Ultracentrifugation Molecular Weight Determination Service
Accurate molecular weight determination is essential in proteomics and biochemistry for understanding protein structure, function, and interactions—crucial factors in elucidating enzyme kinetics, designing effective drugs, and exploring cellular mechanisms. At MtoZ Biolabs, our Ultracentrifugation Molecular Weight Determination Service leverages the powerful technique of ultracentrifugation, which utilizes the principles of sedimentation under high gravitational forces to achieve precise molecular weight measurements. Our service employs two main approaches: sedimentation velocity and sedimentation equilibrium. Sedimentation velocity analyzes the rate at which particles move in a centrifugal field, providing detailed insights into their size and shape. Sedimentation equilibrium, on the other hand, measures the distribution of particles at equilibrium, enabling direct molecular weight calculations without the need for external standards.
Analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) offers significant advantages over conventional methods. It enables the analysis of samples in their native state, preserving functional conformations and interactions. This high-resolution technique can handle a wide range of biomolecules, from small peptides to large macromolecular complexes. Unlike methods requiring immobilization or labeling, AUC minimizes sample manipulation, reducing the risk of introducing artifacts or altering molecular behavior.
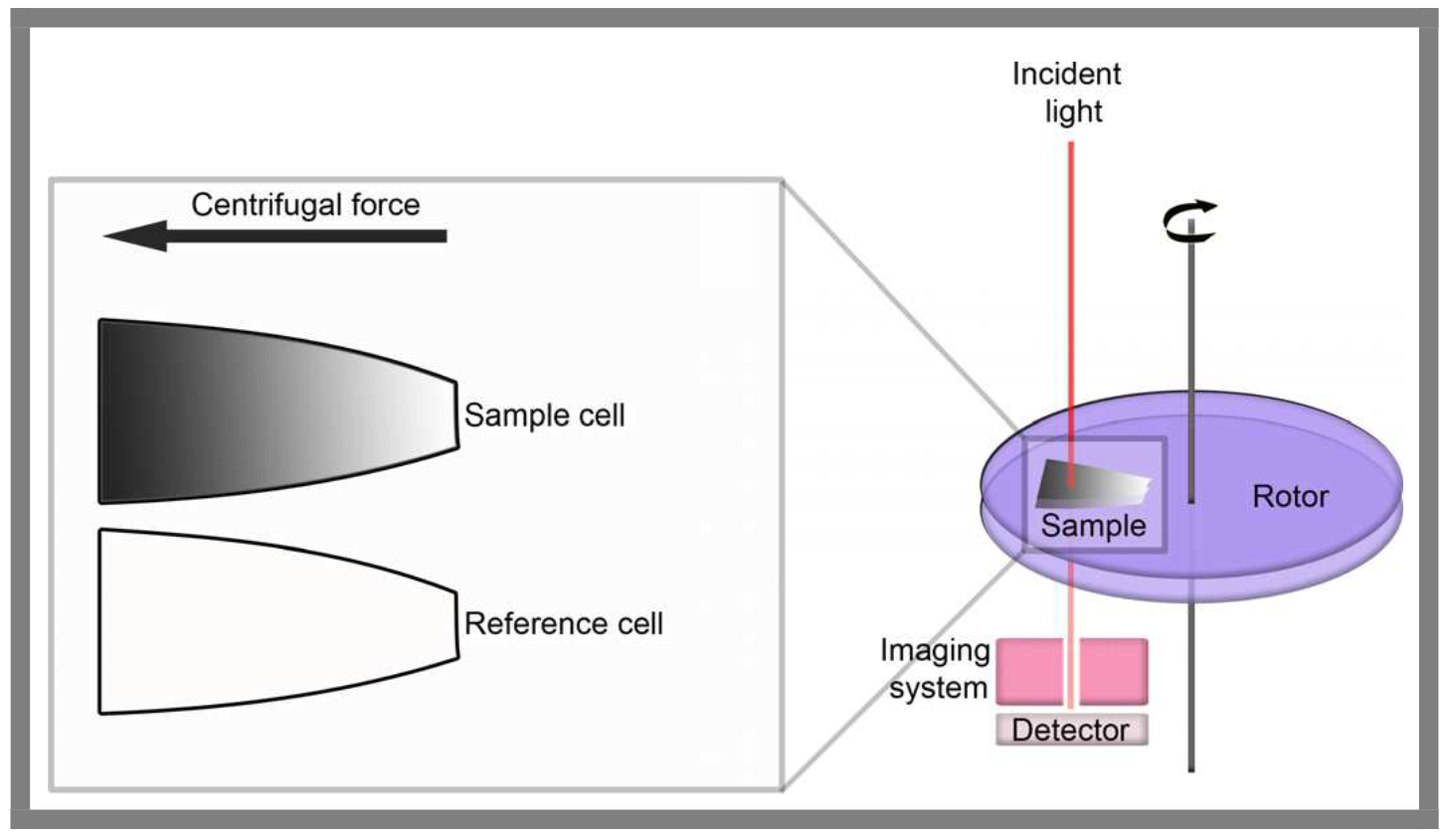
Figure 1. Illustration of The Principle Technology of Analytical Ultracentrifugation
Service Advantages
1. Advance Analysis Platform
MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Ultracentrifugation Molecular Weight Determination Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. One-Time-Charge
Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. High-Data-Quality
Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all ultracentrifugation molecular weight determination data providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
4. Minimal Sample Preparation
Reduce preparation time and avoid sample manipulation, minimizing the risk of introducing artifacts.
5. Non-Destructive Analysis
Preserve the integrity of your samples by analyzing them without alteration, allowing for further experiments and ensuring consistent results.
Applications
1. Protein Complex Characterization: Determine the composition and size of protein assemblies.
2. Biopharmaceutical Quality Control: Ensure purity and molecular weight accuracy of therapeutic proteins.
3. Enzyme Kinetics Studies: Investigate enzyme-substrate interactions and complex formations.
4. Antibody Characterization: Verify the molecular weight and integrity of monoclonal antibodies.
Case Study
1. Sedimentation Equilibrium Analysis of Hop Polyphenolic Extracts
Ultracentrifugation molecular weight determination was applied to analyze the molecular weight distribution of polyphenolic extracts from Saaz and Magnum hop varieties. Sedimentation equilibrium analytical ultracentrifugation (SE-AUC) was conducted at increasing speeds from 20,000 rpm to 40,000 rpm, allowing equilibrium at each step. The Saaz extract revealed three distinct peaks: a primary component at approximately 3 kDa (62% of total area), a secondary peak around 12 kDa (26%), and a minor high-molecular-weight component at 85 kDa (12%). In contrast, the Magnum extract displayed two peaks, with a major component at 5 kDa (97% of total area) and a smaller peak at 52 kDa (<3%). These findings demonstrate that the Saaz extract contains a wider range of molecular weights, while the Magnum extract is predominantly low-molecular-weight.
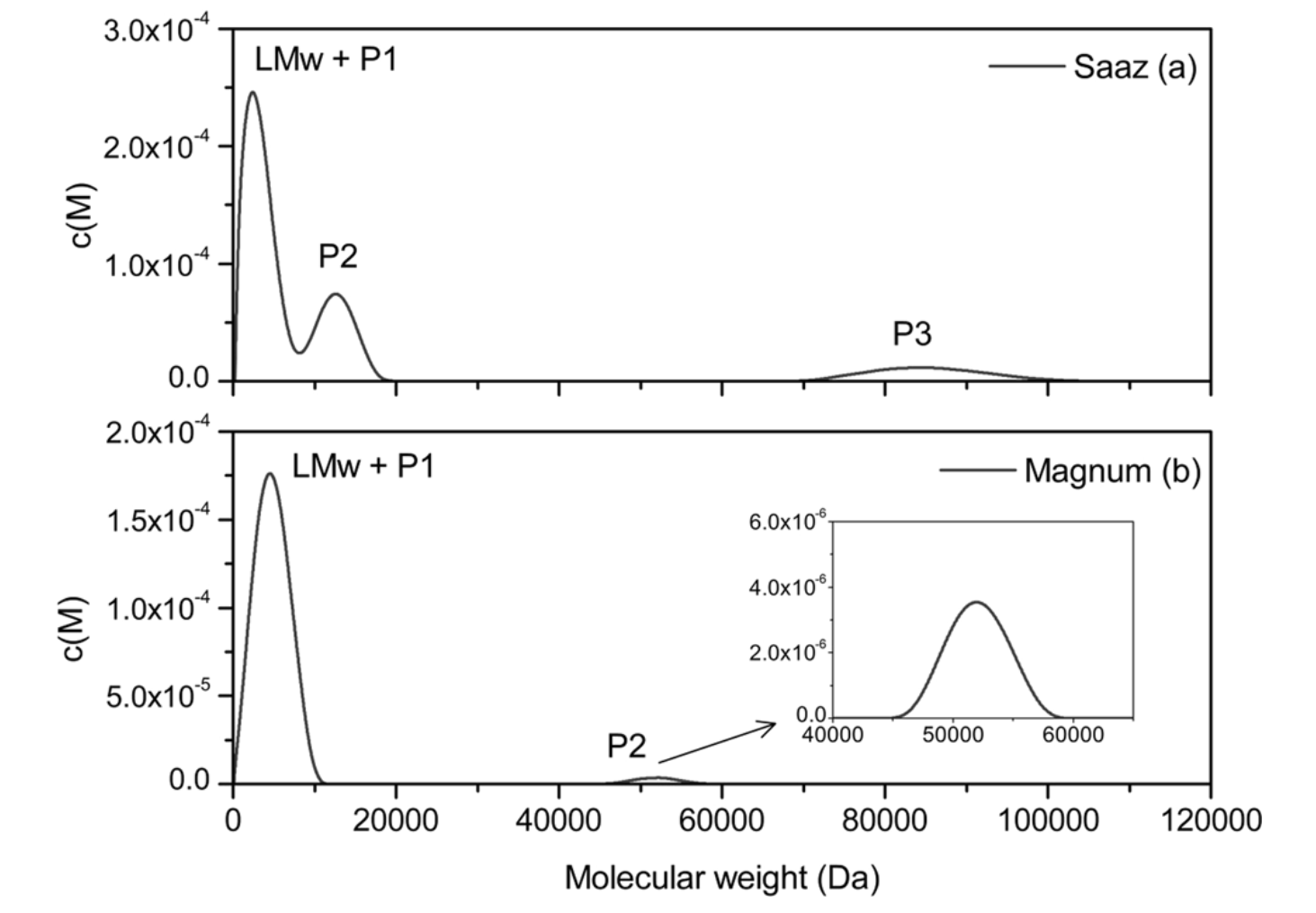
Figure 2. The c(M) Molecular Weight Distribution of (a) Saaz and (b) Magnum Hop Polyphenolic Extracts (40-Fold Diluted, in Methanol)
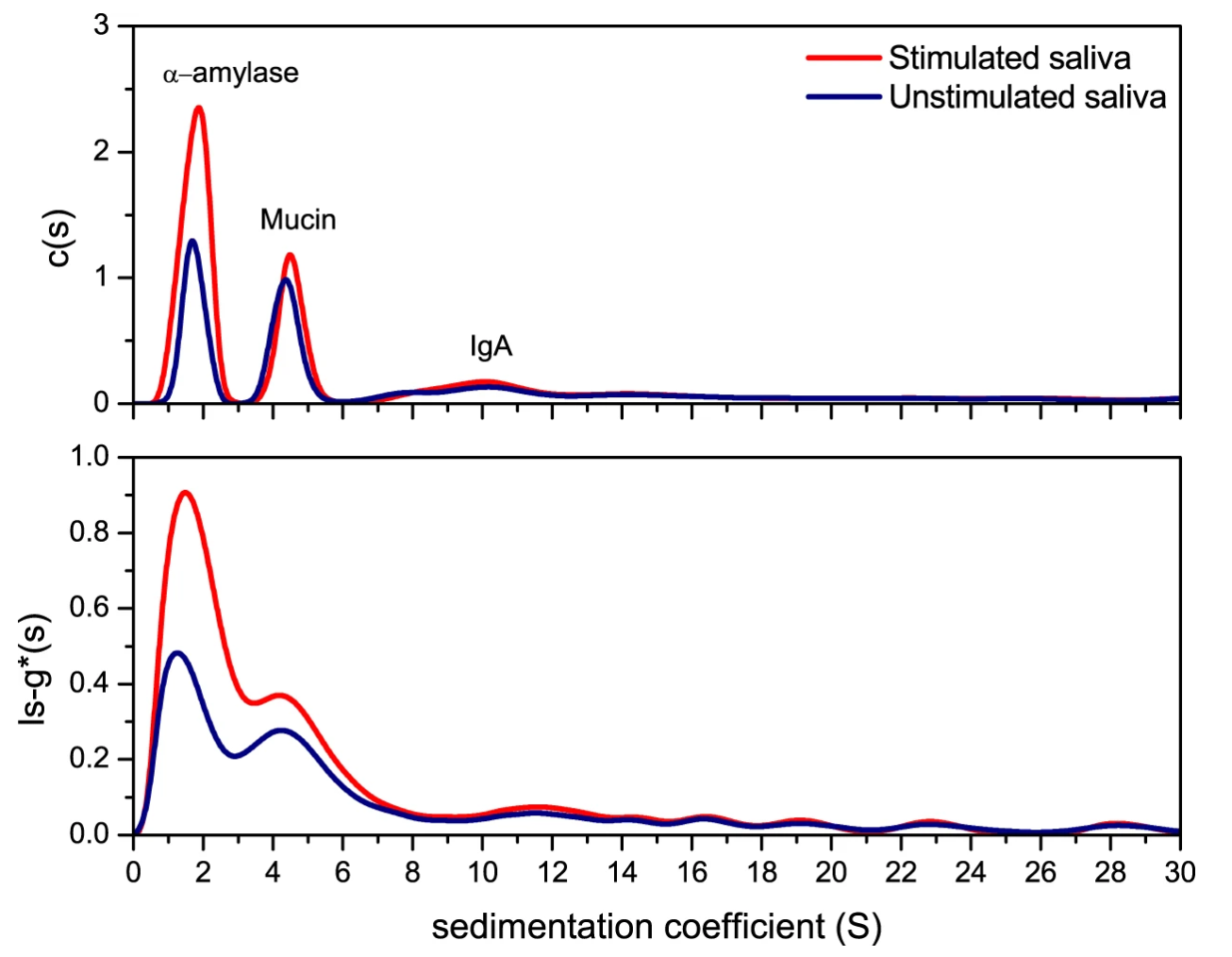
2. Sedimentation Velocity Analysis of Saliva Macromolecules
This study used ultracentrifugation molecular weight determination through sedimentation velocity analysis to examine the molecular composition of stimulated (SS) and unstimulated (US) human saliva. Sedimentation coefficient distributions were obtained using both ls-g*(s) and c(s) methods in SEDFIT, with centrifugation at 40,000 rpm at 20°C. Results revealed three primary macromolecular components: α-amylase (1.5S), mucin (4S), and secretory IgA (11S). The SS sample, shown in red, displayed higher peak intensities across these components compared to the US sample (blue), indicating a higher concentration of these proteins in stimulated saliva. This sedimentation velocity approach allows precise identification of saliva’s molecular weight distribution, providing insight into the relative concentrations and sizes of major protein species within complex biological fluids.
Dinu, V. et al. Sci Rep. 2018.
Figure 3. Sedimentation Velocity, ls-g*(s) and c(s) Analysis for Pooled Saliva
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Detailed Information on Molecular Weight Determination
4. Raw Data Files
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. If you are interested in our Ultracentrifugation Molecular Weight Determination Service, please feel free to contact us.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Analytical Ultracentrifugation Molecular Weight Determination Service
How to order?







