Rhamnan Analysis Service
Rhamnan is a type of polysaccharide composed of rhamnose monosaccharide units linked by different glycosidic bonds. Its main chain structures can be classified into two types, α-type and β-type, with common forms including linear Rhamnan, branched Rhamnan, and heteropolysaccharide Rhamnan. It is widely found in bacterial cell walls, seaweed, and plant-derived polysaccharides, possessing unique physicochemical properties and biological activities. Through systematic Rhamnan analysis, its structural composition and molecular characteristics can be revealed, providing a scientific basis for research and applications in food, pharmaceutical, and biomaterial fields.
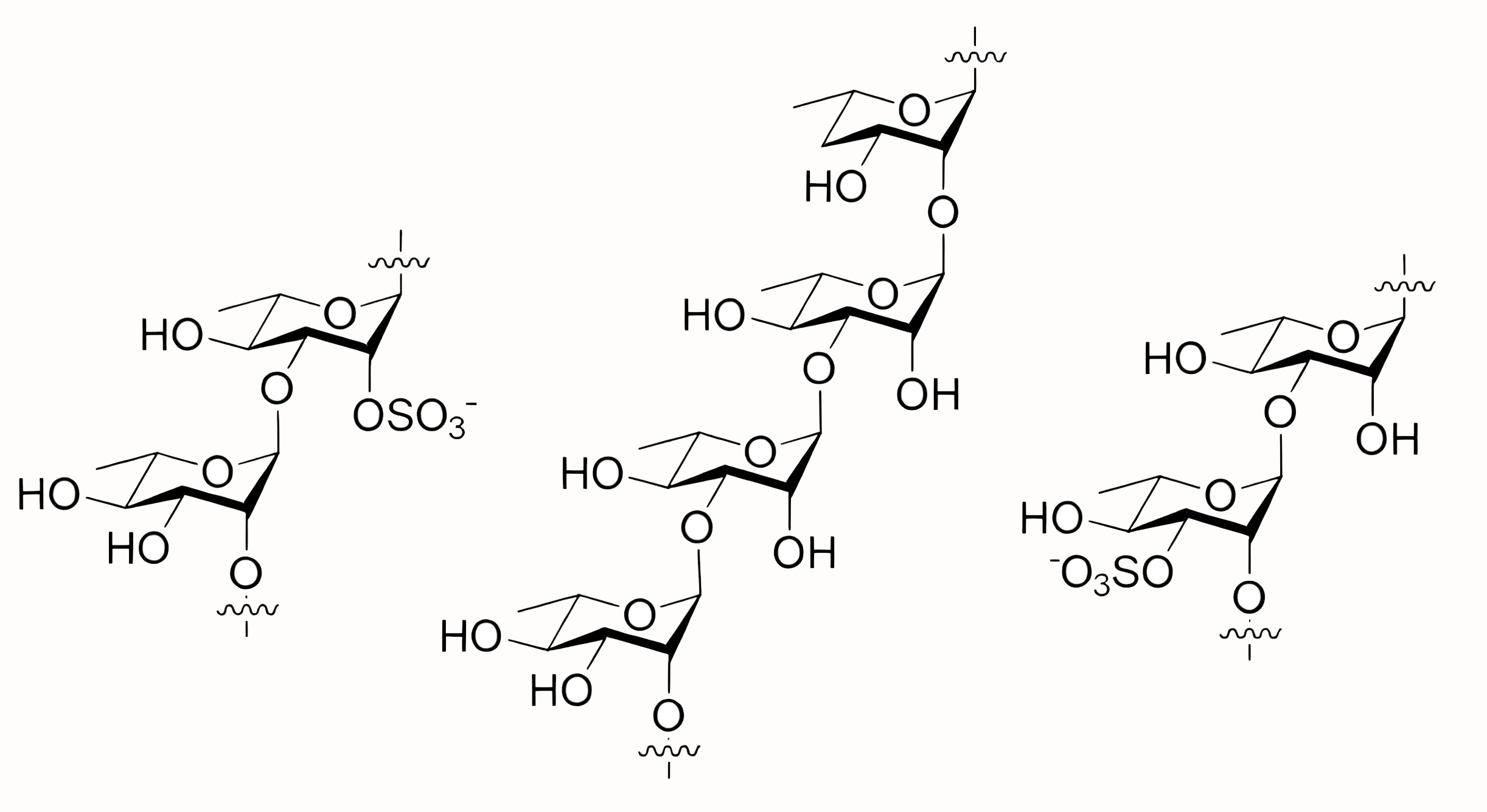
Kohout, V. et al. Carbohydrate Research, 2019.
Figure 1. Rhamnan and Rhamnan Sulfate Fragment Structures.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced instruments and analytical platforms, MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive rhamnan analysis service to accurately characterize the composition and properties of Rhamnan. MtoZ Biolabs provides the following services, including but not limited to:
1. Molecular Weight Determination
Rhamnan molecular weight and distribution characteristics are measured using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
2. Thermal Stability Evaluation
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) are combined to assess the thermal stability of Rhamnan.
3. Structural Characterization
Ultraviolet spectroscopy (UV), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are used to confirm the main-chain configuration, branching structure, and functional group characteristics of Rhamnan.
4. Surface and Morphological Analysis
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is used to observe sample morphology and particle characteristics, while Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) is applied to study the aggregation state and spatial conformation of Rhamnan.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Purified Rhamnan powder, lyophilized samples, solution samples, or crude extracts are accepted. A purity level of ≥90% is recommended to ensure analytical accuracy.
2. Sample Storage
Solid samples should be kept in a dry, dark environment at 4°C or −20°C. Solution samples should be stored at low temperatures and protected from repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
3. Sample Transportation
Samples should be sealed and moisture-proof during transport. Liquid samples require cold-chain shipping, while powder samples can be shipped at ambient temperature for short periods, avoiding heat and humidity.
Service Advantages
1. Multi-Platform Analytical Integration
Combines multiple analytical techniques to comprehensively characterize the structural and physicochemical properties of Rhamnan.
2. High Accuracy and Reproducibility
Implements standardized analytical procedures and strict quality control to ensure accurate, stable, and repeatable results.
3. Extensive Polysaccharide Analysis Experience
The technical team possesses extensive experience in polysaccharide and biopolymer analysis, with expertise in various Rhamnan types and analytical requirements.
4. Customized Analytical Solutions
Provides flexible testing combinations and data analysis plans tailored to sample type and research objectives.
Applications
1. Food Science Research
The rhamnan analysis service can be used to evaluate the structural and functional properties of Rhamnan as a natural thickener, emulsifier, and dietary fiber in food applications.
2. Algal and Plant Polysaccharide Research
Identifies and analyzes Rhamnan from different sources to compare structural variations and physicochemical properties.
3. Biomedical Research
The rhamnan analysis service supports studies on the structural basis of Rhamnan’s antioxidant, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory activities.
4. Quality Control and Product Development
Provides structural characterization and purity validation data for Rhamnan extracts and related products through comprehensive analytical testing.
FAQ
Q1: Can Rhamnan Mixture Samples Be Separated into Individual Components?
A1: Yes. For mixtures containing multiple types of Rhamnan or heteropolysaccharides, we can perform fractionation using liquid chromatography coupled with MS or NMR. This approach enables the identification of major polysaccharide types and the establishment of structural profiling databases.
Q2: What Are the Respective Roles of FTIR and NMR in Rhamnan Analysis?
A2: FTIR is primarily used to rapidly identify functional groups, glycosidic bond types, and characteristic vibrations of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups in Rhamnan. NMR (including 1D and 2D spectra) provides detailed insights into backbone linkages, branching patterns, and configuration differences. Together, these techniques confirm the α/β configuration and degree of polymerization, serving as essential tools for structural characterization.
How to order?







