Polysaccharide Metabolism Analysis Service
Polysaccharide metabolism refers to the processes of synthesis, degradation, and transformation of polysaccharides within living organisms, which are involved in essential biological activities such as energy storage, structural construction, and signal regulation. By analyzing polysaccharides and their metabolites, it is possible to reveal their roles in energy metabolism balance, cellular homeostasis, and physiological regulation. This analysis is widely applied in biology, medicine, agriculture, and industrial biotechnology, providing key data support for studying polysaccharide functional mechanisms, fermentation optimization, and biomaterial development.
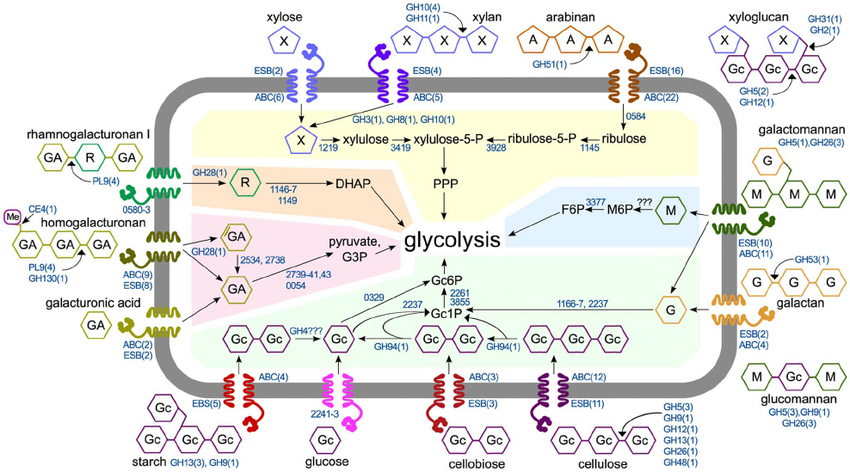
Boutard, M. et al. PLOS Genetics, 2014.
Figure 1. Model of Polysaccharide Degradation and Metabolism by C. Phytofermentans.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced analytical platforms such as LC-MS/MS, NMR, and GC-MS, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the polysaccharide metabolism analysis service which focuses on the systematic detection and quantitative analysis of polysaccharides and their related metabolites. This service enables precise evaluation of the composition, structural characteristics, and content variation of polysaccharides and their metabolites. Through high-precision mass spectrometry detection and database comparison, comprehensive metabolite profiles and abundance data can be obtained, providing reliable data support for studies on polysaccharide metabolic mechanisms, functional analysis, and process optimization. MtoZ Biolabs provides services including but not limited to the following:
1. Component Analysis
High-resolution mass spectrometry and chromatographic techniques are used to detect the composition of polysaccharides and their metabolites, identifying the types and proportions of monosaccharides and metabolic molecules.
2. Molecular Weight Analysis
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) or multi-angle laser light scattering (MALS) is applied to determine the molecular weight and distribution characteristics of polysaccharides and their metabolites, assessing sample homogeneity.
3. Structural Analysis
NMR, MS, and infrared spectroscopy are combined to analyze the structural characteristics of polysaccharides and their metabolites, including glycosidic linkage patterns, branching configurations, and spatial conformations.
4. Quantitative Analysis
The highly sensitive LC-MS/MS platform is used for precise quantification of polysaccharides and their metabolites, revealing changes in content and metabolic dynamics.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
A wide range of sample types is accepted, including plant tissues, microbial fermentation products, plant cell cultures, and purified polysaccharide samples. Samples should be free of visible impurities and degradation to ensure analytical accuracy.
2. Sample Storage
Samples should be sealed and stored in the dark at -80°C for long-term preservation or at -20°C for short-term storage. Repeated freeze-thaw cycles and exposure to high temperatures should be avoided to prevent metabolite degradation or compositional changes.
3. Sample Transportation
Lyophilized samples can be shipped at room temperature for short periods, while liquid samples should be transported under cold-chain conditions to maintain low temperature and airtightness, preventing oxidation, volatilization, or ongoing metabolic reactions.
Service Advantages
1. Multi-Platform Integrated Analysis
Combining LC-MS/MS, GC-MS, and NMR technologies enables comprehensive detection and accurate characterization of polysaccharides and their metabolites.
2. High Sensitivity and Resolution
With high-resolution mass spectrometry systems, trace metabolites can be sensitively detected and accurately quantified.
3. High Stability and Reproducibility
Standardized procedures and rigorous quality control throughout the workflow ensure the stability and reproducibility of analytical results.
4. One-Stop Service Support
Providing end-to-end solutions from sample preparation to data analysis and report generation, ensuring efficient experimental progress.
Applications
1. Pharmaceutical Polysaccharide Research
By characterizing the structure, purity, and physicochemical properties of pharmaceutical polysaccharides and their metabolites, this service ensures pharmacological stability and quality consistency.
2. Natural Product Research
The polysaccharide metabolism analysis service can be used to analyze the composition and variation characteristics of polysaccharides and their metabolites derived from plants, fungi, and microorganisms.
3. Plant Physiology and Development Research
By studying the accumulation patterns of polysaccharides and their metabolites in plant tissues, this service helps reveal metabolic features related to growth and development.
4. Microbial Metabolism Research
The polysaccharide metabolism analysis service enables the detection of polysaccharide metabolites in microbial cells or culture media, providing insights into metabolic pathways and interspecies cooperation within microbial communities.
FAQ
Q1: Is It necessary to Purify Polysaccharide Samples before Detection?
A1: Yes, purification is recommended. Impurities such as proteins, lipids, or salts may interfere with detection signals and affect result accuracy.
Q2: Can Intermediate Metabolites in Polysaccharide Metabolism Be Detected?
A2: Yes. Using LC-MS/MS or GC-MS, degradation products and intermediates in polysaccharide metabolic pathways—such as oligosaccharides, uronic acids, and sugar alcohols—can be quantitatively analyzed.
Q3: Can This Analysis Be Integrated with Other Omics Data?
A3: Yes. The results can be combined with transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data to construct comprehensive regulatory network models of polysaccharide metabolism.
How to order?







