Single Crystal X-ray Diffractometer Analytical Service
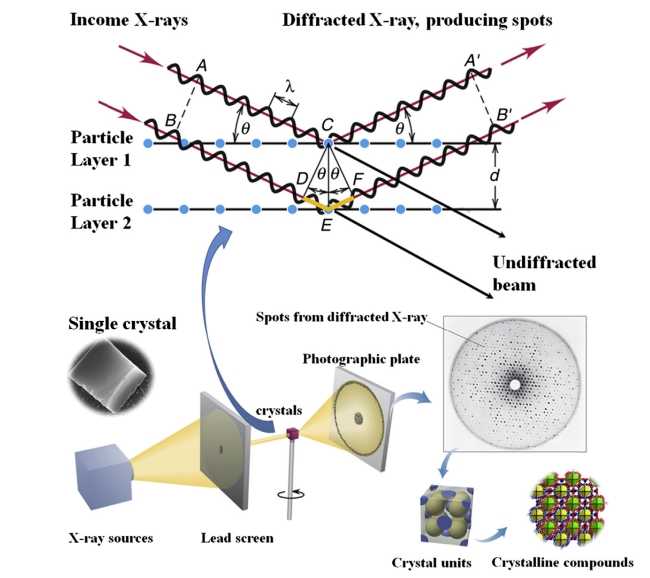
Single crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD) is a technique that enables high-resolution three-dimensional structural analysis of single crystal samples. Its basic principle is to irradiate the single crystal sample with X-rays, record the three-dimensional lattice diffraction pattern generated, and then use mathematical methods to analyze structural information such as lattice constants, atomic positions, bond lengths, bond angles, and symmetry. Compared with powder X-ray diffraction, SCXRD provides more precise and comprehensive molecular and crystal structure analysis. It is widely applied in pharmaceutical polymorphism studies, molecular structure elucidation, and excipient performance verification, offering critical support for drug development, formulation optimization, and quality control.
Bashir, S. et al. Advanced Nanomaterials and Their Applications in Renewable Energy, 2015.
Figure 1. The Schematic Presentation of Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on an advanced single crystal X-ray diffractometer platform, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the single crystal X-ray diffractometer analytical service, which enables high-precision detection and analysis of the structural characteristics of single crystal samples. This service uses high-resolution X-ray diffractometer instruments to perform accurate diffraction data collection and structural analysis of samples, allowing the acquisition of information such as molecular three-dimensional structures, atomic spatial arrangements, bond lengths and bond angles, lattice constants, and symmetry. The final data provided not only include detailed crystallographic parameters but also reveal the molecular-level structural characteristics of the samples, offering reliable data support for drug development, polymorphism analysis, and quality control in the biopharmaceutical field.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Applicable to single crystal samples, including organic compounds, inorganic materials, and biological macromolecules. Samples must have good crystallinity.
2. Sample Purity
Samples should avoid impurities or polycrystalline components as much as possible to ensure clear diffraction signals and obtain high-quality crystallographic data.
3. Sample Storage
Crystals should be stored in dry and dark conditions to avoid deliquescence, decomposition, or structural changes. For volatile or sensitive samples, storage under an inert atmosphere or at low temperatures is recommended.
4. Sample Transportation
It is recommended to use sealed containers or specialized fixation devices during transportation to ensure that samples are not affected by vibration, breakage, or environmental factors, thereby maintaining crystal integrity.
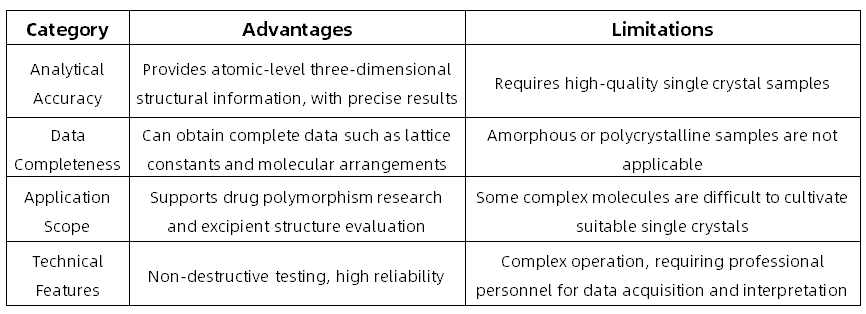
Advantages and Limitations
Applications
1. Pharmaceutical Polymorphism Research
Single crystal X-ray diffractometer analytical service can be used to analyze different polymorphs of drugs, evaluate their stability, solubility, and bioavailability, and provide data support for new drug development and formulation optimization.
2. Excipient Structure Characterization
By characterizing the molecular arrangement and crystal properties of pharmaceutical excipients, it ensures quality consistency and stability during the formulation process.
3. Formulation Development and Quality Control
Verifying the compatibility between drugs and excipients and detecting local structural differences in formulations it supports quality monitoring and batch-to-batch consistency studies.
4. Biomolecules and Complexes Research
Single crystal X-ray diffractometer analytical service can be applied to single-crystal structural analysis of proteins, peptides, or other bioactive molecules, revealing their three-dimensional structures and functional mechanisms.
FAQ
Q1: Can Amorphous Samples Be Analyzed?
A1: No. Amorphous substances lack long-range order and cannot produce diffraction patterns suitable for single-crystal analysis. Such samples are more appropriate for other analytical techniques (such as SAXS or solid-state NMR).
Q2: Is This Service Suitable for Both Small-Molecule and Macromolecular Samples?
A2: Yes. Small-molecule samples are generally easier to resolve, while macromolecules such as proteins require higher-quality crystals and more complex data collection conditions.
Q3: Are There Requirements for Crystal Transparency or Color?
A3: Typically, transparent or translucent crystals are more suitable for diffraction experiments, but colored crystals can also be analyzed as long as they have an appropriate size and integrity.
Related Services
How to order?







