Microbial Glycan Microarray Service
- Sample Types
- Storage and Transportation
- Pathogen Recognition Mechanism Studies: Analyze the binding specificity between bacteria, viruses, fungi, and host cell surface glycans.
- Pathogen Identification and Tracing: Identify different microbial species and their variants based on specific glycan-binding patterns, enabling rapid and accurate pathogen classification and tracking.
- Vaccine and Drug Development: Screen and validate microbial glycan-binding sites that can serve as vaccine antigens or drug targets.
- Biomarker Discovery: Identify glycan-binding patterns associated with infection, inflammation, or immune responses, providing a basis for biomarker development.
- Microbial Community and Ecological Studies: Investigate the role of glycans in biofilm formation, community stability, and inter-microbial signaling.
Microbial Glycan Microarray Service is a specialized analytical service that utilizes a high-throughput microarray platform to immobilize glycans derived from various microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, onto a solid support surface, followed by binding analysis with host molecules such as antibodies, receptor proteins, and lectins. This approach enables rapid and systematic elucidation of the structural specificity of microbial glycans and their functional significance in host-pathogen interactions, immune responses, and antigen screening.
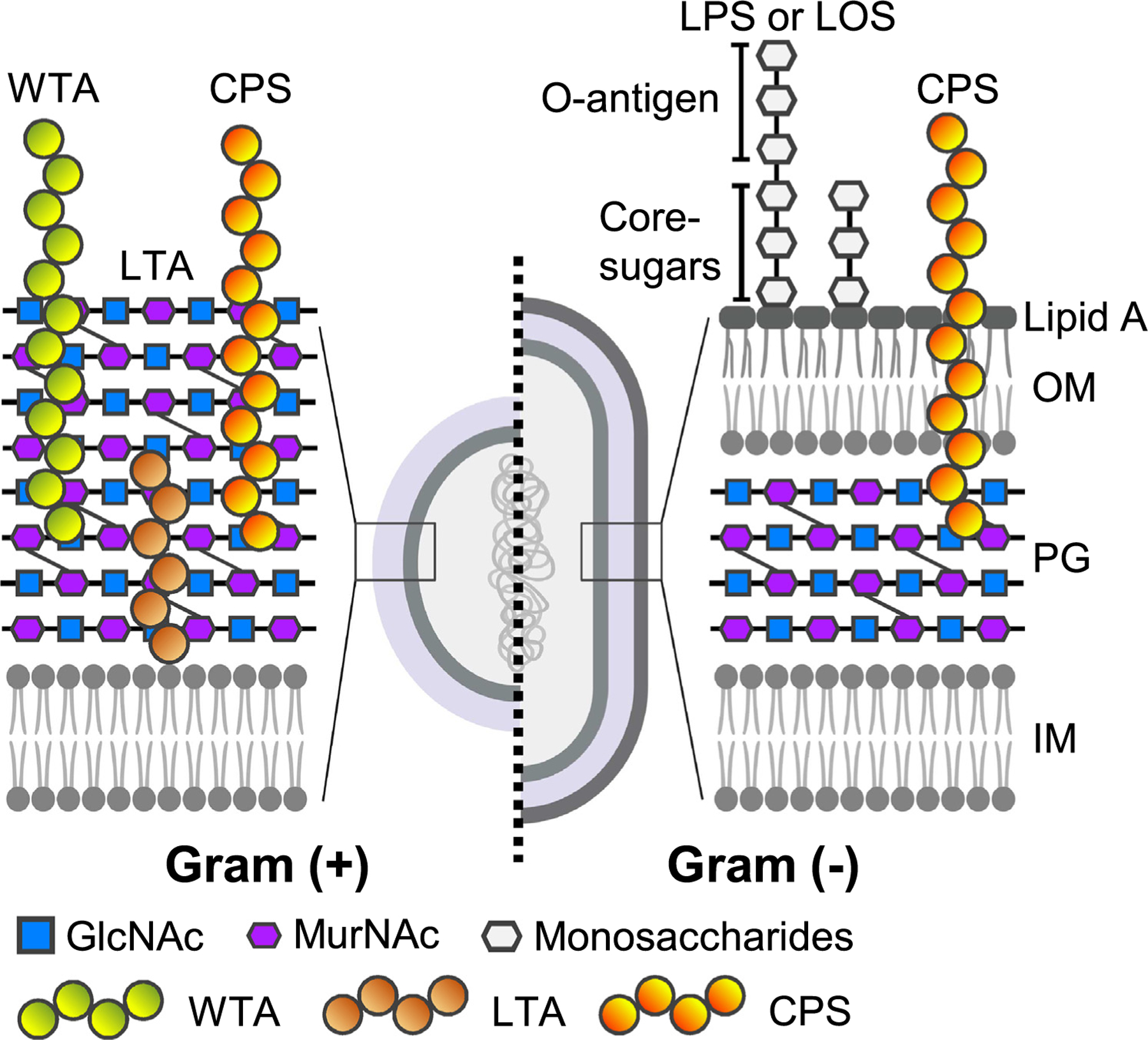
Lee S. et al. Trends Microbiol. 2022.
Figure 1. Common Bacterial Glycoconjugates Located on Bacterial Cell Surfaces and Membranes.
Microbial glycans are polysaccharide structures present on the surfaces or in the secreted products of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms, including lipopolysaccharides (LPS), peptidoglycans, capsular polysaccharides, and glycoprotein glycans. These glycans are not only essential components of the outer structure of microorganisms but also play critical roles in processes such as host recognition, adhesion, invasion, immune regulation, and immune evasion. Investigating the structures of microbial glycans and their interactions with host molecules is crucial for elucidating infection mechanisms, developing vaccines, and identifying disease biomarkers. The Microbial Glycan Microarray can rapidly and systematically map the binding profiles of microbial glycans, enabling the identification of glycan-protein interactions, the screening of glycosylation targets, and the validation of biomarkers.
MtoZ Biolabs offers Microbial Glycan Microarray Service to perform high-throughput analyses of the binding specificity and affinity between glycans from diverse microbial sources and host molecules, systematically revealing their functional roles in host-pathogen interactions, immune recognition, and antigen screening. This service provides reliable data support for vaccine development, infection mechanism research, and disease diagnosis.
Analysis Workflow
The main workflow of the Microbial Glycan Microarray Service is as follows:
1. Preparation of Microbial Glycans
Target glycans are prepared according to project requirements, ensuring structural integrity and biological activity.
2. Array Construction
Target glycans are immobilized onto the surface of a functionalized solid support through chemical coupling or noncovalent adsorption to generate a high-density glycan microarray.
3. Sample Incubation and Binding Reaction
Samples containing target molecules for detection, such as antibodies, receptors, cytokines, or intact cells, are incubated with the array surface to enable binding to specific glycans.
4. Detection and Signal Acquisition
Fluorescent labeling, enzymatic labeling, or other signal amplification systems are applied for detection, and binding signals are acquired using a high-sensitivity scanner or imaging system.
5. Data Analysis and Result Interpretation
Fluorescence signals are quantitatively analyzed to evaluate the binding specificity, affinity, and relative abundance of different glycans, followed by the generation of visualized results and a comprehensive analysis report.
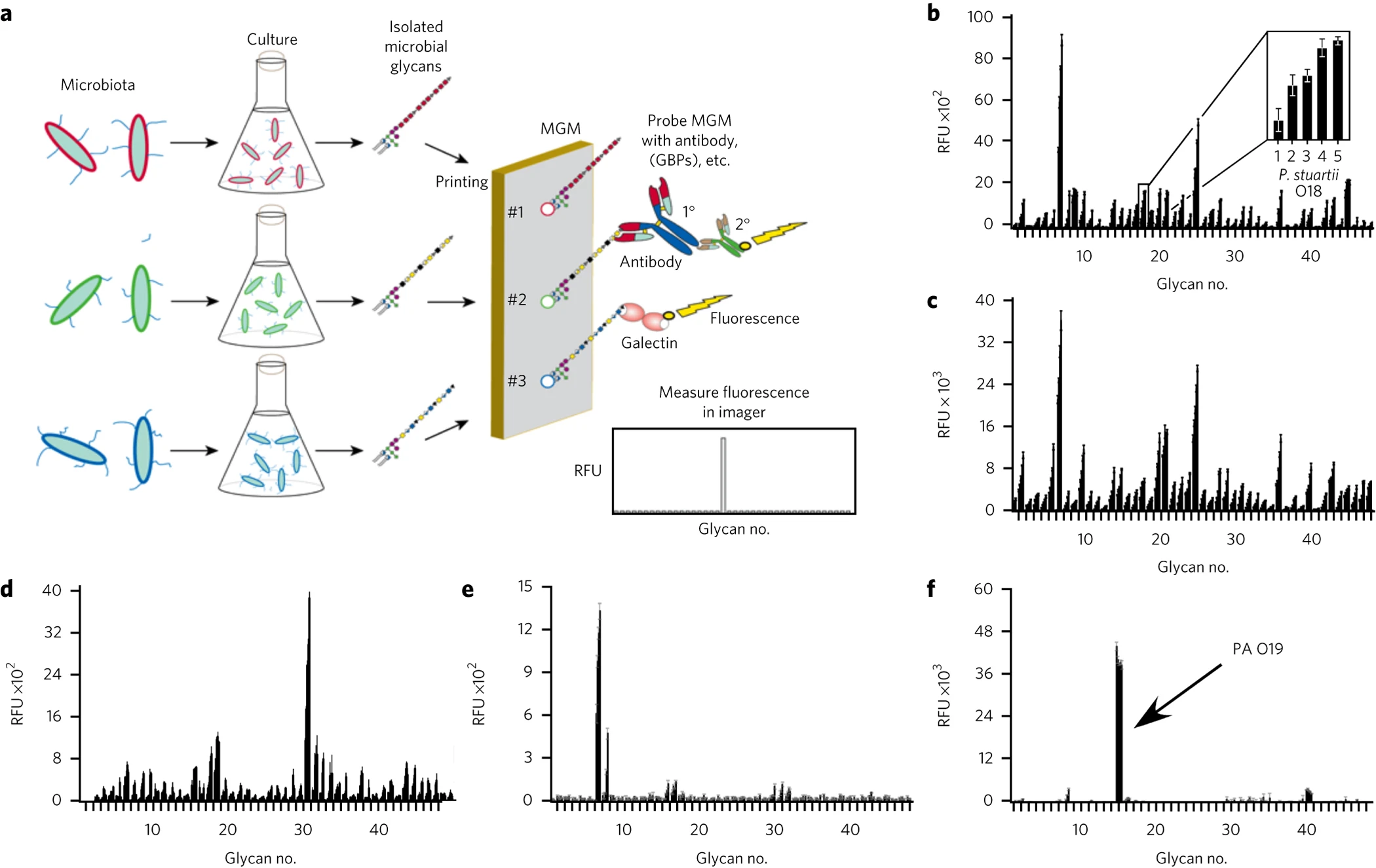
Stowell SR. et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2014.
Figure 2. Production and Validation of MGM and Recognition of Microbial Glycan Structures by Sera.
Service Advantages
High-throughput Detection Capability: A single experiment can simultaneously analyze hundreds of microbial-derived glycans, greatly improving screening efficiency.
High Sensitivity and Specificity: Accurately detects low-abundance binding events and distinguishes structurally similar glycan molecules.
Extensive Glycan Coverage: Includes a wide range of microbial-related glycan types, suitable for studying various microorganisms.
Customized Experimental Design: Flexibly adjusts glycan types, detection conditions, and data analysis strategies according to the client’s research objectives.
Strict Quality Control: Multiple quality control steps are implemented throughout the entire process to ensure data reliability and reproducibility.
Sample Submission Suggestions
Accepts various sample types including serum, plasma, cell lysates, and purified antibodies.
Samples should be stored at low temperatures (≤ -20°C) and transported on dry ice. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
It is recommended to consult with the MtoZ Biolabs technical team prior to sample submission to discuss experimental objectives and sample characteristics in order to obtain detailed and targeted guidelines for sample preparation and submission.
Applications
Example applications of the Microbial Glycan Microarray Service:
Related Services
Pathogen-Associated Glycan Microarray Service
How to order?







