Rheometer Analytical Service
- Multi-Mode Testing Capability: Supports various testing modes, including rotational, oscillatory, creep recovery, and yield stress.
- Wide Applicability: Covers a full range of samples from low-viscosity liquids to high-viscosity melts and soft solids.
- High-Precision Control: Accurate temperature regulation and high-resolution sensors ensure data reliability.
- Professional Technical Support: An experienced technical team provides experimental design, data interpretation, and application guidance to help clients effectively translate results into evidence for research and quality control.
Rheometer Analytical Service is a professional service that uses a rheometer to systematically analyze the flow and deformation behavior of liquids, semi-solids, and soft solid materials under applied forces. Rheology, as an important tool that links the microstructure of materials with their macroscopic performance, has broad applications in pharmaceuticals, biomedical materials, polymer science, food engineering, and chemical industries. Through controlled stress or controlled strain modes, the rheometer can measure key parameters such as viscosity, storage modulus (G′), loss modulus (G″), yield stress, and creep and recovery characteristics, providing precise and reliable data for rheological characterization of materials.
Technical Principles
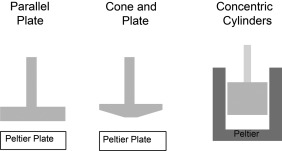
The core principle of a rheometer is to apply controlled stress or strain to a sample and measure its flow and deformation response in order to obtain the rheological parameters of the material. During testing, the sample is placed between specific geometries such as parallel plates, cone-plate systems, or concentric cylinders. The instrument applies shear force through rotation or oscillation and records the relationship between stress and strain. For viscous materials, the test yields the functional relationship between viscosity and shear rate. For viscoelastic systems, oscillatory testing provides indicators such as storage modulus (G′), loss modulus (G″), and phase angle. These data systematically reveal the flow behavior, elasticity, and stability of materials under different conditions, thereby providing a scientific basis for evaluating their processing performance and application properties.
Marangoni AG. Structure-Function Analysis of Edible Fats (Second Edition). 2018.
Figure 1. Three Different Geometries and Their Corresponding Base Plates, Commonly Used in Rotational Rheometers
Analysis Workflow
The general process of Rheometer Analytical Service is as follows:
1. Sample Preparation
Pre-treat the sample according to its properties (liquid, gel, paste, or soft solid) to ensure uniformity and avoid bubbles or impurities that could interfere with measurement.
2. Instrument Setup
Select the appropriate geometry and test mode (rotational or oscillatory), and set the temperature range along with stress or strain conditions.
3. Experimental Testing
Conduct measurements under controlled conditions while recording stress, strain, and flow behavior.
4. Data Processing
Generate rheological curves and calculate viscosity, modulus, and other rheological parameters.
5. Result Analysis
Evaluate the material’s flowability, stability, and structural characteristics in relation to the experimental objectives.
6. Report Output
Provide a complete report including experimental data, curve plots, and result interpretation.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs provides Rheometer Analytical Service to comprehensively evaluate the viscoelastic properties of materials, including storage modulus (G′), loss modulus (G″), viscosity curves, and shear thinning or thickening behavior. This service is applicable to a wide range of systems such as ointments, gels, protein formulations, nanogels, and biomaterials, not only revealing their flowability and structural stability but also providing data support for formulation optimization, material design, and quality control.
Service Advantages
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
A wide range of samples is acceptable, including ointments, gels, protein formulations, and nanogels.
2. Storage and Transportation
Samples should be sealed to prevent evaporation, contamination, or degradation. Temperature-sensitive samples are recommended to be transported under low-temperature conditions.
It is recommended to contact the MtoZ Biolabs technical team prior to sample submission to obtain detailed and tailored guidelines for sample preparation and submission.
Applications
Application examples of Rheometer Analytical Service:
1. Pharmaceuticals and Biopharmaceuticals
Evaluate the flowability and stability of injections, protein solutions, gels, and sustained-release carriers.
2. Polymers and Materials Science
Study the relationship between molecular structure and rheological behavior to support polymer modification and process development.
3. Food and Cosmetics
Analyze the texture and thixotropy of creams, pastes, and beverages to optimize sensory experience and product stability.
4. Industrial Materials and Composites
Assess the rheological properties of coatings, adhesives, and composite materials to predict processing performance and service life.
How to order?







