Protein Modification Profiling Service
Protein modification profiling is a high-throughput analytical method designed for the systematic study of protein post-translational modifications (PTMs). It aims to comprehensively identify and quantify protein modification states, including phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, and benzoylation. PTMs play a crucial role in regulating protein function, stability, interactions, and signal transduction. This technology is typically based on high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), combined with specific enrichment strategies and bioinformatics analysis, enabling precise identification of modification sites and dynamic monitoring of their changes.
Protein modification profiling service is widely applied in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders, immune diseases, and drug development. For example, in cancer research, this analysis can reveal key modification signals driving cancer cell proliferation and drug resistance; in neuroscience, it can be used to study the role of abnormal protein modifications in diseases such as Alzheimer's disease; in drug discovery, it assists in screening therapeutic targets and optimizing drug candidate mechanisms. This service provides a powerful tool for exploring the role of protein modifications in biological processes and disease progression.
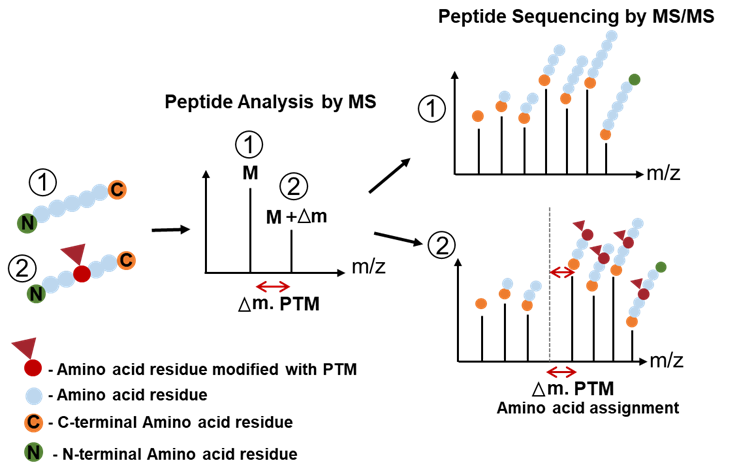
Larsen, M R. et al. Biotechniques, 2006.
Figure 1. The Principle of Detecting PTMs with Tandem Mass Spectrometry.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Leveraging a high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platform combined with specific modification enrichment techniques, the protein modification profiling service provided by MtoZ Biolabs enables precise identification and quantitative analysis of protein post-translational modifications (PTMs). This service covers a wide range of modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, and benzoylation, ensuring high sensitivity and comprehensive data coverage. Through optimized mass spectrometry parameters and advanced bioinformatics analysis, clients receive detailed modification site information, dynamic changes in modification levels, and potential functional correlations, providing reliable experimental data support for biological research, disease mechanism exploration, and drug development.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Proteins are extracted and enzymatically digested to obtain high-quality peptides for modification analysis.
2. Specific Enrichment
Antibody enrichment, affinity labeling, or chemical derivatization techniques are used to selectively capture specific types of post-translational modifications (PTMs), such as phosphorylation, acetylation, and glycosylation.
3. Mass Spectrometry Detection
High-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is employed for high-throughput identification and quantitative analysis of enriched modified peptides.
4. Bioinformatics Analysis
Professional analytical software is used for modification site identification, quantitative assessment, functional enrichment, and pathway analysis, uncovering key modified proteins and their biological significance.
5. Data Reporting and Interpretation
A comprehensive analysis report is provided, including modification site information, protein functional annotations, and potential regulatory mechanisms, supporting clients in further biological research and validation.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution LC-MS/MS Platform
MtoZ Biolabs utilizes a high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platform to ensure precise identification of low-abundance protein modifications, enhancing modification site coverage.
2. Comprehensive Modification Type Detection
We offer analysis of various post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, and benzoylation, providing a comprehensive modification proteomics dataset.
3. Specific Enrichment Strategy
Utilizing highly efficient modification-specific antibodies or affinity capture techniques to enhance the enrichment efficiency of target modified peptides, improving data accuracy.
4. In-Depth Data Analysis
Employing advanced bioinformatics tools to provide modification site identification, quantitative analysis, functional enrichment, and pathway analysis, uncovering the biological roles of modifications.
5. Customized Services
MtoZ Biolabs offers tailored experimental solutions based on client research needs, supporting disease mechanism exploration, drug development, and biomarker discovery.
Applications
1. Cancer Research
By analyzing modification changes in key proteins, the protein modification profiling service can reveal regulatory mechanisms driving cancer initiation, progression, and drug resistance, facilitating the discovery of novel anticancer targets.
2. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Investigating abnormal protein modifications (such as phosphorylation and acetylation) in diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's to explore potential therapeutic strategies.
3. Metabolic Diseases
Through modification proteomics analysis, the protein modification profiling service can investigate metabolic regulatory mechanisms in diseases such as diabetes and obesity, identifying key modified proteins and therapeutic targets.
5. Immune and Infectious Diseases
Analyzing protein modifications in immune signaling pathways to elucidate regulatory mechanisms associated with autoimmune diseases and viral infections (e.g., COVID-19).
6. Drug Discovery
The protein modification profiling service can assess the impact of drug candidates on protein modification states, identify potential biomarkers, optimize drug targets and mechanisms of action, and accelerate advancements in precision medicine.
Case Study
1. Altered ureido protein modification profiles in seminal plasma extracellular vesicles of non-normozoospermic men
This study aimed to investigate changes in ureido protein modification profiles in seminal plasma extracellular vesicles (EVs) of men with abnormal sperm morphology (non-normozoospermic) to uncover their potential role in male fertility disorders. The study subjects included seminal plasma samples from normozoospermic and non-normozoospermic men. Extracellular vesicles were isolated, and high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was used for systematic identification and quantitative analysis of protein modification patterns. The results demonstrated significant alterations in ureido protein modifications in seminal plasma EVs from non-normozoospermic patients, with certain modified proteins closely associated with sperm function regulation and fertility potential. Further functional analysis revealed that these modifications might influence intercellular communication mediated by EVs and the sperm maturation process. The study concluded that abnormal ureido protein modifications could serve as potential molecular biomarkers for non-normozoospermia, providing new insights into the mechanisms of male infertility and potential biomarkers for fertility assessment and diagnosis.
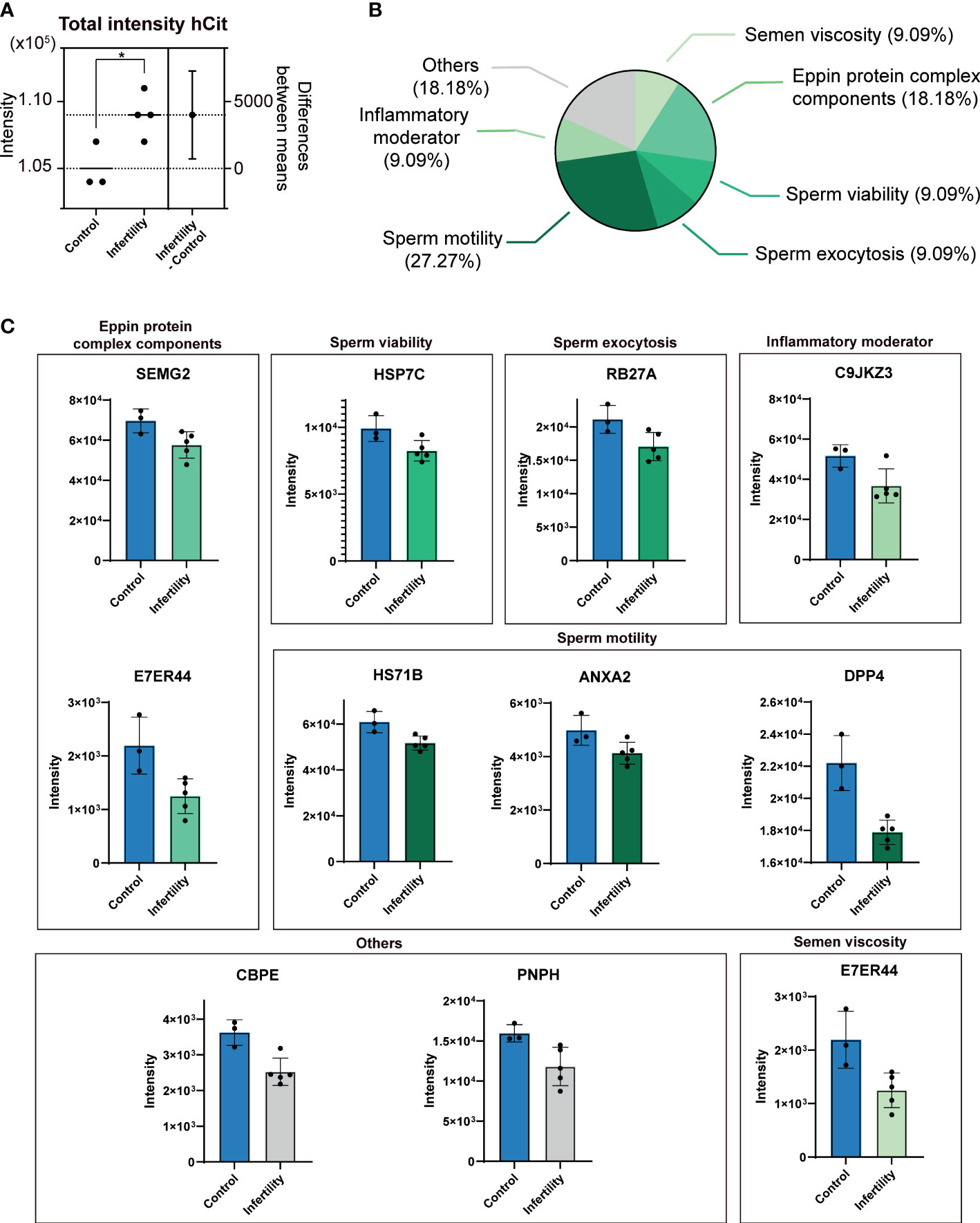
Roy, R. et al. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2023.
Figure 2. Differential Presence of Ureido Protein Modifications (uPMs) in sEV Proteomes of Non-normozoospermic Men Compared to Healthy Controls.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation
4. Bioinformatics Analysis
5. Raw Data Files
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Service
How to order?







