Polysaccharide Methylation Analysis Service
Based on high-resolution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platforms, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the polysaccharide methylation analysis service which enables systematic detection and quantitative analysis of methylation modifications in natural or synthetic polysaccharide samples. This service allows for the identification and quantification of methylated monosaccharides, and through standard calibration and spectrum interpretation, it provides key information such as the distribution of methylation sites, modification ratios, and structural features of polysaccharides, offering precise data support for further polysaccharide research.
What Is Polysaccharide Methylation?
Polysaccharide methylation refers to a chemical modification in which hydroxyl groups (-OH) in the polysaccharide molecular structure are replaced by methyl groups (-CH₃). This modification can alter the solubility, viscosity, thermal stability, and biological activity of polysaccharides, thereby affecting their structural conformation and functional performance in biological systems. Polysaccharide methylation analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms of polysaccharide biosynthesis, structural modification, and functional optimization, and it has been widely applied in natural product structure elucidation, medicinal polysaccharide research, biomaterial development, and fermentation product quality control, providing essential evidence for understanding the relationship between polysaccharide structure and function.
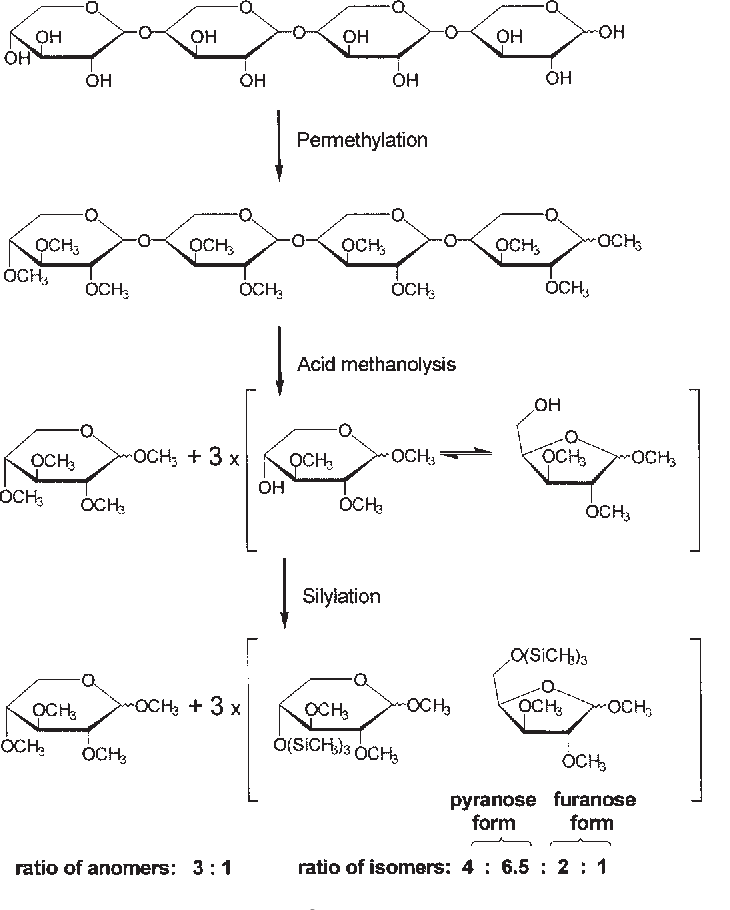
C. Laine, et al. Holzforschung, 2002.
Figure 1. The Reactions during Methylation Analysis with 1,4-β-xylotetraose.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Pretreatment
Polysaccharides are extracted from the samples, followed by desalting, deproteinization, and purification.
2. Methylation Reaction
Under anhydrous alkaline conditions, hydroxyl groups of polysaccharides are methylated to generate stable methyl ether derivatives.
3. Hydrolysis and Derivatization
The methylated polysaccharides are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides and further subjected to derivatization.
4. Mass Spectrometry Detection
High-resolution GC-MS or LC-MS/MS platforms are used to separate and detect methylated monosaccharide signals, providing modification information.
5. Data Analysis and Result Output
By comparing with standards and analyzing spectra, methylation sites and ratios are determined, and a comprehensive polysaccharide methylation analysis report is generated.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Plant extracts, plant tissue extracts, and purified polysaccharide samples are acceptable.
Note: Samples should be free of proteins, salts, and residual organic solvents to avoid interference with the methylation reaction and detection results.
2. Sample Storage
Samples should be stored in a sealed, light-protected, and dry environment. For short-term storage, keep at -20°C; for long-term preservation, store at -80°C to prevent oxidation or moisture-induced structural changes.
3. Sample Transportation
Lyophilized samples can be shipped at ambient temperature for short periods, while liquid samples are recommended to be transported under low-temperature cold-chain conditions to ensure component stability and prevent alterations of methylation sites.
Service Advantages
1. High-Sensitivity Detection Platform
With advanced GC-MS and LC-MS/MS systems, this service enables high-resolution separation and precise quantification of methylated monosaccharides.
2. Comprehensive Structural Analysis
Simultaneously characterizes methylation types, positions, and ratios within polysaccharides, revealing branching features and linkage patterns.
3. Standardized Experimental Workflow
Every step, from sample preparation to data interpretation, follows strict quality control to ensure result reproducibility and reliability.
4. Customized Analytical Solutions
Analysis strategies are flexibly tailored to sample types and research objectives, meeting the diverse needs of different scientific fields.
Applications
1. Plant Structural Studies
The polysaccharide methylation analysis service can be used to analyze methylation patterns of polysaccharides in plant cell walls, revealing their structural characteristics and physiological roles.
2. Natural Product Structure Identification
By determining glycosidic linkage types and branching configurations through methylation analysis, this service supports the structural elucidation of natural products.
3. Polysaccharide Modification and Derivative Development
The polysaccharide methylation analysis service enables evaluation of methylation features in chemically or enzymatically modified polysaccharides, guiding the design of functionalized biomaterials.
4. Environmental and Ecological Metabolism Research
By analyzing methylation differences in microbial or plant-derived polysaccharides from environmental samples, this service helps reveal ecological adaptation mechanisms.
FAQ
Q1: Can Methylation Analysis Distinguish Different Linkage Patterns in Polysaccharides?
A1: Yes. By combining methylation derivatization with mass spectrometry detection, the glycosidic bond types and branching linkages can be inferred, allowing detailed structural characterization of polysaccharides.
Q2: Will the Polysaccharide Structure Be damaged during the Analysis?
A2: Methylation analysis involves chemical modification steps that may partially alter the original structure, so it is primarily used for structural inference rather than native structure preservation.
Q3: Can Methylation Analysis Be Performed Alongside Other Structural Analyses?
A3: Yes. Methylation analysis is often combined with monosaccharide composition analysis, NMR, or infrared spectroscopy to obtain comprehensive structural information.
How to order?







