DIA/SWATH-Based Quantitative PTM Analysis Service
DIA/SWATH-based quantitative PTM analysis is a post-translational modification (PTM) quantification technique based on data-independent acquisition (DIA) and sequential window acquisition of all ions (SWATH-MS) technologies. Unlike traditional DDA (Data-Dependent Acquisition), the DIA/SWATH technology does not select specific precursor ions during the mass spectrometry acquisition process. Instead, it systematically fragments all peptide segments within preset m/z windows, enabling full scan, unbiased high-throughput acquisition. Combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms and specific modification peptide enrichment strategies, this technique can sensitively identify and accurately quantify various PTM types, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, and more.
DIA/SWATH-based quantitative PTM analysis service is widely used in signal pathway regulation studies, disease biomarker screening, drug mechanism analysis, and protein dynamic modification research. It is particularly suitable for research projects requiring large sample sizes, multiple comparisons, and high quantitative reproducibility. DIA/SWATH technology, with its high coverage and stable quantitative ability, provides strong support for building comprehensive PTM maps and conducting systems biology research.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms, MtoZ Biolabs' DIA/SWATH-based quantitative PTM analysis service enables comprehensive quantification of various post-translational modifications (PTMs), including phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, and ubiquitination. This service combines specific modification enrichment with the DIA/SWATH high-throughput data acquisition strategy to provide high coverage and reproducible quantitative data for modification sites. The output includes modification peptide sequences, spectra, site localization, and changes in modification abundance across different groups, aiding mechanism research, drug efficacy evaluation, and biomarker screening.
Analysis Workflow
1. Protein Extraction and Digestion
Target proteins are extracted from cells, tissues, or purified samples, reduced and alkylated, followed by digestion with trypsin to generate peptides suitable for mass spectrometry analysis, preserving post-translational modification information.
2. Specific Modification Enrichment
Based on the target PTM type (e.g., phosphorylation, acetylation), TiO₂, IMAC, antibody affinity, and other enrichment strategies are used to enhance the detection of low-abundance modified peptides.
3. DIA/SWATH Mass Spectrometry Detection
High-resolution DIA/SWATH mode is used for unbiased full-scan acquisition, recording all ion pairs comprehensively to ensure high reproducibility and coverage of the data.
4. Data Analysis and Quantitative Analysis
Professional software (e.g., Spectronaut, DIA-NN, etc.) is used for peptide identification, modification site localization, and quantitative analysis. The output includes modification abundance, spectral data, and differential analysis results, supporting subsequent functional annotation and mechanism studies.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Supports various sample forms, including cells, tissues, serum/plasma, bodily fluids, and purified proteins. It is recommended to provide fresh or frozen samples with sufficient protein expression levels to ensure effective detection of modified peptides.
2. Buffer Requirements
Avoid using buffers containing SDS, glycerol, EDTA, DTT, or other components that may interfere with enzymatic digestion or mass spectrometry analysis. MS-compatible buffers are recommended. If specific buffers are used, please communicate with the technical staff for confirmation.
3. Sample Storage and Transportation
Samples should be stored at –80°C and transported on dry ice with a cold chain. Repeated freeze-thaw cycles must be avoided to prevent protein degradation and modification loss. For liquid samples, it is recommended to submit them in freeze-dried or concentrated form to improve stability and detection efficiency.
Service Advantages
1. High-throughput Comprehensive Detection
The DIA/SWATH mode collects MS/MS data for all ionizable peptides in the entire sample, achieving panoramic capture of various post-translational modifications (PTMs) with broad coverage, and no dependence on precursor selection.
2. Excellent Quantitative Consistency
By using a unified scanning window and unbiased acquisition strategy, the reproducibility and comparability of quantification across different batches and samples are significantly improved, making it especially suitable for time-series or multi-omics integration studies.
3. High Sensitivity for Modification Site Identification
Combining targeted data analysis algorithms with high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms, this service can accurately identify low-abundance modification peptides and sites, especially useful for complex backgrounds or early signaling event monitoring.
4. Supports Data Re-mining
Data collected in one run can be re-analyzed, updated in the database, or used to identify new modification sites without the need for re-instrumentation, allowing for continuous expansion of research depth and scope.
Applications
1. Signal Pathway Regulation Research
DIA/SWATH-based quantitative PTM analysis service can quantitatively analyze the modification changes in key molecules such as kinase substrates and transcription factors, revealing the dynamic regulatory mechanisms in complex signaling pathways.
2. Disease Mechanism Exploration
By constructing post-translational modification maps under different pathological states, this service helps to uncover abnormal modification events related to tumors, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, etc., assisting in mechanism research and target discovery.
3. Drug Mechanism Evaluation
DIA/SWATH-based quantitative PTM analysis service can compare the modification level changes in pre- and post-treatment samples, evaluating the impact of drugs on signaling regulation or metabolic pathways, and supporting functional validation of candidate drugs and target screening.
4. Multi-Omics Integration Analysis
By combining transcriptomic, metabolomic, and other data, this service systematically analyzes the relationship between modification changes and transcriptional regulation, metabolic reprogramming, constructing multi-dimensional regulatory networks to expand research depth.
Case Study
1. Quantification of Lysine Acetylation and Succinylation Stoichiometry in Proteins Using Mass Spectrometric Data-Independent Acquisitions (SWATH)
This study aims to quantitatively assess the stoichiometry of lysine acetylation and succinylation modifications in proteins using Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA/SWATH) mass spectrometry technology, enhancing the accuracy and throughput of post-translational modification (PTM) quantification. The study focused on total protein from human cell lysates, employing chemical labeling to distinguish modified and unmodified peptides, and constructing an ion library containing both. SWATH-MS was used to perform site-level quantitative analysis. The results demonstrate that this method accurately distinguishes and quantifies multiple PTM sites with excellent sensitivity, reproducibility, and dynamic range, making it suitable for high-throughput PTM stoichiometry research in complex samples. The study concludes that this strategy provides a powerful quantitative tool for elucidating the biological significance of modifications such as acetylation and succinylation in cellular function regulation.
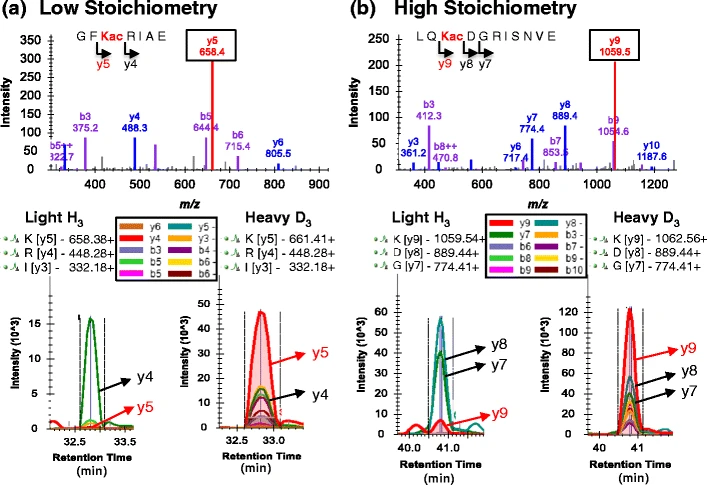
Meyer, J G. et al. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2016.
Figure 1. Lysine Acetylation Site Occupancy Examples from E. coli Whole Cell Lysate.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation
4. Bioinformatics Analysis
5. Raw Data Files
FAQ
Q1: What Advantages Does DIA/SWATH Have Over DDA?
A1: DIA/SWATH is a full-scan, data-independent acquisition method that repeatedly captures all peptide signals, avoiding the missed detection issue inherent in DDA's random sampling. It offers higher data reproducibility and more accurate modification quantification, making it especially suitable for multi-sample comparisons and low-abundance PTM analysis.
Q2: What Quantitative Analyses Can Be Performed with DIA Data?
A2: This service supports Label-Free relative quantification, allowing for accurate comparison of modification abundance changes between different treatment groups, making it suitable for dynamic monitoring, drug efficacy evaluation, and other studies.
How to order?







