DIA MS (Data-Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry)-Based Quantitative Service
DIA MS (Data-Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry)-Based Quantitative Service utilizes next-generation proteomics technology to enable comprehensive, reproducible, and high-throughput protein quantification. Unlike Data-Dependent Acquisition (DDA), which stochastically selects precursor ions for fragmentation, DIA systematically fragments all ions within a given m/z range, ensuring consistent and deep proteome coverage across multiple conditions. The DIA-MS-based quantitative method enhances quantification accuracy, and enables high-throughput, large-scale studies in biomedical and clinical research.
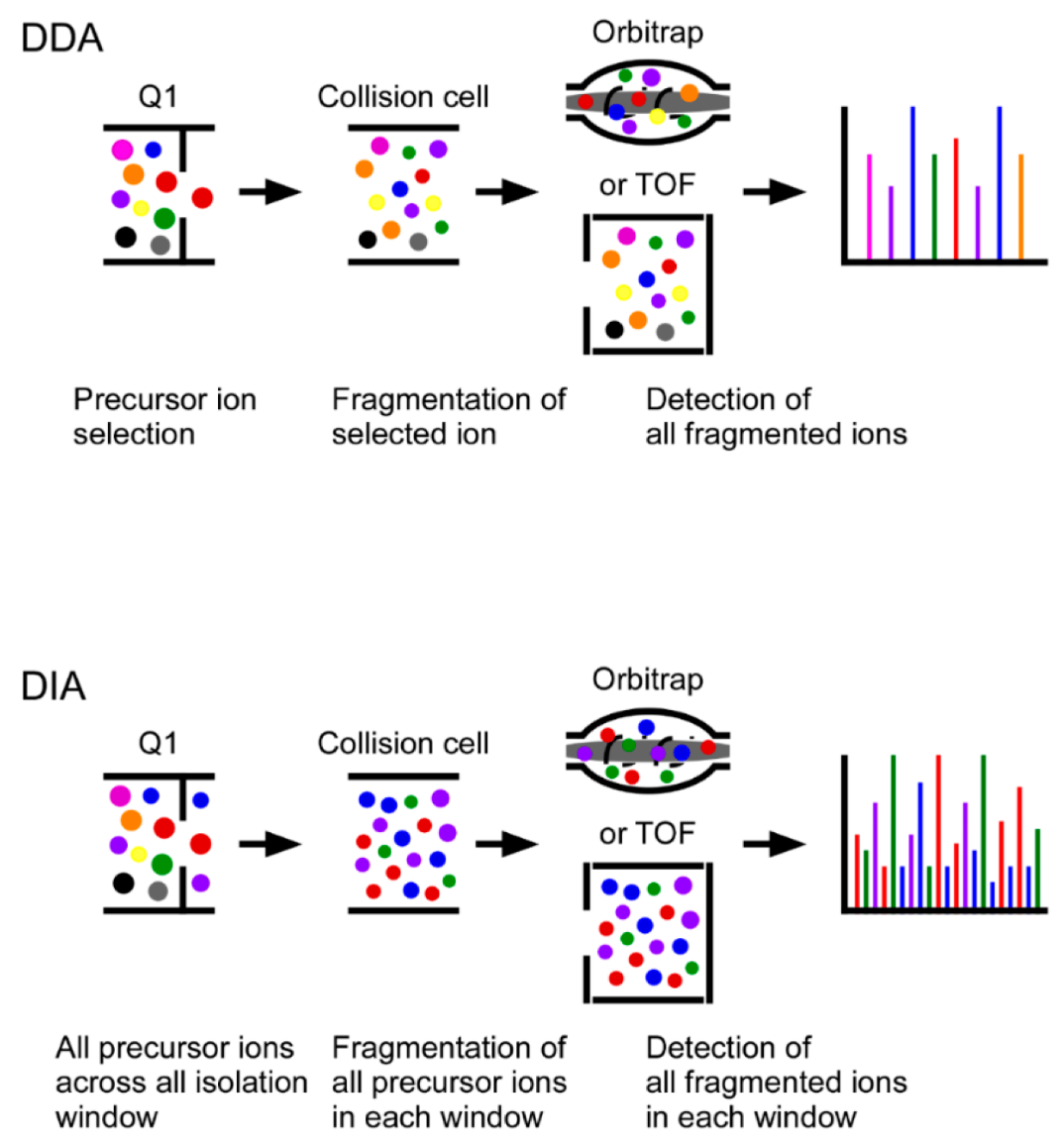
Figure 1. Principles of Data-Dependent Acquisition (DDA) and Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) in Untargeted Quantitative Proteomics
In phosphoproteomics, precise quantification of phosphorylation events is essential for understanding cell signaling, kinase activity, and disease mechanisms. DIA-MS outperforms DDA-MS by detecting low-abundance phosphorylated peptides with higher accuracy and reproducibility. MtoZ Biolabs offers a DIA MS (Data-Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry)-Based Quantitative Service that integrates optimized phosphopeptide enrichment, high-resolution LC-MS/MS, and advanced bioinformatics to deliver reliable phosphorylation site quantification. Whether investigating kinase-substrate interactions, drug responses, or phosphorylation-based biomarkers, the DIA MS (Data-Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry)-Based Quantitative Service provides the precision and scalability needed for cutting-edge phosphoproteomic research.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation: Extract proteins, quantify concentration, and enzymatically digest into peptides.
2. Phosphopeptide Enrichment: Phosphorylated peptides are selectively enriched using IMAC, TiO₂, or antibody-based methods to improve detection sensitivity.
3. LC-MS/MS Analysis: Peptides are separated by liquid chromatography (LC) and analyzed using DIA-MS, where all precursor ions are fragmented simultaneously, ensuring comprehensive phosphopeptide detection with high reproducibility.
4. Spectral Library Generation and Data Processing: Custom DIA-specific spectral libraries and bioinformatics algorithms enable precise phosphorylation site identification and quantification.
5. Bioinformatics Analysis and Functional Interpretation: Phosphorylation sites are mapped to kinases, signaling pathways, and regulatory networks, with statistical analysis providing biological insights.
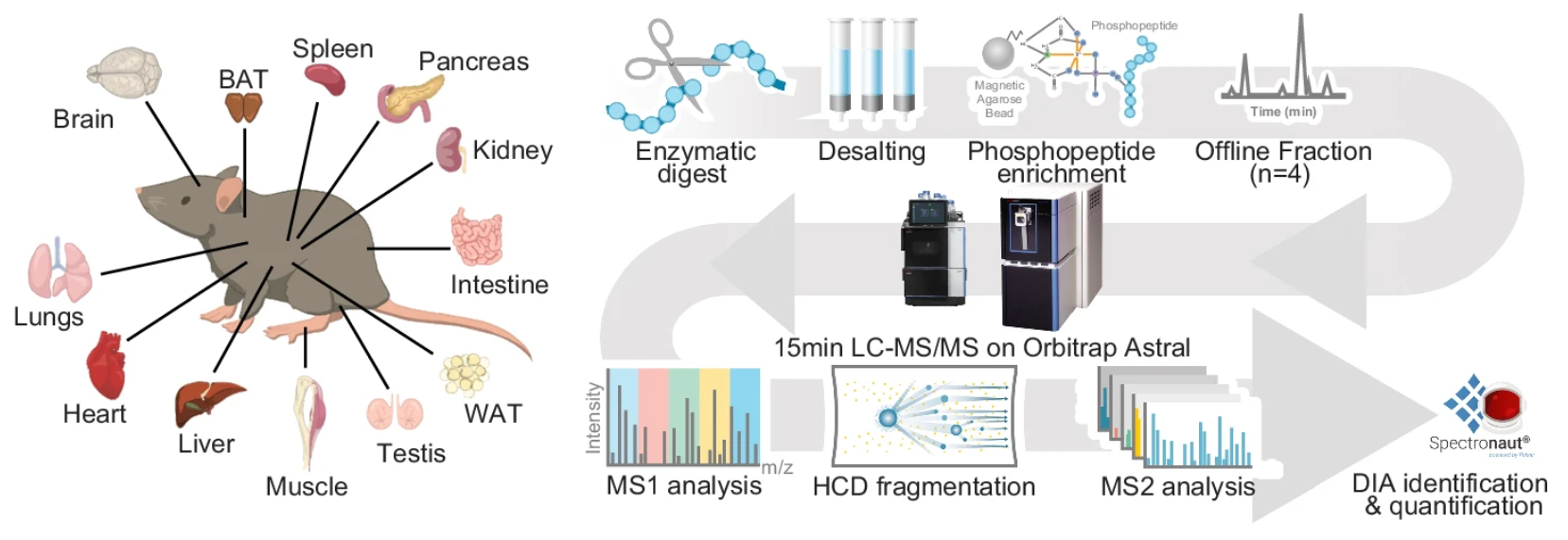
Figure 2. Workflow of DIA MS (Data-Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry)-Based Quantitative Service
Service Advantages
✅DIA provides unbiased, comprehensive scans, ensuring greater protein resolution and fewer missing values than DDA and standard LFQ methods.
✅Achieves quantitative precision comparable to PRM, enabling reliable phosphorylation site quantification across different experimental conditions.
✅Captures low-abundance phosphorylation sites with high sensitivity, ensuring deep phosphoproteomic profiling.
✅Suitable for analyzing blood, exosomes, FFPE tissues, urine, and other disease-relevant samples, supporting diverse biomedical research.
Applications
1. Biomarker Discovery and Validation
DIA MS enables precise quantification of phosphorylation-based biomarkers, facilitating early disease detection, prognosis, and patient stratification.
2. Tumor Subtype Classification
By profiling phosphorylation signatures across tumor samples, DIA MS-Based Quantitative Service helps classify tumor subtypes, guiding personalized oncology treatments.
3. Drug Mechanism and Response Studies
DIA MS quantifies phosphorylation changes in drug-treated samples, providing insights into kinase inhibitor efficacy, off-target effects, and resistance mechanisms. This data-driven approach supports drug development by monitoring dynamic phosphorylation alterations in response to targeted therapies.
4. Personalized Medicine and Treatment Optimization
DIA MS-Based Quantitative Service provides quantitative phosphorylation profiling for individualized treatment strategies, enabling clinicians to tailor targeted therapies based on a patient’s unique phosphoproteomic signature. It aids in treatment monitoring and response prediction to improve clinical outcomes.
5. Comparative Studies in Agriculture and Forestry
DIA MS-Based Quantitative Service enables researchers to systematically analyze protein expression patterns in crops, trees, and other plant species. By leveraging DIA technology, researchers can generate large-scale proteomic datasets to study stress resistance, trait improvement, and genetic adaptation, advancing sustainable agriculture and forestry management.
Case Study
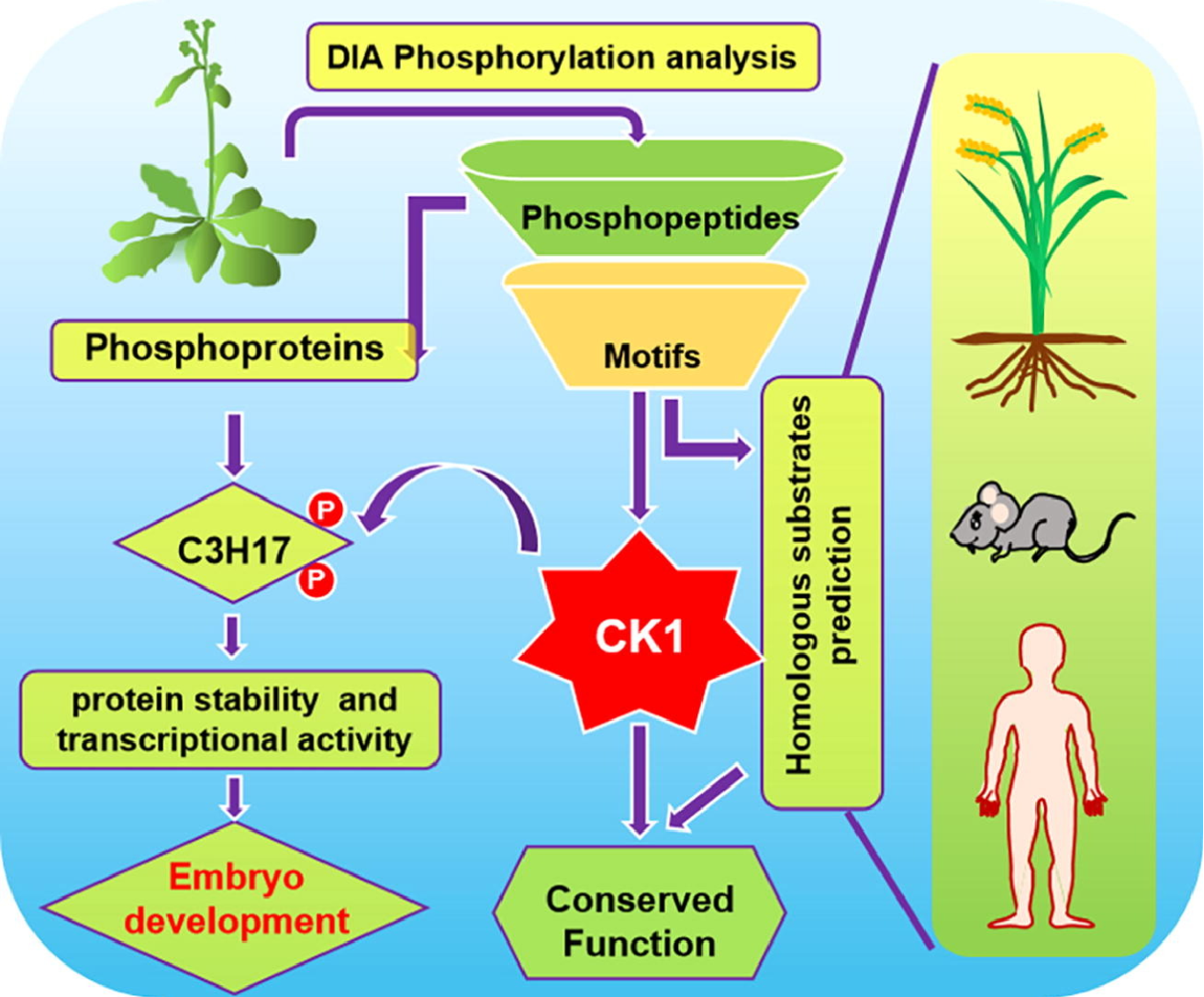
DIA-MS-Based Quantitative Phosphoproteomics for CK1 Substrate Identification
Casein kinase 1 (CK1) plays a crucial role in phosphorylation-mediated signaling pathways across eukaryotes. To systematically identify CK1 substrates, researchers employed DIA-MS-based quantitative phosphoproteomics, analyzing phosphopeptide abundance in Arabidopsis seedlings overexpressing or lacking specific AEL CK1 isoforms. By comparing phosphopeptide profiles between wild-type, overexpression, and mutant lines, researchers identified 3,985 upregulated phosphopeptides and 1,032 phosphoproteins associated with CK1 activity. Motif enrichment analysis revealed eight conserved CK1 phosphorylation motifs, enabling the prediction of novel substrates, including C3H17, a CCCH-type zinc finger transcription factor. Biochemical validation confirmed CK1-mediated phosphorylation stabilizes C3H17, enhancing its transactivation function in embryogenesis. Extending motif searches to rice, mouse, and human proteomes uncovered numerous potential CK1 substrates, demonstrating the power of DIA-MS for cross-species phosphoproteome mapping. This study highlights the high sensitivity and reproducibility of DIA-MS-based phosphoproteomics in unraveling kinase-substrate networks and regulatory mechanisms, offering valuable insights into plant and human signaling pathways.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
MtoZ Biolabs' DIA MS (Data-Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry)-Based Quantitative Service delivers reproducible, publication-ready data to drive innovative research and clinical advancements. Connect us to explore custom solutions tailored to your scientific goals.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Data-Dependent Acquisition Service
How to order?







