Glycosaminoglycan Analysis Service
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are a class of linear polysaccharides composed of alternating units of amino sugars and uronic acids. The major types include hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, heparan sulfate, and heparin. GAGs are widely distributed in animal connective tissues, extracellular matrices, and cell surfaces, playing essential roles in maintaining tissue structure, regulating cell signaling, and mediating molecular recognition. Their structural diversity and sulfation patterns are closely associated with various physiological and pathological processes.
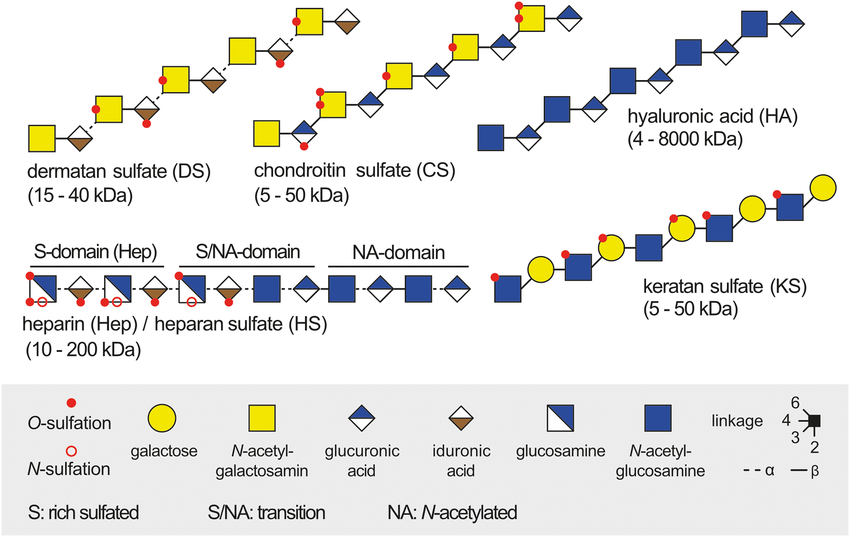
Zappe, A. et al. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2021.
Figure 1. Representation of the Five Types of Glycosaminoglycan Structures
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Relying on advanced mass spectrometry and multidimensional structural analysis platforms, MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive glycosaminoglycan analysis service that enables systematic investigation of the chemical composition, spatial structure, and physicochemical properties of glycosaminoglycans, providing high-quality data to support both basic research and applied development. The service includes, but is not limited to, the following aspects:
1. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
Using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS), the amino sugar and uronic acid composition of glycosaminoglycans is quantitatively determined to clarify the compositional patterns of different GAG types.
2. Structural Characterization
By integrating nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and ultraviolet spectroscopy (UV), the linkage mode of main and side chains, glycosidic bond characteristics, and spatial conformations are analyzed.
3. Molecular Weight and Purity Determination
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is employed to evaluate molecular weight distribution and sample purity.
4. Morphology and Microstructure Observation
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) are used to observe the microscopic morphology and aggregation state of samples.
5. Physicochemical Stability Evaluation
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) are applied to investigate the thermal properties and stability of glycosaminoglycans.
Analysis Workflow
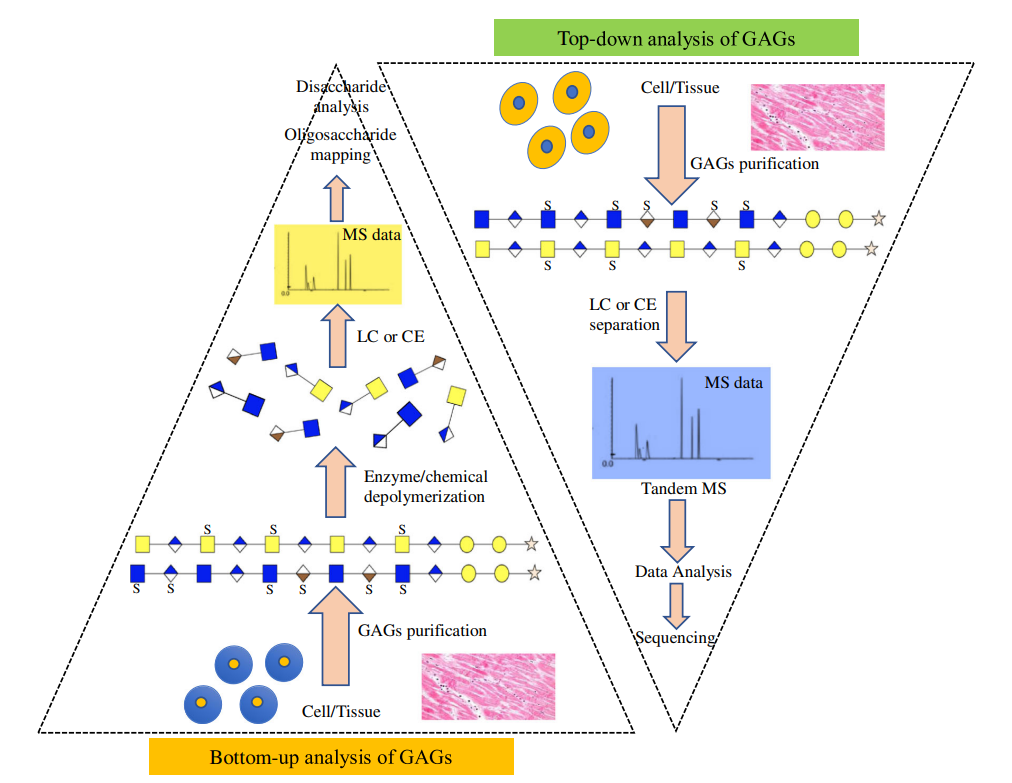
Solakyildirim, K. et al. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2018.
Figure 2. Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approaches for the Analysis of Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Purified glycosaminoglycan samples (powder, lyophilized, or solution) as well as unextracted raw samples (such as tissues, cells, or biological extracts) are accepted. A sample purity of ≥90% is recommended to ensure analytical accuracy and reproducibility.
2. Sample Storage
Solid samples should be stored in sealed, light-protected containers at 4°C or −20°C. Solution samples should be kept refrigerated at low temperatures and protected from repeated freeze–thaw cycles to prevent degradation.
3. Sample Transportation
Samples should be shipped in sealed, moisture-proof packaging. Liquid samples require cold-chain transportation, while powder samples can be sent at ambient temperature for short periods, avoiding exposure to heat and humidity.
Service Advantages
1. High-Sensitivity Detection
Utilizes high-sensitivity mass spectrometry and chromatography platforms to accurately detect low-abundance components and trace impurities.
2. Standardized Quality Control System
Implements quality control procedures throughout the entire workflow to ensure data accuracy, stability, and reproducibility.
3. Experienced Technical Team
Our specialists possess extensive experience in carbohydrate research and are proficient in analyzing the physicochemical properties of different types of GAGs.
4. Comprehensive Research Support
From sample preparation to final report delivery, every step is managed by professional experts, providing a fully integrated analytical solution.
Applications
1. Tissue and Extracellular Matrix Research
The glycosaminoglycan analysis service can be used to analyze the composition and structural differences of GAGs in various tissues or extracellular matrices.
2. Drug and Biomaterial Development
By evaluating the molecular characteristics of pharmaceutical-grade GAGs, this service provides data support for drug delivery and biomaterial design.
3. Cell Signaling and Molecular Interaction Studies
Assesses the binding properties of GAGs with proteins, receptors, or growth factors to explore their roles in signal regulation.
4. Environmental and Microbial Research
The glycosaminoglycan analysis service can be applied to investigate the composition and ecological functions of GAGs in environmental samples or microbial extracellular matrices.
FAQ
Q1: Can Different Types of Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) Be Distinguished?
A1: Yes. Using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS), various types of GAGs—such as hyaluronic acid, heparin, chondroitin sulfate, and dermatan sulfate—can be accurately differentiated, and their monosaccharide composition and substituent features can be determined.
Q2: Can the Sulfate or Carboxyl Group Content of GAGs Be Quantitatively Analyzed?
A2: Yes. By employing elemental analysis (EA), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), the proportions of sulfur, oxygen, and metal ions in GAG samples can be precisely measured, indirectly reflecting their substituent group content.
How to order?







