Protein Ubiquitination Identification Service
- Sample Preparation: Protein extraction and enzymatic digestion with deubiquitinase inhibitors to preserve modifications.
- Ubiquitinated Peptide Enrichment: Selective capture using antibody-based methods or K-ε-GG labeling.
- Mass Spectrometry Detection: High-resolution LC-MS/MS for sensitive and accurate data acquisition.
- Data Analysis: Database searching with modification-specific fragment screening to identify sites and annotate functions.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Detailed reports including workflows, parameters, annotated sites, spectra, and raw data files.
- Comprehensive Experimental Details
- Materials, Instruments, and Methods
- High-quality Spectra and Visualized Charts
- Site-specific Ubiquitination Identification with Detailed Annotation
- Bioinformatics Analysis
- Raw Data Files
Protein ubiquitination identification based on mass spectrometry is a powerful approach to studying protein post-translational modifications, enabling precise site-specific detection of ubiquitination events and their distribution. Ubiquitination is a covalent process mediated by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1), conjugating enzymes (E2), and ligases (E3), in which ubiquitin, a 76–amino acid protein, is attached to substrate proteins through lysine residues or the N-terminus. This modification not only regulates protein degradation but also plays critical roles in signal transduction, DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, immune responses, and disease progression.
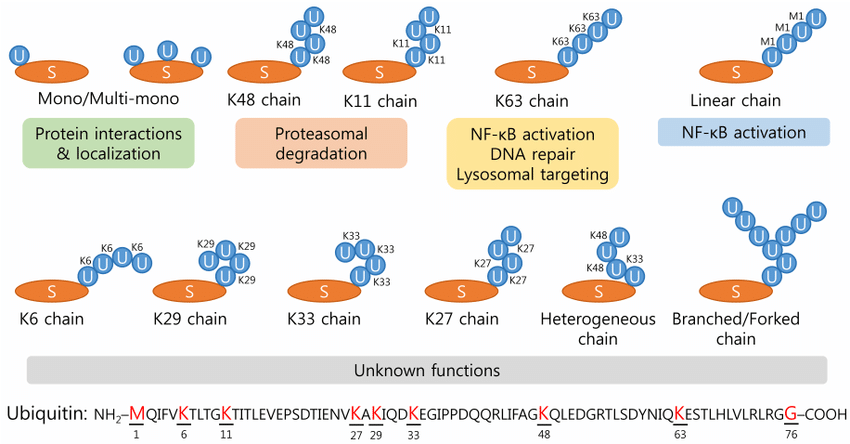
Park, C. et al. BMB Rep. 2014.
Figure 1. Various Types of Ubiquitination and the Specific Role of Ub Chain Linkages
By identifying ubiquitination events, researchers can systematically map modification networks, uncover their role in disease mechanisms, and generate valuable insights for drug discovery and biomarker development. Leveraging advanced LC-MS/MS platforms and comprehensive bioinformatics pipelines, MtoZ Biolabs provides high-quality Protein Ubiquitination Identification Service to support in-depth and reliable ubiquitination analysis.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs Protein Ubiquitination Identification Service addresses the inherent challenges of ubiquitination analysis, including detection difficulty, low abundance, and wide dynamic range. We employ advanced enrichment strategies such as anti-ubiquitin antibody capture and K-ε-GG residue labeling, combined with high-resolution LC-MS/MS, to achieve precise identification even in complex biological backgrounds. Our integrated bioinformatics analysis further delivers comprehensive ubiquitination maps and functional interpretation.
Analysis Workflow

Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
✔ High-Resolution Platforms: Equipped with advanced LC-MS/MS systems, enabling sensitive detection of low-abundance ubiquitinated peptides with accuracy and reliability.
✔ Advanced Enrichment Strategies: Utilization of antibody-based capture and K-ε-GG residue labeling methods ensures efficient isolation and enhanced coverage of ubiquitination sites.
✔ Site-Specific Accuracy: Provides precise identification and annotation of lysine modification sites, delivering high-confidence data for downstream analysis.
✔ Broad Sample Compatibility: Supports a wide range of biological samples, including cells, tissues, serum, plasma, and other bodily fluids, to meet diverse research requirements.
✔ Transparent Pricing: One-time-charge model with clear cost structure, ensuring no hidden fees and straightforward project planning.
Sample Submission Suggestions
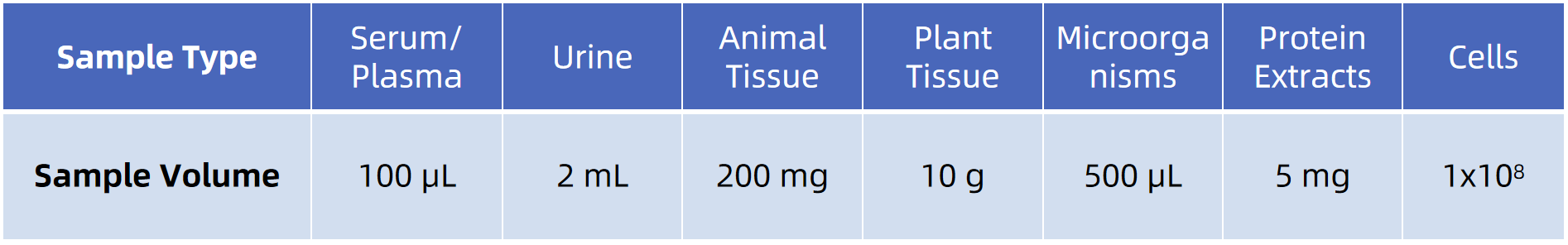
Note: Provide details on sample collection and handling. If you need further details, our technical support team is happy to assist and provide comprehensive guidance on sample submission.
Our Protein Ubiquitination Identification Service is suitable for disease mechanism studies, signaling pathway analysis, protein homeostasis research, and drug development. With advanced MS platforms and expert teams, MtoZ Biolabs delivers high-confidence ubiquitination identification services to support research in disease mechanisms, molecular pathways, and therapeutic discovery.
What Could Be Included in the Report?
FAQs
Q1: Can Different Types of Polyubiquitin Linkages Be Identified?
A1: Yes. By analyzing characteristic fragment ion patterns and database matches, MtoZ Biolabs distinguishes linkages such as K48 and K63, providing insights into ubiquitination roles in protein stability and signaling pathways.
Q2: Can Ubiquitination Analysis Be Combined With Other PTM Studies?
A2: Yes. Ubiquitination often works together with modifications such as phosphorylation and acetylation to regulate protein function. MtoZ Biolabs integrates ubiquitination identification with other PTM analyses, enabling comprehensive protein modification network studies and supporting systems-level research.
How to order?







