Fucoidan Analysis Service
Fucoidan is a class of sulfated polysaccharides composed mainly of fucose residues and often containing sulfate groups, glucuronic acid, and other neutral sugars. It is widely found in brown algae, sea cucumbers, and certain invertebrate tissues. Its unique structural characteristics confer a wide range of biological activities, including antioxidant, anticoagulant, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects. MtoZ Biolabs provides comprehensive analytical services for Fucoidan, offering reliable data support for functional research, drug development, and quality control of natural products.
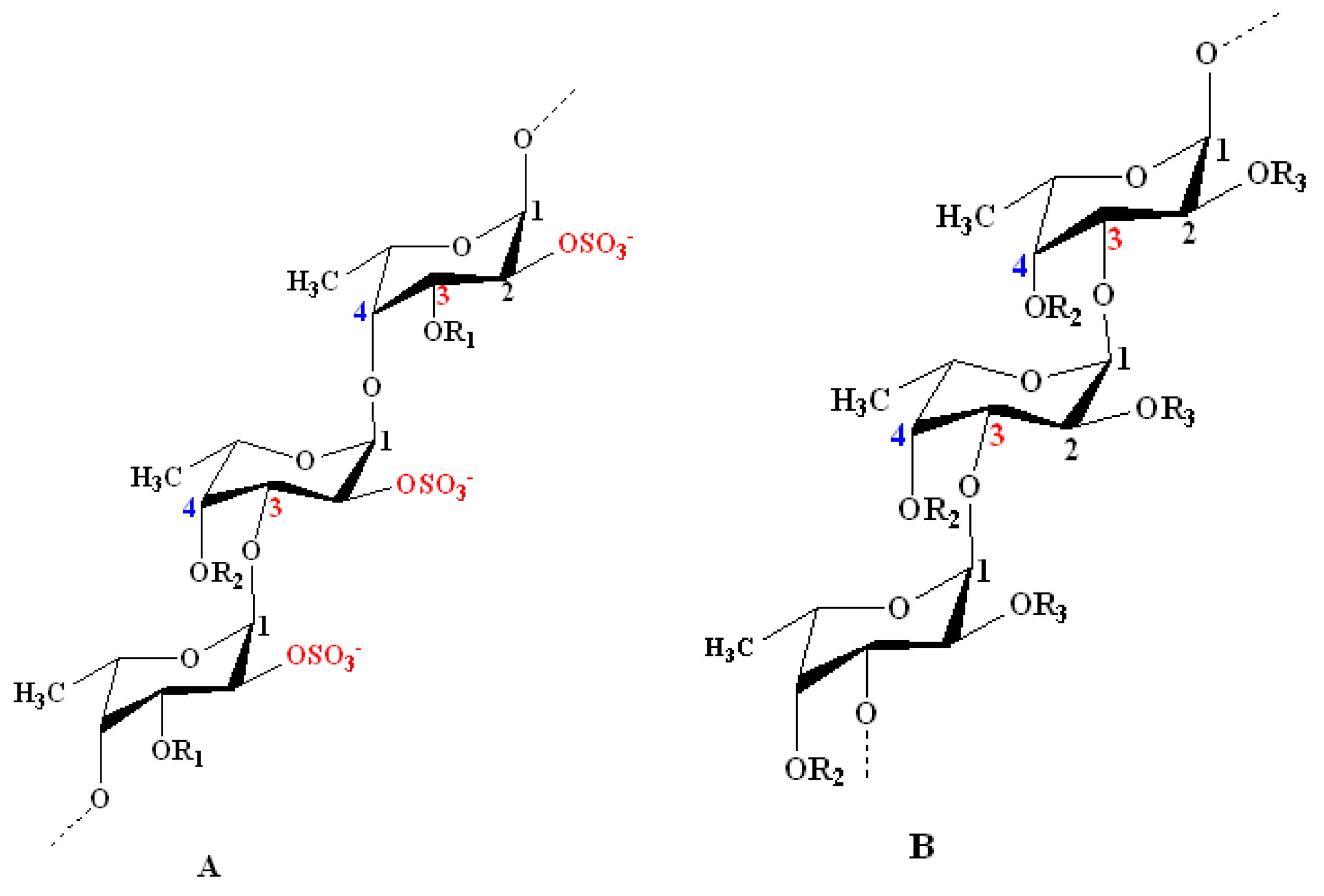
Zayed, A. et al. Marine Drugs, 2020.
Figure 1. Structural Models for the Chemical Structure of Fucoidans Derived from Some Species of Seaweeds.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on high-resolution mass spectrometry and multidimensional analytical platforms, MtoZ Biolabs provides a comprehensive fucoidan analysis service that enables systematic characterization of its composition, physicochemical properties, and structural features. The service includes but is not limited to the following aspects:
1. Molecular Weight Determination
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is used to determine the molecular weight and distribution characteristics of Fucoidan, assessing its degree of polymerization and homogeneity.
2. Structural Analysis
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and ultraviolet spectroscopy (UV) are employed to analyze the backbone configuration, degree of sulfation, branching structure, and functional group distribution of Fucoidan, identifying its key structural characteristics.
3. Component and Elemental Analysis
High-resolution mass spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) are applied to detect the monosaccharide composition and sulfate content of Fucoidan, as well as to analyze metal elements and potential impurities.
4. Surface and Morphological Characterization
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) are used to observe the microstructure, aggregation state, and spatial morphology of Fucoidan samples.
5. Thermal Stability Evaluation
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) are conducted to evaluate the thermal stability and physical characteristics of Fucoidan.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Purified Fucoidan powder, lyophilized samples, or solution samples are acceptable; crude extracts or mixed samples can also be analyzed. A purity of ≥90% is recommended to ensure the accuracy of structural and compositional analysis.
2. Sample Storage
Solid samples should be sealed, protected from light, and stored at 4°C or −20°C. Solution samples should be kept at low temperatures and protected from repeated freeze–thaw cycles to prevent degradation.
3. Sample Transportation
Sealed and moisture-proof packaging is recommended. Liquid samples should be transported via a cold chain, while powder samples can be shipped at room temperature for short periods but must be protected from heat and humidity.
Service Advantages
1. Multidimensional Analytical Platform
Integration of mass spectrometry, spectroscopy, and microscopy techniques enables comprehensive analysis of Fucoidan’s structure, composition, and physicochemical characteristics.
2. High Resolution and Accuracy
High-performance systems such as Orbitrap-MS, FTIR, and NMR ensure precise and reliable analytical results.
3. Rigorous Quality Control
Standardized quality control procedures are implemented throughout the entire workflow to ensure data stability and reproducibility.
4. Customized Service Solutions
Experimental plans can be tailored based on sample characteristics and research objectives to meet diverse analytical needs.
Applications
1. Marine Bioactive Component Research
By analyzing Fucoidan from different seaweed sources, structural variations and bioactive characteristics can be identified.
2. Functional Mechanism Exploration
Fucoidan analysis service helps investigate its potential roles in cell protection, signal regulation, and immune response.
3. Product Performance Evaluation
By testing Fucoidan in formulated products, its stability, compatibility, and bioactivity performance can be assessed.
4. Process and Extraction Optimization
Fucoidan snalysis service provides structural and quantitative evaluation to support extraction and purification process improvement.
FAQ
Q1: How Is the Degree of Sulfation in Fucoidan Determined?
A1: The degree of sulfation is typically determined by detecting characteristic absorption peaks using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), supplemented with elemental analysis or mass spectrometry to measure sulfur content, thereby calculating the sulfation ratio and substitution positions.
Q2: Can Fucoidan from Different Sources Be Distinguished?
A2: Yes. By combining monosaccharide composition analysis, structural characterization, and functional group comparison, Fucoidan derived from brown algae, microorganisms, or mixed extracts can be differentiated.
Q3: Do Impurities in the Sample Affect the Analytical Results?
A3: Yes. Impurities such as proteins, salts, and other polysaccharides may interfere with spectral interpretation and quantification accuracy; therefore, moderate purification or desalting treatment is recommended.
How to order?







