Extracellular Vesicle Functional Research and Verification Service
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are small membrane-bound vesicles secreted by cells and are widely present in the bodily fluids of various organisms, playing important biological roles. They can carry a variety of biomolecules such as proteins, RNA, and lipids, participating in intercellular communication and regulating physiological and pathological processes including immune responses, inflammatory responses, and tumor metastasis. The extracellular vesicle functional research and verification service aims to extract, isolate, and purify EVs, and, combined with modern molecular biology techniques such as proteomics, RNA analysis, and functional assays, deeply investigate their roles in disease progression and validate their biological functions.
Extracellular vesicle functional research and verification service is widely applied in oncology, immunology, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and other fields. It holds significant research and clinical value, particularly in tumor immune evasion, immunotherapy, drug delivery, and early disease diagnosis. Functional research of EVs provides strong data support and theoretical basis for understanding disease mechanisms, advancing precision medicine, and developing new therapeutics.
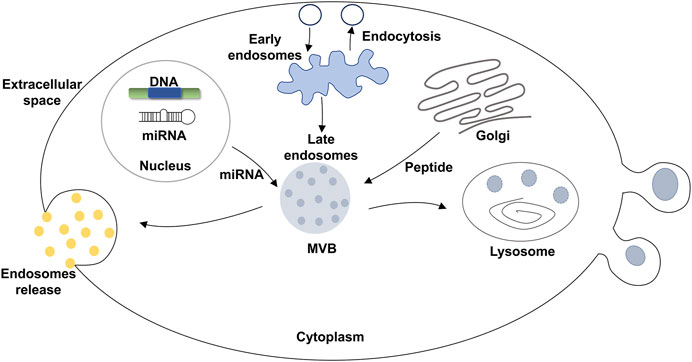
Zhang, X Y. et al. Frontiers in Cell and Development Biology, 2021.
Figure 1. Formation of EVs.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on multiple advanced technology platforms, the extracellular vesicle functional research and verification service provided by MtoZ Biolabs ensures comprehensive evaluation and verification of extracellular vesicle functions. The service includes the extraction, purification, molecular composition analysis, functional validation, and mechanistic studies of extracellular vesicles. Through these platforms, the vesicle size, morphology, protein and RNA components can be accurately analyzed, along with verification of their roles in biological processes such as intercellular communication, immune regulation, and tumor metastasis. This ensures the acquisition of high-quality, reliable data to support in-depth biological research and clinical applications.
Service Advantages
1. Multi-platform Validation
By integrating technologies such as high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), RNA sequencing, and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), we provide comprehensive functional validation to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
2. High-quality Data Support
Using techniques like flow cytometry (FACS), we perform precise analyses of extracellular vesicle size, morphology, molecular composition, and function, delivering high-quality experimental data to support your research.
3. Flexible Customized Services
Customized extraction, analysis, and functional validation plans are provided based on client requirements, meeting the needs of various research areas.
4. Comprehensive Technical Support
From sample preparation to data analysis, MtoZ Biolabs' expert team offers end-to-end technical support to ensure smooth project execution.
Applications
1. Tumor Research
Extracellular vesicle functional research and verification service enables analysis of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles to investigate their roles in tumor metastasis, immune evasion, and the tumor microenvironment, providing new strategies for cancer therapy.
2. Disease Diagnosis and Biomarker Discovery
Molecules carried by extracellular vesicles serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers, especially valuable for the early detection of metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases.
3. Immune Regulation
Extracellular vesicle functional research and verification service investigates the role of extracellular vesicles in signal transmission and immune modulation among immune cells, contributing to the advancement of immunotherapies.
4. Drug Delivery System Optimization
By exploring the behavior and efficacy of extracellular vesicles as drug carriers, this service supports the optimization of nanomedicine delivery systems.
Case Study
1. Biogenesis and Function of Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer
This study aims to systematically investigate the biogenesis mechanisms and functions of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in cancer development and progression. The research focuses on tumor cell-derived exosomes and microvesicles, utilizing literature review and mechanistic analysis to elucidate EV biogenesis pathways, sorting mechanisms, and their roles within the tumor microenvironment. The results indicate that EVs participate in cancer progression by transporting miRNAs, proteins, and lipids, thereby regulating processes such as cell proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis, and immune evasion. EVs also mediate signal transduction through membrane fusion or endocytosis with recipient cells, contributing to the remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. The study concludes that EVs are not only critical modulators in tumor biology but also hold potential as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets, offering new perspectives for early cancer detection and precision therapy.
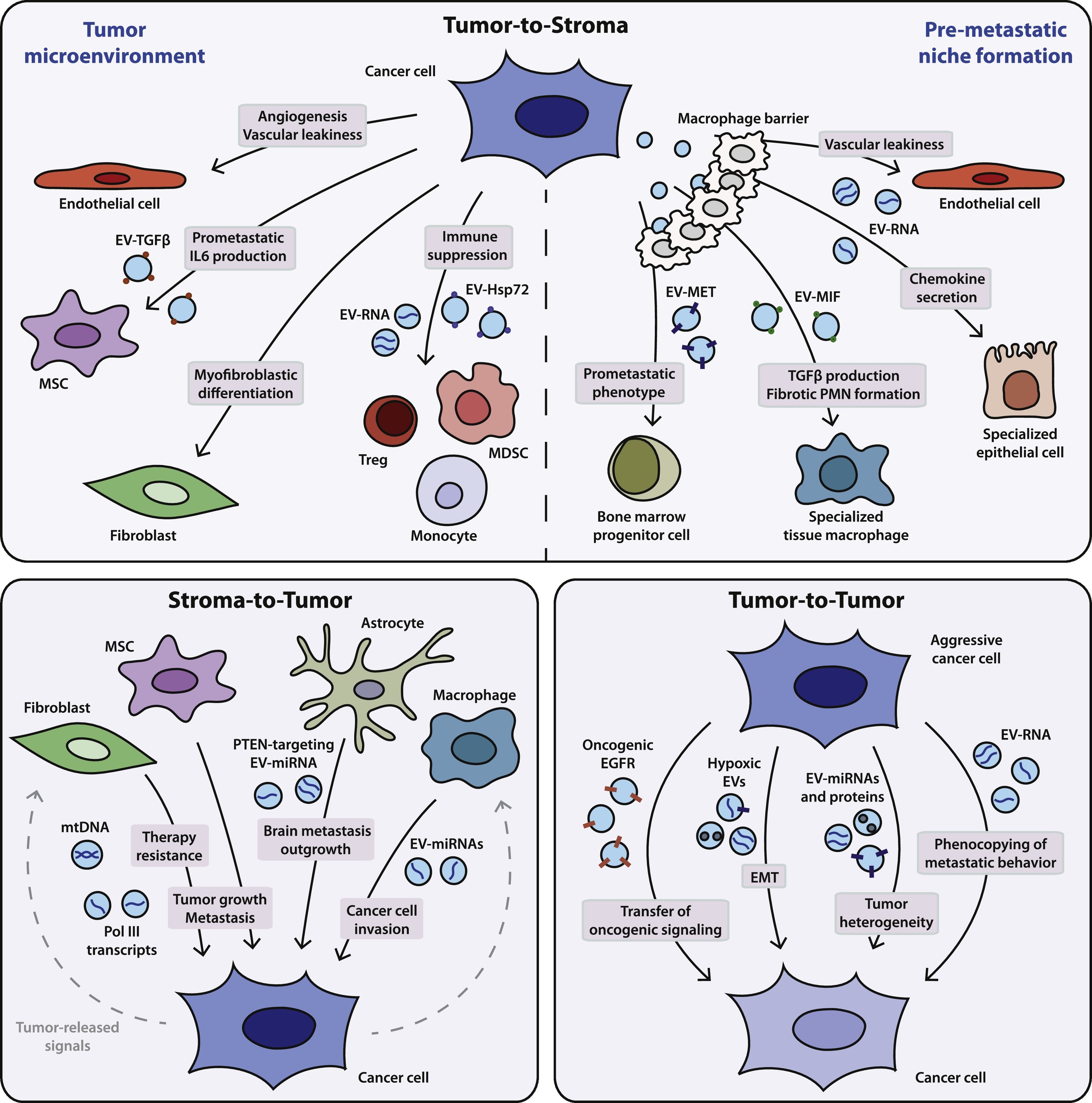
Bebelman, M P. et al. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2018.
Figure 2. Function of EVs in the Tumor-to-Stroma, Stroma-to-Tumor and Tumor-to-Tumor Communication Fueling Cancer Progression.
2. Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Functions in Gram-Positive Bacteria
This study aims to explore the biogenesis mechanisms and biological functions of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in Gram-positive bacteria, focusing on various species such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. By integrating existing experimental data and literature, the research analyzes how these bacteria, despite lacking an outer membrane, are capable of producing EVs. Using electron microscopy, mass spectrometry, and functional validation assays, the study investigates the mechanisms of EV formation and the cargo they carry. Results show that Gram-positive bacteria can release EVs through cell wall remodeling or the involvement of specific enzymes. These vesicles are rich in virulence factors, enzymes, and signaling molecules, and can mediate host cell responses, enhance bacterial survival, and promote the spread of infection. The study concludes that EVs derived from Gram-positive bacteria play crucial roles in host-pathogen interactions, virulence expression, and antibiotic resistance, providing new directions for the development of anti-infective strategies.
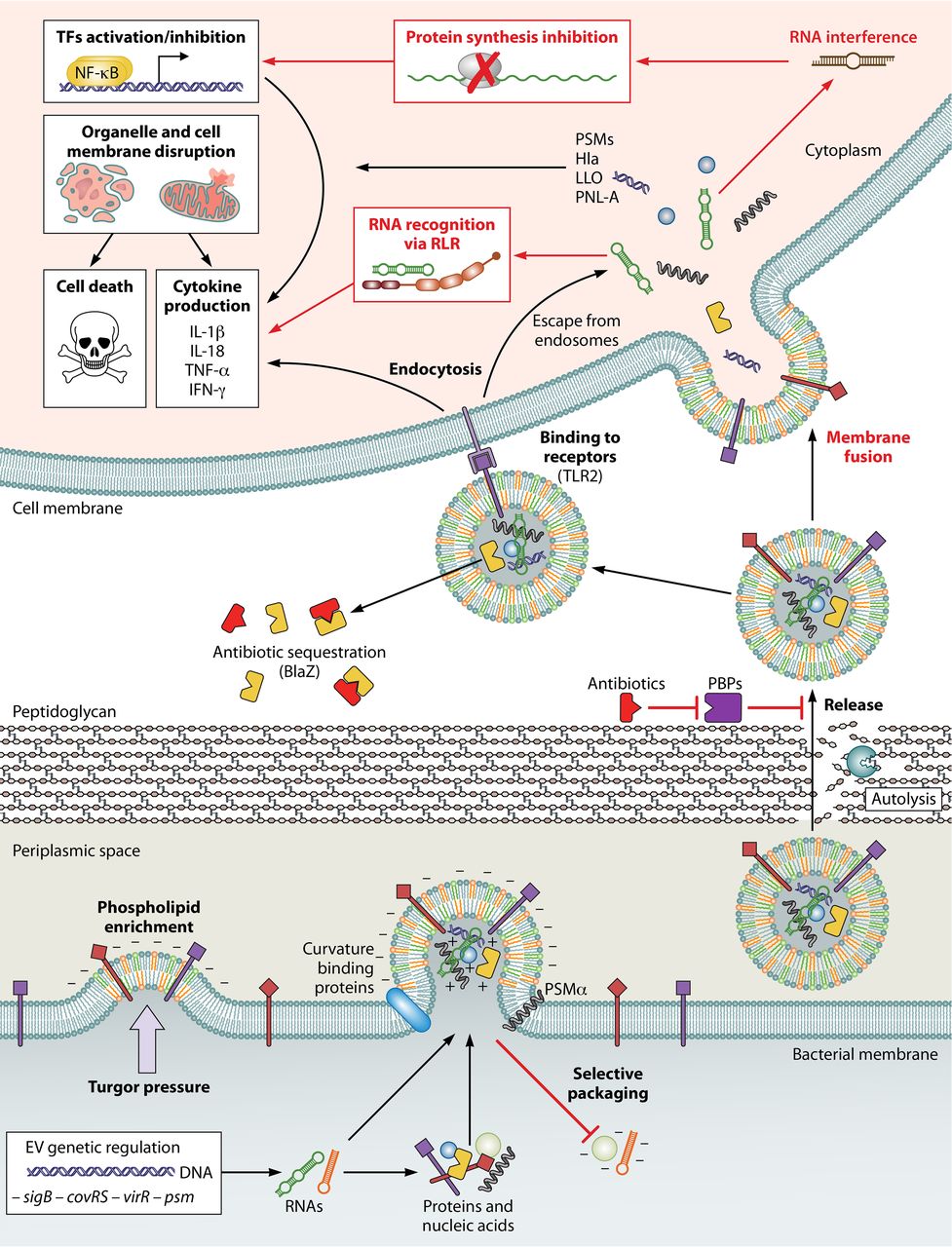
Briaud, P. et al. Infection and Immunity, 2020.
Figure 3. Biogenesis and Functions of Gram-Positive EVs.
FAQ
Q1: Are Extracellular Vesicles the Same as Exosomes?
A1: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are a collective term for various types of vesicles, including exosomes and microvesicles. Exosomes are a subtype of EVs with a diameter of 30–150 nm, originating from multivesicular bodies (MVBs), whereas microvesicles are formed by direct budding from the plasma membrane. Although they share similar structures, their biological origins and mechanisms of formation differ.
Q2: Can Customer-Provided Vesicle Samples Be Used for Analysis?
A2: Yes. MtoZ Biolabs supports the use of customer-provided vesicle samples. We will assess the quality of the samples and recommend suitable functional verification experiments, along with providing customized technical advice and experimental design services.
Q3: Is it Necessary to Label Vesicles to Validate their Function?
A3: It is not mandatory. Some functional validations, such as cytokine release and target gene regulation, do not require labeling; however, if one needs to observe the distribution or uptake process of vesicles, fluorescent dyes or virus-mediated stable labeling are recommended.
How to order?







