SDS-PAGE vs. HPLC: Which Method Is More Suitable for Protein Purity Assessment?
- Simplicity and Versatility: The method does not require extensive sample pretreatment and is suitable for a wide range of protein samples.
- Direct Visualization for Preliminary Screening: Staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue or silver allows rapid assessment of protein purity and major contaminants.
- Low Cost and Minimal Equipment Needs: Well-suited for routine laboratory analyses and small-scale sample evaluation.
- Superior Resolution and Sensitivity: Capable of distinguishing proteins with closely related molecular weights or structures, making it suitable for complex biological samples.
- Accurate Quantification: When coupled with UV, fluorescence, or mass spectrometric detection, HPLC enables precise quantification of protein components.
- Methodological Flexibility: By tailoring chromatographic conditions (e.g., reverse-phase, ion-exchange, size-exclusion), it accommodates diverse protein types and analytical requirements.
- Preliminary Screening: For rapid evaluation of purity or optimization of expression conditions, SDS-PAGE offers significant advantages due to its simplicity and straightforward visualization.
- High-Standard Quality Assessment: In biopharmaceutical quality control, therapeutic protein development, and regulatory submission, HPLC is considered essential for its high resolution and quantitative accuracy.
- Complementary Application: In practice, SDS-PAGE and HPLC are often applied sequentially. SDS-PAGE serves for initial screening, followed by HPLC to confirm purity and identify impurities, thereby providing multidimensional data to support experimental design and product quality assurance.
In proteomics research and biopharmaceutical development, protein purity assessment is a critical process for ensuring experimental reproducibility and product quality. SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) and HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) are two widely used yet complementary analytical approaches, each characterized by specific strengths and limitations. This article examines their respective application scenarios, core technical features, and comparative advantages and drawbacks, with the aim of informing methodological choices in protein analysis.
SDS-PAGE: Electrophoretic Separation Based on Molecular Weight
SDS-PAGE employs SDS to confer a uniform negative charge density to proteins, enabling their separation in a gel matrix according to molecular weight and producing distinct banding patterns. Its main features include:
Nevertheless, SDS-PAGE exhibits limited resolution, particularly for proteins of similar molecular weight or samples with highly disparate abundances. Its quantitative capability is also restricted, as staining efficiency and sample loading can compromise accuracy. Consequently, SDS-PAGE is inadequate for applications demanding high-precision quantification or detection of low-abundance impurities.
HPLC: High-Resolution Separation Based on Physicochemical Properties
HPLC operates through interactions between the stationary and mobile phases, achieving efficient separation of protein mixtures. Its principal advantages are:
The limitations of HPLC include demanding sample preparation and stringent instrument maintenance, as well as substantial operational costs. Additionally, exposure to high pressure and organic solvents may induce protein denaturation or activity loss, necessitating optimized protocols for specific targets.
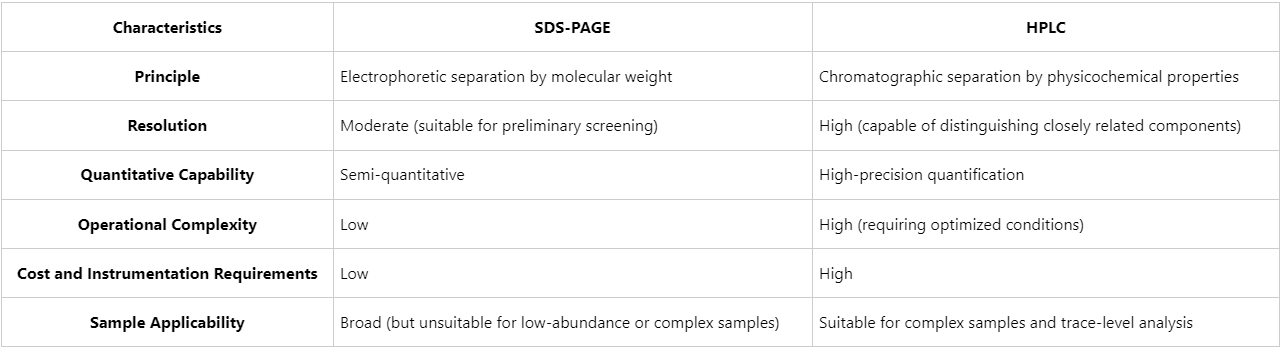
Comparative Analysis: Selecting the Appropriate Method
The choice between SDS-PAGE and HPLC in protein purity assessment should consider sample complexity, analytical objectives, and precision requirements:
Protein purity not only underpins experimental reproducibility but also has direct implications for product safety and therapeutic efficacy. The choice of assessment method should align with the analytical requirements and be supported by robust technical platforms. Leveraging advanced liquid chromatography systems and high-resolution mass spectrometry, MtoZ Biolabs can achieve precise separation and quantification of complex protein samples, while offering tailored analytical solutions to meet diverse research and development needs.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







