Structural Role and Stability of Disulfide Bonds in Proteins
-
Intramolecular disulfide bonds, which connect two distinct Cys residues within the same protein chain and primarily contribute to the stabilization of local or global tertiary structure.
-
Intermolecular disulfide bonds, which link independent peptide chains or protein subunits and participate in the establishment of quaternary structure.
Within the intricate landscape of protein three-dimensional architecture, disulfide bonds represent a prominent structural constraint. Formed as covalent linkages between cysteine residues, disulfide bonds play essential roles in maintaining higher-order protein structures, enhancing conformational stability, and modulating functional activity. In particular, in extracellular proteins, membrane proteins, and antibody-based therapeutics, disulfide bonds are often indispensable for proper folding and biological function.
What Is a Disulfide Bond?
A disulfide bond, also referred to as a disulfide bridge, is a covalent linkage (-S-S-) generated through the oxidation of sulfur atoms between two cysteine (Cys) residues. Such bonds can form either within a single polypeptide chain or between different protein chains.
Types of disulfide bonds include:
Compared with noncovalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding or hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bonds exhibit substantially higher stability and are typically formed under oxidative conditions, including those present in the endoplasmic reticulum or extracellular environments.
Core Roles of Disulfide Bonds in Protein Structure
1. Stabilization of Tertiary Structure
In many secreted and extracellular proteins, disulfide bonds constrain conformational flexibility by bridging amino acid residues that are distant in sequence but proximal in space, thereby enhancing thermal stability and improving folding efficiency.
2. Maintenance of Quaternary Structure
The structural integrity of multimeric proteins, particularly antibodies, often relies on intermolecular disulfide bonds. In IgG molecules, disulfide linkages connect heavy chains with each other and with light chains, which is essential for antibody assembly and antigen recognition.
3. Regulation of Conformational Dynamics and Functional Switching
In certain proteins, disulfide bonds participate in regulating functional states. For example, in signaling or receptor proteins, disulfide bond cleavage and rearrangement upon ligand binding may induce conformational transitions that activate or terminate signal transduction pathways.
Specific Contributions of Protein Disulfide Bonds to Stability
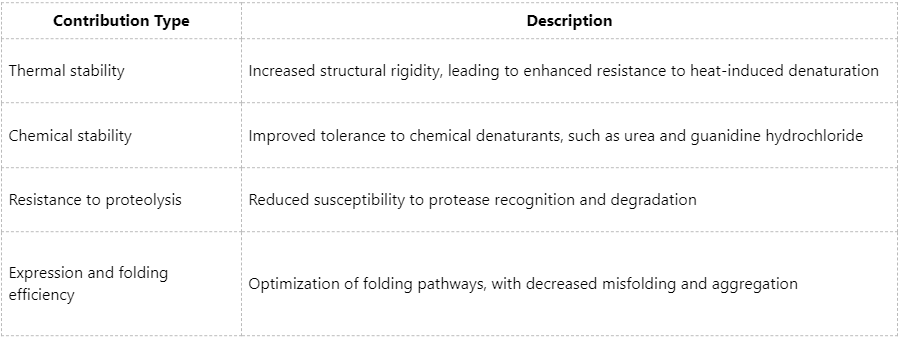
It is important to note that disulfide bonds are not universally beneficial in greater numbers. Their structural impact depends on precise positioning, correct pairing, and biological context. Improper disulfide bond formation can result in misfolding, aggregation, or complete loss of protein function.
Techniques for Detection and Characterization of Disulfide Bonds
1. Reducing and Non-Reducing SDS-PAGE
This approach allows preliminary assessment of disulfide bond presence by comparing protein migration patterns before and after treatment with reducing agents such as DTT or β-mercaptoethanol. However, it does not provide quantitative or site-specific information.
2. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
Currently the most widely used strategy for disulfide bond site identification and pairing analysis. Typical workflows involve non-reducing enzymatic digestion, enrichment of disulfide-linked peptides, LC-MS/MS analysis, and computational identification using specialized algorithms such as Byonic or pLink.
Based on Orbitrap Exploris 480 and FAIMS Pro platforms, MtoZ Biolabs has developed a sensitive and low-background mass spectrometry workflow for disulfide bond analysis, enabling the characterization of proteins containing both glycan modifications and disulfide bonds.
3. Structural Biology Approaches (e.g., X-ray Crystallography and Cryo-EM)
These methods allow direct visualization of disulfide bond locations and spatial conformations within protein structures, particularly in large macromolecular complexes, although they require high sample purity and stringent experimental conditions.
Applications of Disulfide Bonds in Protein Engineering and Drug Development
1. Enhancement of Protein Therapeutic Stability
The introduction of engineered disulfide bonds can improve the thermal stability and in vivo half-life of protein therapeutics. For instance, rational incorporation of specific Cys pairs into interferons or enzyme-based drugs has been shown to enhance their physicochemical properties.
2. Optimization of Antibody Design and Conjugation
In antibody-based therapeutics, reducible disulfide bonds serve as effective anchoring sites for drug conjugation, such as in antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs). Engineered disulfide bond strategies also facilitate control over drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) and conjugation geometry.
3. Regulation of Protein Folding Pathways
In synthetic biology, rational disulfide bond design can redirect protein folding pathways, reduce misfolding, and improve expression yield and functional recovery.
Service Capabilities of MtoZ Biolabs in Disulfide Bond Research
MtoZ Biolabs provides integrated, one-stop technical solutions for the structural characterization and quantitative analysis of protein disulfide bonds, including:
1. Non-reducing mass spectrometry analysis: Qualitative characterization of disulfide bond pairing patterns without prior reduction.
2. Characterization of proteins containing both glycans and disulfide bonds: Applicable to complex biomolecules such as glycoproteins and antibody-based therapeutics.
3. Disulfide bond site validation: Combined strategies involving optimized enzymatic digestion and high-resolution MS/MS data analysis to confirm disulfide linkage sites.
4. Structural modeling and functional prediction: Integrated analysis based on AlphaFold2 predictions and experimental mass spectrometry data to support structural interpretation and functional assessment.
Although small in size, protein disulfide bonds exert profound effects on conformational stability, functional activity, and in vivo behavior. As advances in protein engineering, structural biology, and mass spectrometry continue, disulfide bonds are increasingly recognized as central elements in functional studies and drug development. MtoZ Biolabs remains committed to supporting in-depth disulfide bond characterization through professional platforms and extensive project experience, thereby facilitating critical stages of biopharmaceutical research and development.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







