Extracellular Vesicle Modification Services
Extracellular vesicle modification analysis refers to the functional modification of naturally secreted extracellular vesicles (EVs) through physical, chemical, or biological methods to endow them with new biological properties or enhance their natural functions. Extracellular vesicles are nanoscale vesicles secreted by cells that carry various molecules, including proteins, RNA, and lipids, and are widely involved in intercellular communication. Through modification techniques, surface markers of vesicles can be altered, specific drugs or genes can be loaded, and targeting ligands can be added to improve their efficacy in drug delivery, gene therapy, and immune modulation.
Extracellular vesicle modification services are widely applied in tumor-targeted therapy, gene delivery, vaccine development, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. Through engineering modifications, extracellular vesicles can achieve precise delivery of small molecule drugs, mRNA, proteins, and other functional molecules, while enhancing vesicle stability, biocompatibility, and targeting ability, providing strong support for the development of novel therapeutic approaches and basic research.
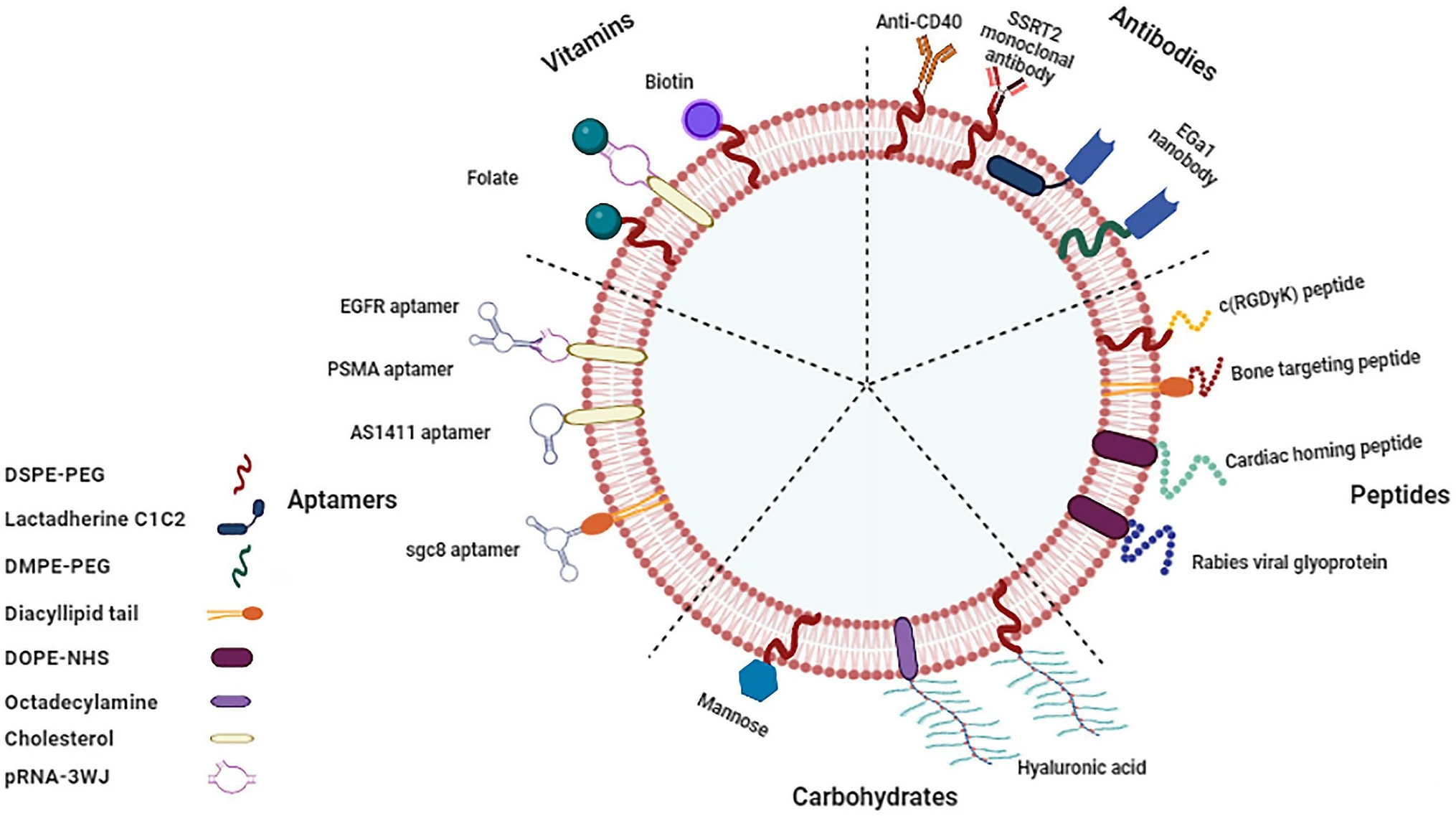
Mohammadi, A H. et al. BioDrugs, 2023.
Figure 1. Chemical Modification of EVs.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Relying on advanced instruments such as high-efficiency ultrasonic processing equipment, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and flow cytometry, the extracellular vesicle modification services provided by MtoZ Biolabs enable precise engineering of extracellular vesicles, including surface labeling, targeted molecule conjugation, and drug or nucleic acid loading. The service ensures the production of high-purity, highly stable, and functionally defined engineered vesicles and provides comprehensive characterization data, to meet both research and application needs.
Service Advantages
1. Precise and Efficient Modification Capability
Utilizing multiple advanced methods, we achieve highly efficient loading and precise modification of both surface and internal molecules of extracellular vesicles, thereby enhancing their functional performance.
2. One-Time-Charge
Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. High-Quality Assurance
Equipped with multiple platforms such as transmission electron microscopy (TEM), flow cytometry, and high-resolution mass spectrometry to verify modification efficiency and functional performance of extracellular vesicles, ensuring their purity, stability, and bioactivity.
4. Customized Service Solutions
Based on customer needs, MtoZ Biolabs can design personalized modification strategies to flexibly support various disease models and drug delivery applications.
Applications
1. Targeted Drug Delivery
By modifying vesicle surfaces with targeting molecules, drugs, RNA, proteins, and other cargos can be effectively loaded into extracellular vesicles to achieve precise delivery to specific cells or tissues.
2. Gene Therapy
Extracellular vesicle modification services enable the delivery of siRNA, miRNA, or CRISPR-based gene editing tools for precise genetic regulation and treatment of hereditary diseases or cancers.
3. Vaccines and Immunotherapy
By loading antigens and immune-stimulating molecules into extracellular vesicles, they can serve as novel vaccine carriers or immunotherapy tools to activate immune responses or modulate immune balance.
4. Tissue Repair and Regeneration
Extracellular vesicle modification services can facilitate the delivery of regenerative factors to support the repair and functional recovery of tissues such as heart and nerve after injury.
Case Study
1. Direct Modification of Extracellular Vesicles and Its Applications for Cancer Therapy
This paper aims to review the methods of direct modification of extracellular vesicles (EVs) and their applications in cancer therapy, exploring how engineering approaches can enhance the therapeutic potential of EVs. The article focuses on various sources of EVs and highlights direct modification strategies, including surface modification (such as conjugation with antibodies, peptides, or glycans to enhance targeting), internal loading (for delivering drugs, RNAs, proteins, and other therapeutic molecules), and regulation of membrane components. The authors systematically summarize current techniques used for EV modification, such as chemical modification, physical methods, and bioengineering strategies, and analyze how these methods affect EV stability, targeting ability, and delivery efficiency. The results indicate that directly modified EVs exhibit improved in vivo targeting and higher drug-loading efficiency, significantly enhancing anti-tumor efficacy while reducing systemic toxicity. The conclusion emphasizes that direct modification of EVs is a promising cancer therapeutic strategy that can overcome many limitations of traditional drug delivery methods; however, challenges such as large-scale production, quality control, and safety validation remain to be addressed for clinical translation.
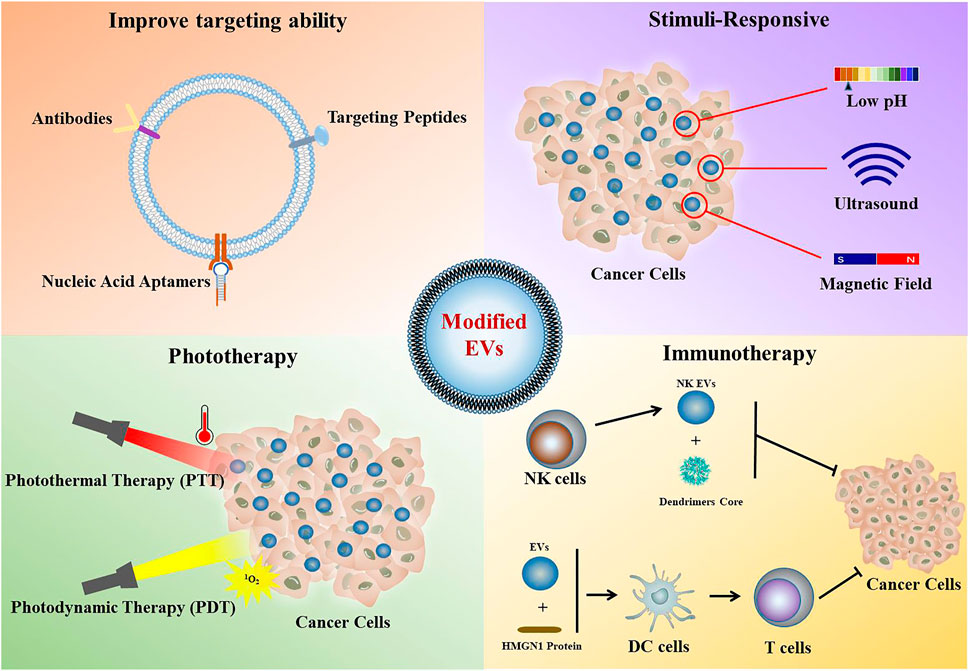
Nan, W B. et al. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022.
Figure 2. Application of Modified EVs in Cancer Therapy.
FAQ
Q1: What Types of Modifications Can Be Applied to Extracellular Vesicles?
A1: We offer various types of extracellular vesicle (EV) modifications, including surface molecule labeling (such as antibodies, peptides, glycans), loading of therapeutic agents (small molecules, RNA, proteins), and modulation of membrane components (such as lipid modifications), to meet diverse research and therapeutic needs.
Q2: What Information Should Clients Provide to Customize EV Modification Strategies?
A2: Clients should provide details on the target disease or research focus, the type of molecules they wish to load or modify (such as RNA, drugs, proteins), and the desired functional outcomes (such as targeting, immune activation). Based on this information, we will design a tailored modification strategy and communicate with the client for confirmation.
How to order?







