What Is DIA and SWATH? Understanding Data-Independent Acquisition in Proteomics?
-
Unbiased acquisition with comprehensive coverage: Enables detection of low-abundance proteins;
-
Fixed acquisition logic and high reproducibility: Suitable for large-scale sample analysis;
-
Complete spectral recording for retrospective analysis: Extends the usable life of acquired data.
-
Continuous window coverage with no acquisition gaps;
-
Mature platform with robust algorithmic support (e.g., OpenSWATH, PeakView, Spectronaut);
-
Effective for highly complex sample types such as plasma and tumor tissues;
-
Extensively applied in translational clinical research and large-scale multicenter cohort studies.
Mass spectrometry is a core technology in modern proteomics research. The choice of acquisition strategy critically influences data coverage, reproducibility, and quantitative accuracy. In recent years, Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) has rapidly gained prominence and is increasingly considered a mainstream alternative to Data-Dependent Acquisition (DDA). Within the DIA framework, the most widely recognized implementation is SWATH-MS (Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Spectra). This article provides a systematic overview of the principles, distinctions, advantages, and representative applications of DIA and SWATH in both basic and clinical research.
What Is DIA?
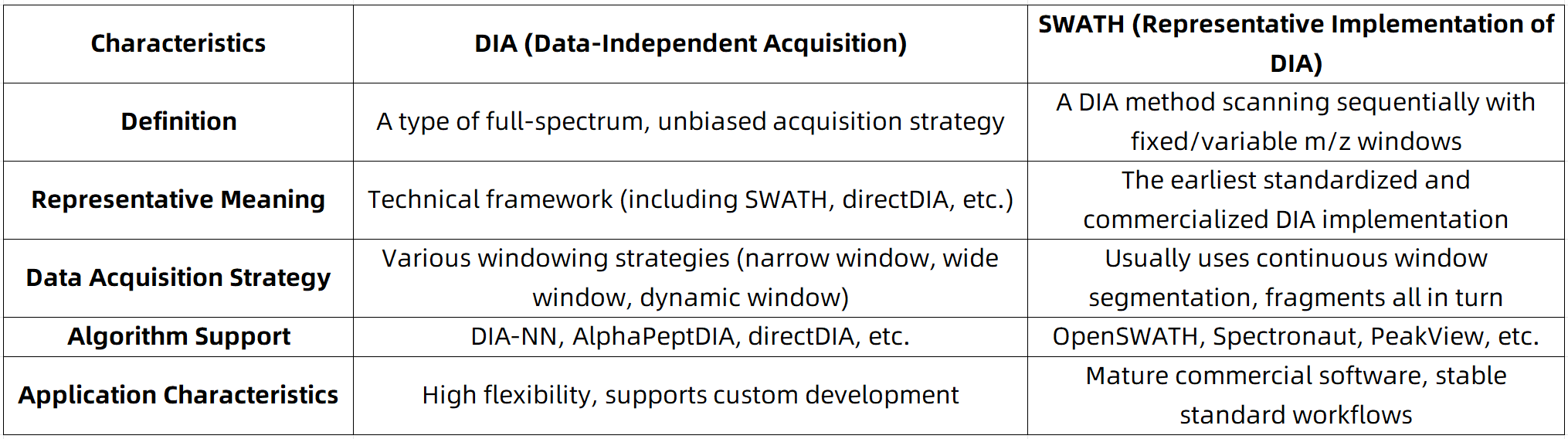
Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) refers to a class of mass spectrometry acquisition strategies characterized by systematically scanning across the entire m/z range, rather than selectively fragmenting precursor ions based on real-time intensity, as in traditional DDA methods. Unlike DDA, which typically targets only the top N most intense precursor ions, DIA follows a comprehensive “all-ion” scanning approach, enabling more extensive and reproducible MS/MS data collection.
Key advantages of DIA include:
What Is SWATH?
SWATH-MS represents the first standardized and commercially available implementation of DIA. The method involves dividing the instrument's scanning range (e.g., 400–1200 m/z) into multiple windows of equal or variable widths (e.g., 25 Da). All precursor ions within each window are fragmented simultaneously, and the spectra of all resulting fragment ions are recorded.
Distinct advantages of SWATH include:
Relationship and Differences Between DIA and SWATH
Technical Advantages of DIA/SWATH
1. Comprehensive Spectral Acquisition Ensuring Complete Signal Coverage
Both the library-free strategy in DIA and the window-based acquisition in SWATH enable exhaustive coverage of precursor ions, markedly enhancing the detection sensitivity for low-abundance proteins.
2. High Reproducibility Suitable for Large-Scale Studies
By employing predefined scanning schemes, DIA/SWATH avoids the variability inherent in DDA’s stochastic sampling, thereby ensuring consistent data across samples and batches. This makes the approach particularly well-suited for multi-center and long-term cohort investigations.
3. Reanalyzable Datasets that Maximize Research Value
As fragment ion data are recorded comprehensively, DIA/SWATH datasets can be reanalyzed retrospectively without requiring additional instrument time, thereby significantly improving data utility and research efficiency.
Representative Application Scenarios
1. Proteomics of Tumor Tissues
SWATH-based quantification demonstrates outstanding stability and cross-sample comparability in tumor tissue analyses, supporting the discovery and validation of cancer-related biomarkers.
2. Mechanistic Studies of Drug Action
The full-spectrum acquisition capability of DIA facilitates systematic profiling of proteomic changes in response to pharmacological intervention, enabling the elucidation of dynamic signaling pathways and offering valuable insights for drug development.
3. High-Throughput Analysis of Complex Clinical Samples
For biologically complex specimens such as plasma and cerebrospinal fluid, SWATH offers superior data consistency and resistance to interference compared to DDA, making it ideal for constructing reliable clinical proteomics databases.
4. Large-Scale, Multi-Center Cohort Studies
The fixed acquisition design of SWATH-MS ensures data alignability and comparability across instruments and experimental batches, making it a preferred platform for large-scale, multi-institutional collaborative research.
DIA technology is propelling proteomics into a new paradigm characterized by comprehensiveness, high throughput, and reproducibility. Among various DIA implementations, SWATH stands out as the most mature and accessible solution, offering researchers a stable and robust entry point. MtoZ Biolabs integrates advanced mass spectrometry platforms with multidimensional data processing algorithms to deliver high-quality, SWATH-based quantitative proteomics services. Whether you are new to DIA or seeking enhanced data quality, MtoZ Biolabs is a reliable partner for your research endeavors.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







