What Is the Difference Between HRMS and LC-MS?
- LC-Orbitrap platform: suitable for untargeted metabolomics and lipidomics research
- LC-QTOF system: designed for high-accuracy metabolite identification and compositional analysis
- LC-QQQ platform (MRM mode): widely employed for targeted quantitative analysis
- Multidimensional data analysis support: offering one-stop solutions from raw spectral interpretation to KEGG pathway enrichment
High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) are among the most widely used techniques in modern analytical chemistry and life sciences. HRMS and LC-MS are not mutually exclusive but represent technical frameworks defined from different perspectives, with potential overlap (e.g., HRMS combined with LC = LC-HRMS). Clarifying their distinctions helps researchers select the most suitable analytical strategy according to experimental objectives.
HRMS vs. LC-MS
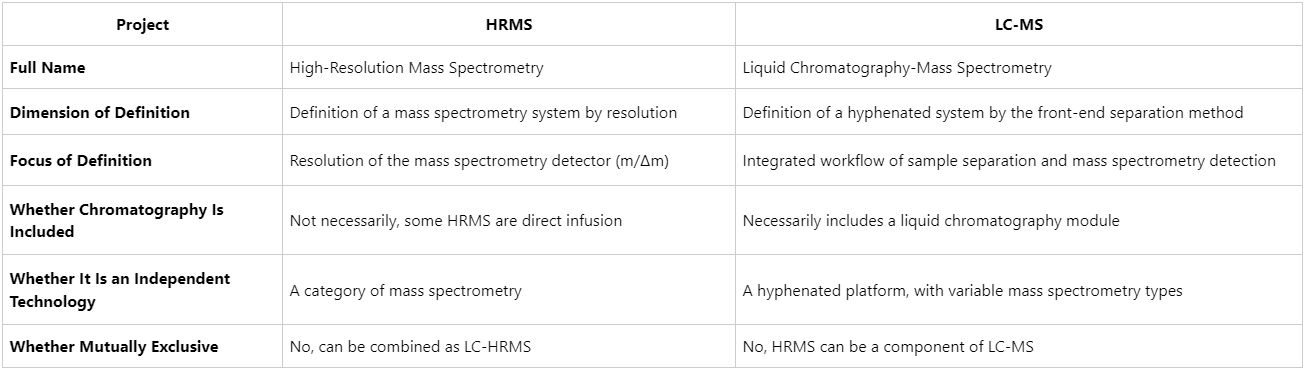
HRMS: Technical Characteristics of High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
1. What Is High Resolution?
A high-resolution mass spectrometer refers to an instrument with an exceptionally high resolving power (typically ranging from 10,000 to 1,000,000 FWHM), capable of differentiating ions with nearly identical masses. For instance, it can distinguish between C₃H₉N (59.0735 Da) and C₂H₇O₂ (59.0491 Da), which are structurally similar species.
2. Common HRMS Instrument Types
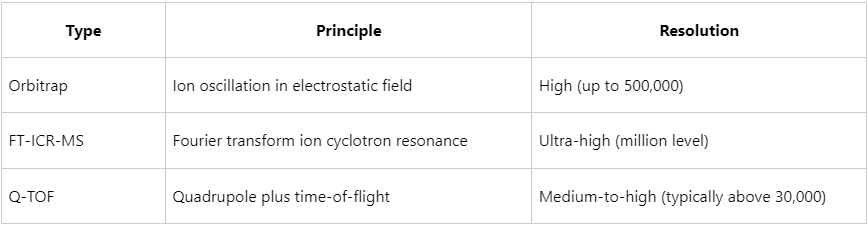
3. Advantages of HRMS
(1) Provides exact molecular mass for reliable molecular formula inference
(2) Enables precise identification of metabolites, pharmaceuticals, and protein modifications
(3) Supports untargeted metabolomics, lipidomics, and proteomics studies
(4) Facilitates structural elucidation when combined with MS/MS approaches (e.g., DDA, DIA modes)
LC-MS: The Technical Framework of Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
1. What Is LC-MS?
LC-MS integrates liquid chromatography (LC) with mass spectrometry (MS) in an online fashion, enabling a workflow of separation followed by detection. LC is responsible for separating complex sample components, whereas MS detects each component at its retention time.
2. Components of LC-MS
(1) Liquid chromatography system: including solvent pump, injector, and chromatographic column, responsible for sample separation
(2) Interface (e.g., ESI source): ionizes liquid samples into ions
(3) Mass spectrometer detector: records the mass information of each component, which may be acquired using either HRMS or low-resolution MS
3. Advantages of LC-MS
(1) Directly applicable to the analysis of complex samples (e.g., plasma, tissue, urine)
(2) Enhances qualitative and quantitative reliability through dual confirmation of retention time and m/z
(3) Compatible with diverse MS platforms, including triple quadrupole, QTOF, and Orbitrap
(4) Widely utilized in metabolomics, pharmacokinetics, food safety, and environmental monitoring
Application Scenarios of HRMS and LC-MS
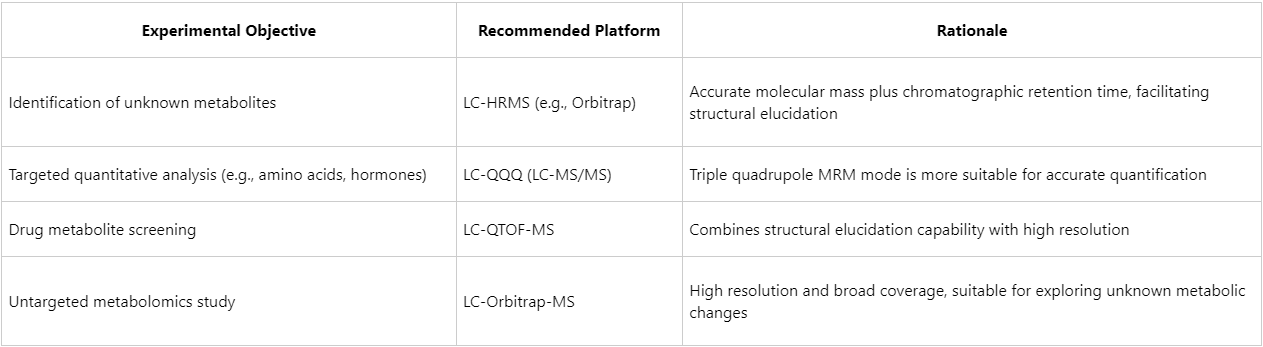
Importantly, HRMS does not exclude LC-MS; instead, they can be combined into a single analytical platform: LC-HRMS = liquid chromatography + high-resolution mass spectrometry. This integrated platform has become a standard in metabolomics, lipidomics, and the study of protein post-translational modifications.
MtoZ Biolabs has established multiple LC-MS platform configurations to meet diverse research requirements, ranging from high-throughput screening to high-precision structural characterization:
For researchers considering HRMS and LC-MS in sample analysis, MtoZ Biolabs provides tailored technical pathways and customized solutions to best support scientific objectives.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







