What Is LC-MS Molecular Weight Analysis? Applicable Targets, Methodologies, and Comparative Evaluation
- Liquid chromatography (LC) separates individual components based on differences in physicochemical properties.
- Mass spectrometry (MS) subsequently ionizes each eluting component and measures its mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), from which the accurate molecular mass can be determined.
- Verification of whether the expressed product exhibits the expected molecular mass.
- Assessment of the presence of post-translational modifications, such as glycosylation or acetylation.
- Monitoring of isoforms, degradation products, and aggregation states.
- Confirmation of structural integrity following chemical synthesis.
- Detection of residual intermediates or side products.
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative molecular characterization.
- Peptide molecules below 10 kDa are well suited for rapid molecular weight confirmation using ESI-MS or MALDI-MS.
- Antisense oligonucleotides and siRNA can likewise be analyzed by LC-MS to assess molecular integrity and modification status.
- High-throughput profiling of thousands of metabolite or lipid species.
- Provision of accurate molecular formula information to support compound identification and functional interpretation.
- Frequently combined with online or offline desalting procedures, such as C4 or C18-based sample preparation.
- Electrospray ionization (ESI) is utilized to accommodate the multiple-charge states characteristic of large biomolecules.
- Computational deconvolution algorithms are applied to derive the intact molecular mass.
- Gradient-elution liquid chromatography is used to resolve components prior to detection.
- High-resolution mass spectrometers, including TOF, Orbitrap, and Q-Exactive platforms, are commonly employed.
- This approach is well suited for screening molecular mass features within complex sample backgrounds.
- Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) enables direct sample ionization and detection.
- This method is particularly suitable for rapid and high-throughput molecular weight confirmation.
Molecular weight represents one of the most fundamental and critical physicochemical parameters of biomolecules. Across diverse life science disciplines, including protein engineering, antibody drug development, synthetic compound validation, and metabolomics, accurate molecular weight determination serves not only as a prerequisite for structural characterization but also as a cornerstone for quality control and functional investigation. Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS), characterized by high sensitivity, high throughput, and the capacity to resolve molecular species across wide mass ranges within complex samples, has increasingly emerged as a mainstream analytical platform in both academic research and the biopharmaceutical industry.
What Is LC-MS Molecular Weight Analysis?
LC-MS molecular weight analysis refers to an integrated analytical approach in which liquid chromatographic separation is coupled with mass spectrometric detection to achieve separation, detection, and molecular mass determination of target analytes in complex samples. Specifically:
In contrast to conventional ultraviolet detection or gel electrophoresis methods, LC-MS does not rely on specific dyes or predefined standards, enabling precise characterization of unknown structures and low-abundance analytes.
Applicable Targets of LC-MS Molecular Weight Analysis
LC-MS is broadly applicable to organic molecules and biomacromolecules with molecular weights ranging from approximately 100 Da to several hundred kilodaltons. Typical application targets include:
1. Recombinant Proteins and Antibody Drugs
2. Synthetic Small Molecules and Chemical Compounds
3. Peptide and Nucleic Acid Therapeutics
4. Metabolomics and Lipidomics
Common Methodologies for LC-MS Molecular Weight Analysis
Distinct analytical objectives and sample characteristics necessitate different LC-MS workflows. Currently, several representative strategies are widely employed:
1. Desalting Plus ESI-MS Analysis (Applicable to Proteins and Peptides)
Advantages: High sensitivity and accurate mass determination.
Limitations: Sensitivity to salt concentration, requiring careful optimization of sample buffers.
2. Full-Scan LC-MS Analysis (Applicable to Complex Mixtures)
Advantages: High throughput and suitability for exploratory or unknown sample analysis.
Limitations: Dependence on database-assisted interpretation and relatively longer analysis times.
3. MALDI-TOF Molecular Weight Analysis (Applicable to Small Molecules and Peptides)
Advantages: Fast analytical speed and strong tolerance to salts.
Limitations: Limited applicability to high-molecular-weight proteins and potential ionization heterogeneity affecting quantitative performance.
LC-MS Molecular Weight Analysis Versus Other Molecular Weight Determination Methods
A comparative overview of commonly used molecular weight determination techniques relative to LC-MS is summarized below:
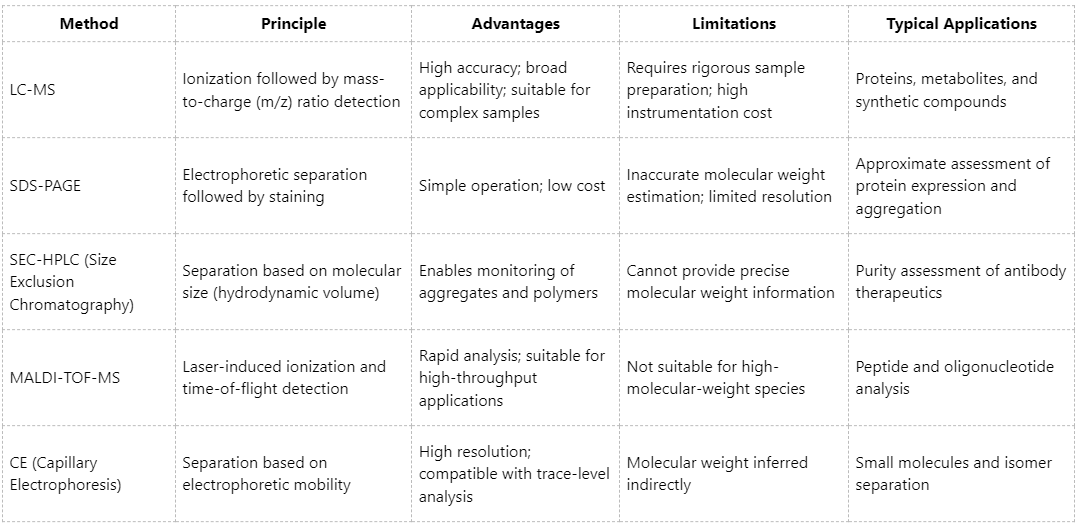
Overall, although LC-MS is not universally optimal for all analytical scenarios, it provides unparalleled advantages in accurate molecular mass determination, complex sample characterization, and high-resolution qualitative analysis.
How Does MtoZ Biolabs Perform LC-MS Molecular Weight Analysis Services?
At MtoZ Biolabs, high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry platforms, including Q-Exactive HF-X and Exploris 480 systems, are integrated with diverse sample preparation workflows to deliver sensitive, rapid, and customizable molecular weight analysis services for both academic researchers and biopharmaceutical enterprises.
The service supports a wide range of sample types, including proteins, peptides, synthetic small molecules, and oligonucleotides. Comprehensive workflows encompassing sample desalting, buffer exchange, and deconvolution-based data processing are provided. Standardized analytical reports include total ion chromatograms (TIC), m/z spectra, and deconvoluted mass results, with optional integration of protein N-terminal/C-terminal sequencing and glycosylation analysis services.
LC-MS molecular weight analysis has become an accurate, efficient, and scalable analytical standard in contemporary life science research and industrial applications. Its performance across diverse molecular classes and complex sample matrices significantly surpasses the limitations of traditional methodologies. Whether applied to fundamental research validation or quality control in drug development, LC-MS represents a critical tool for enhancing data reliability and experimental efficiency. Researchers seeking professional, high-throughput molecular weight analysis services are encouraged to contact MtoZ Biolabs, where advanced instrumentation and rigorous data interpretation support reliable scientific advancement.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







