a more comprehensive coverage of the proteome composition.
SWATH (Sequential Windowed Acquisition of all Theoretical fragment ions), developed by AB SCIEX, is a specific implementation of the DIA. SWATH enhances mass spectrometry data coverage and reproducibility by dividing the entire m/z values into multiple consecutive windows and cyclically acquiring data from each window.
In fact, SWATH can be considered an instance of DIA. Their relationship is analogous to a general concept (DIA) and its specific implementation (SWATH). Both DIA and SWATH aim to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of proteomics research by acquiring more comprehensive mass spectrometry data.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Relevant Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Parameters
4. The Detailed Information of Proteomics
5. Mass Spectrometry Image
6. Raw Data
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
DIA based Protein Quantitative Service
How to order?







